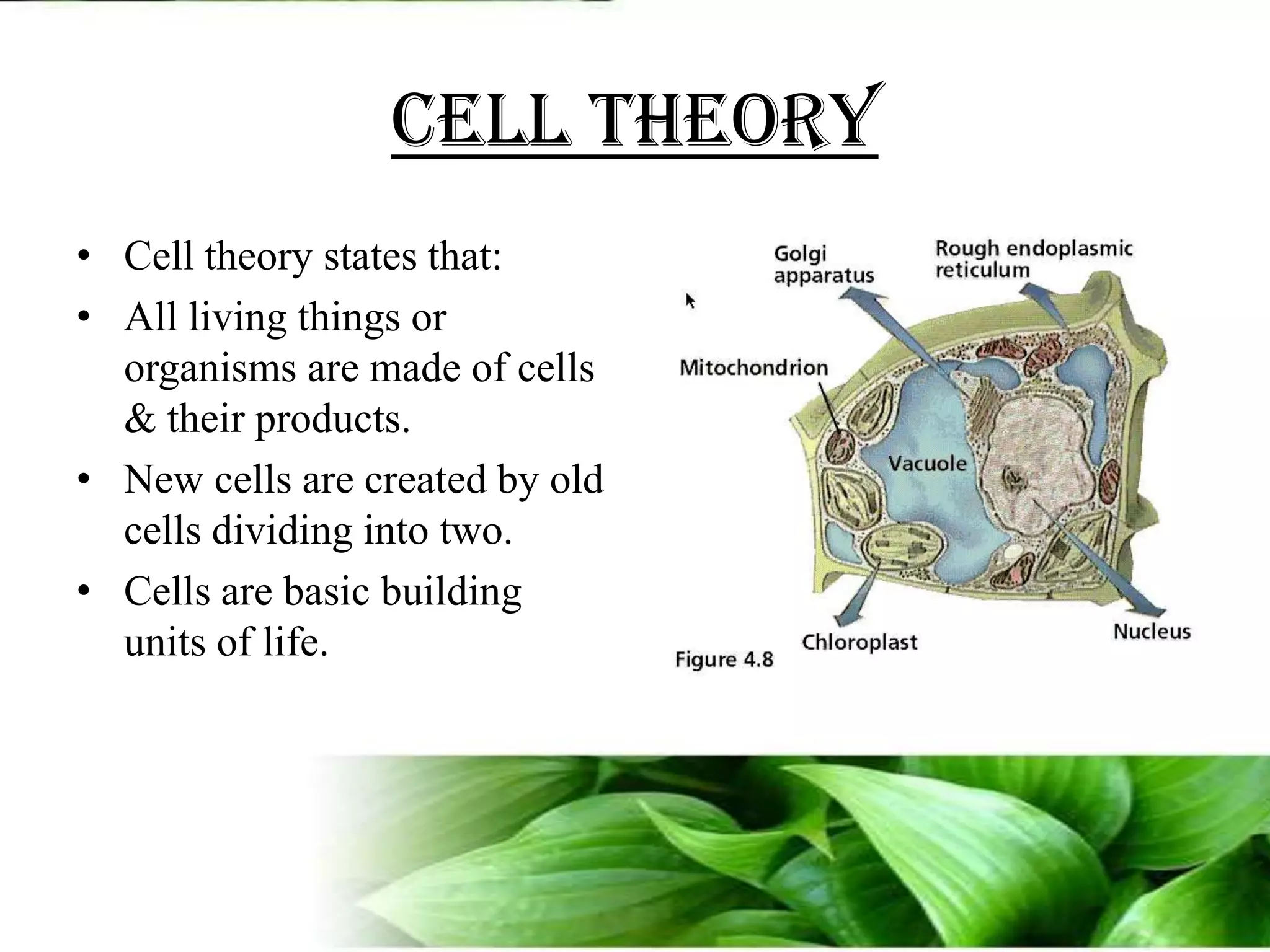
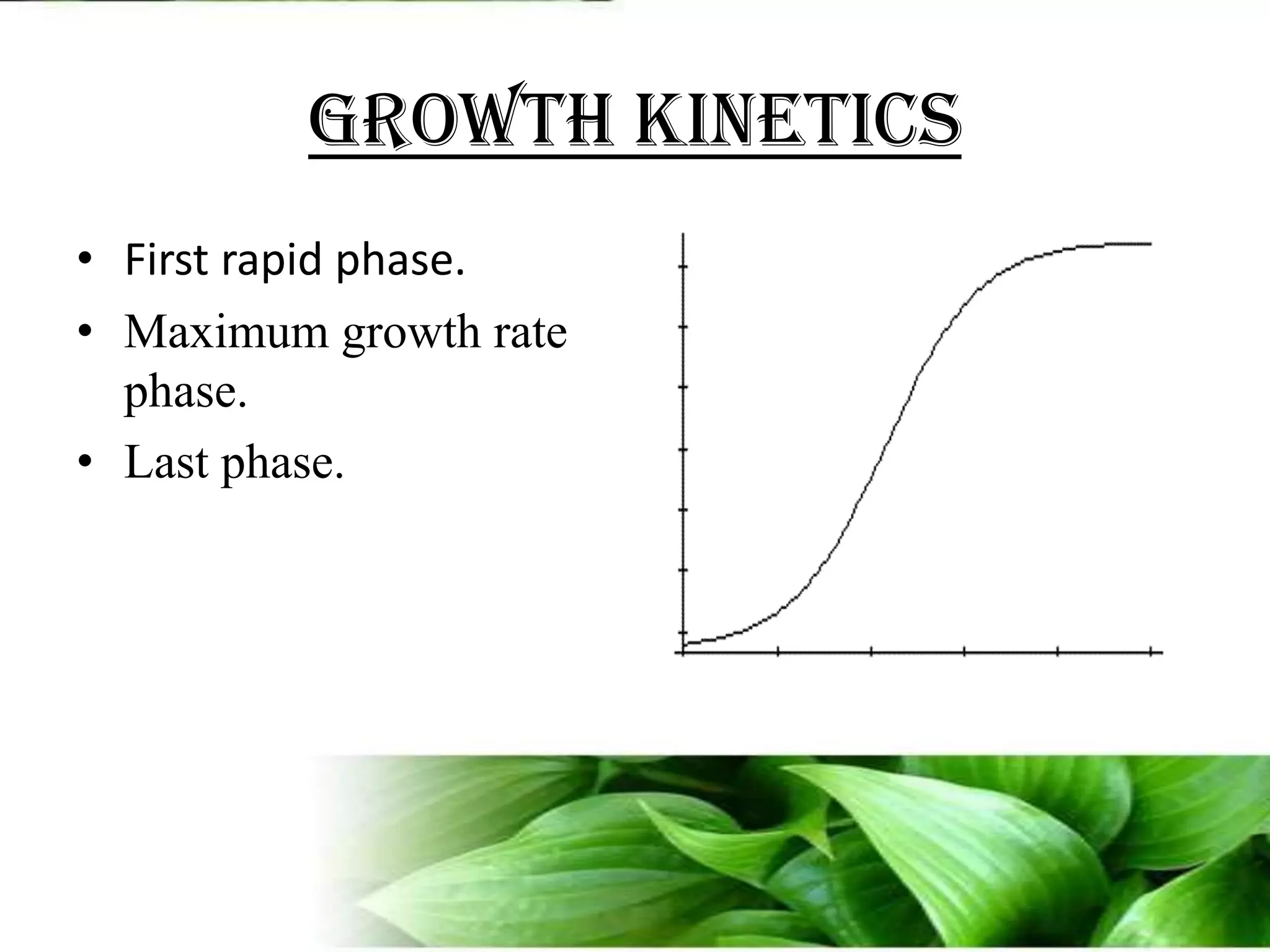
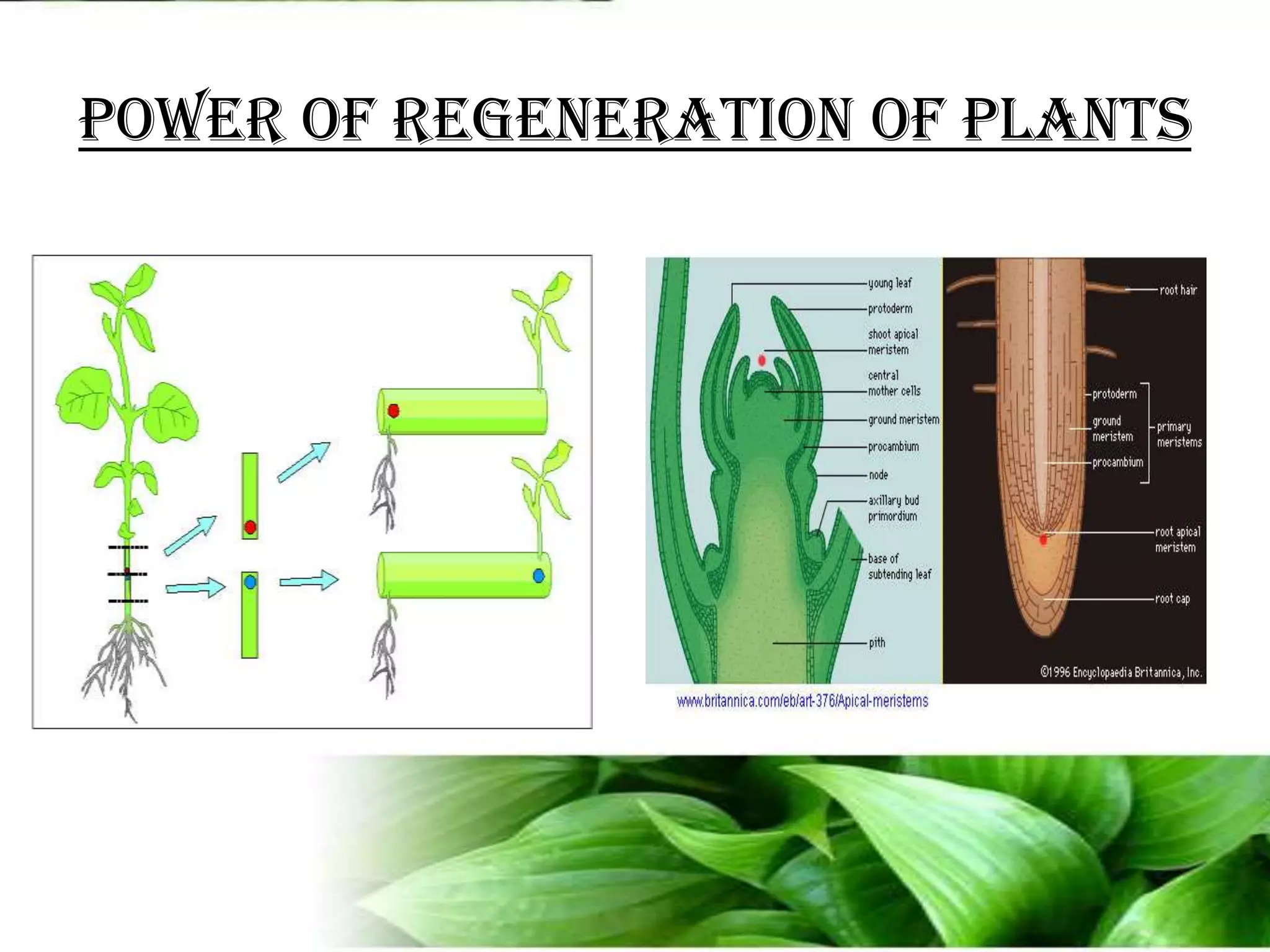
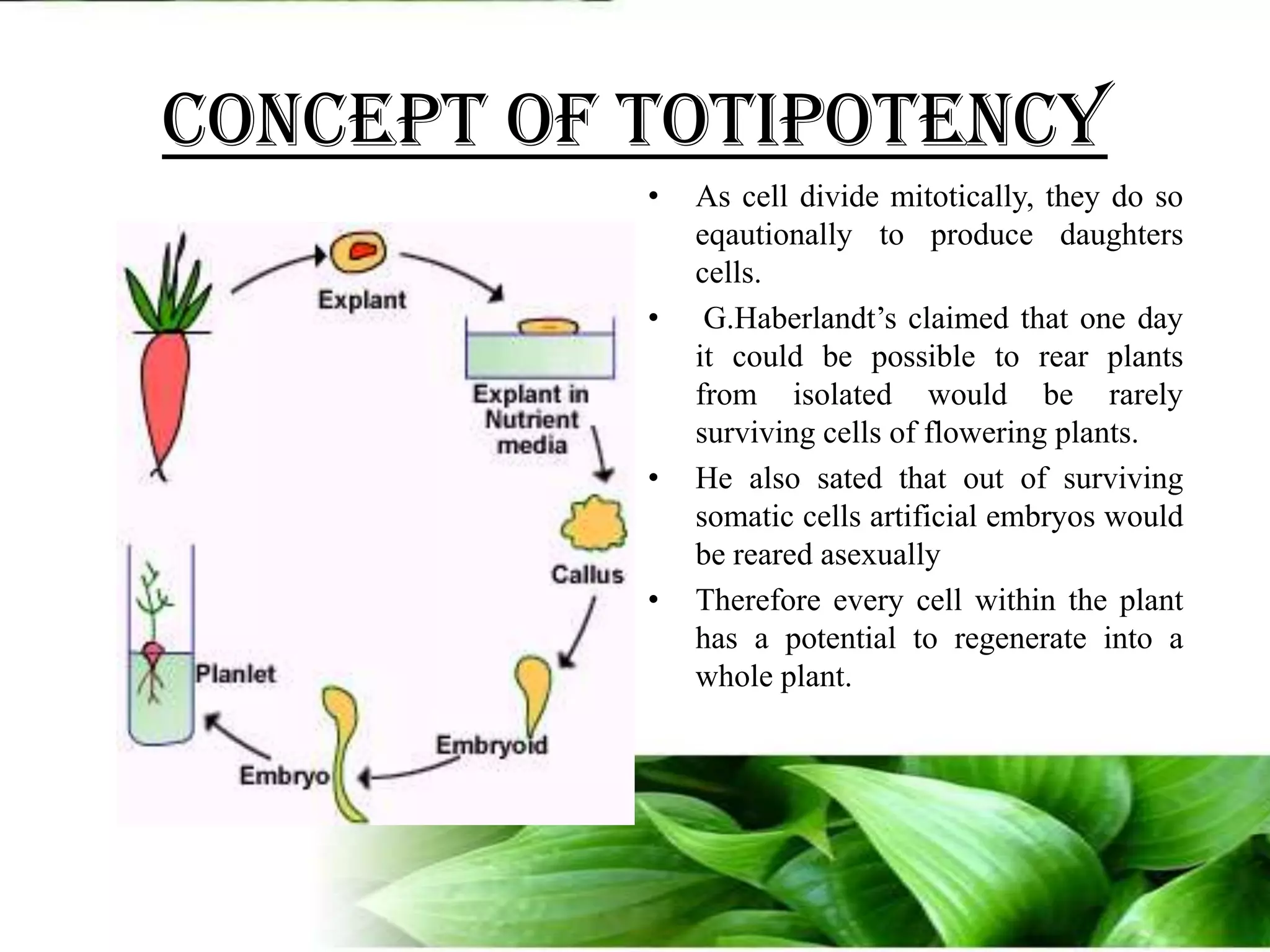
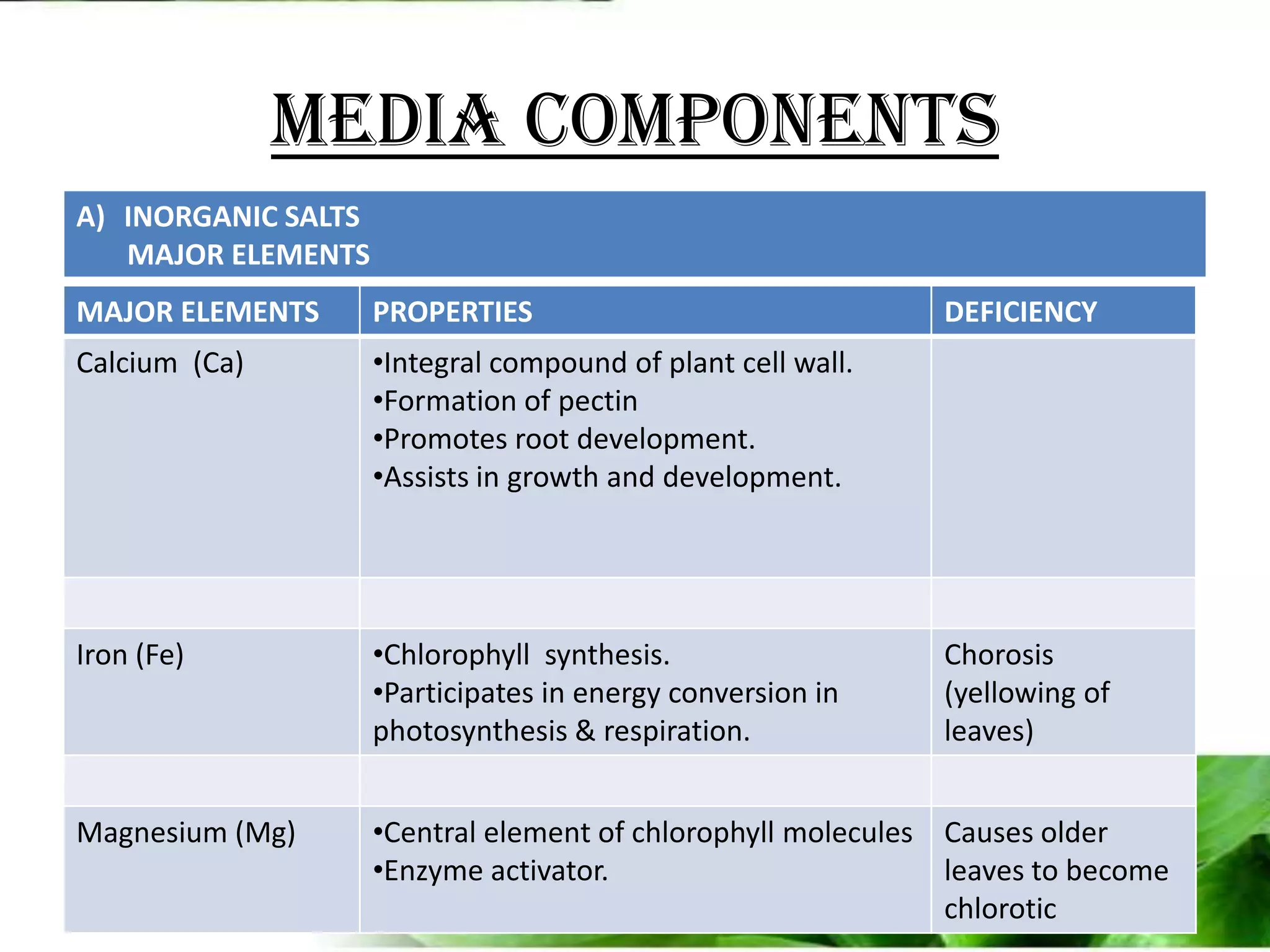
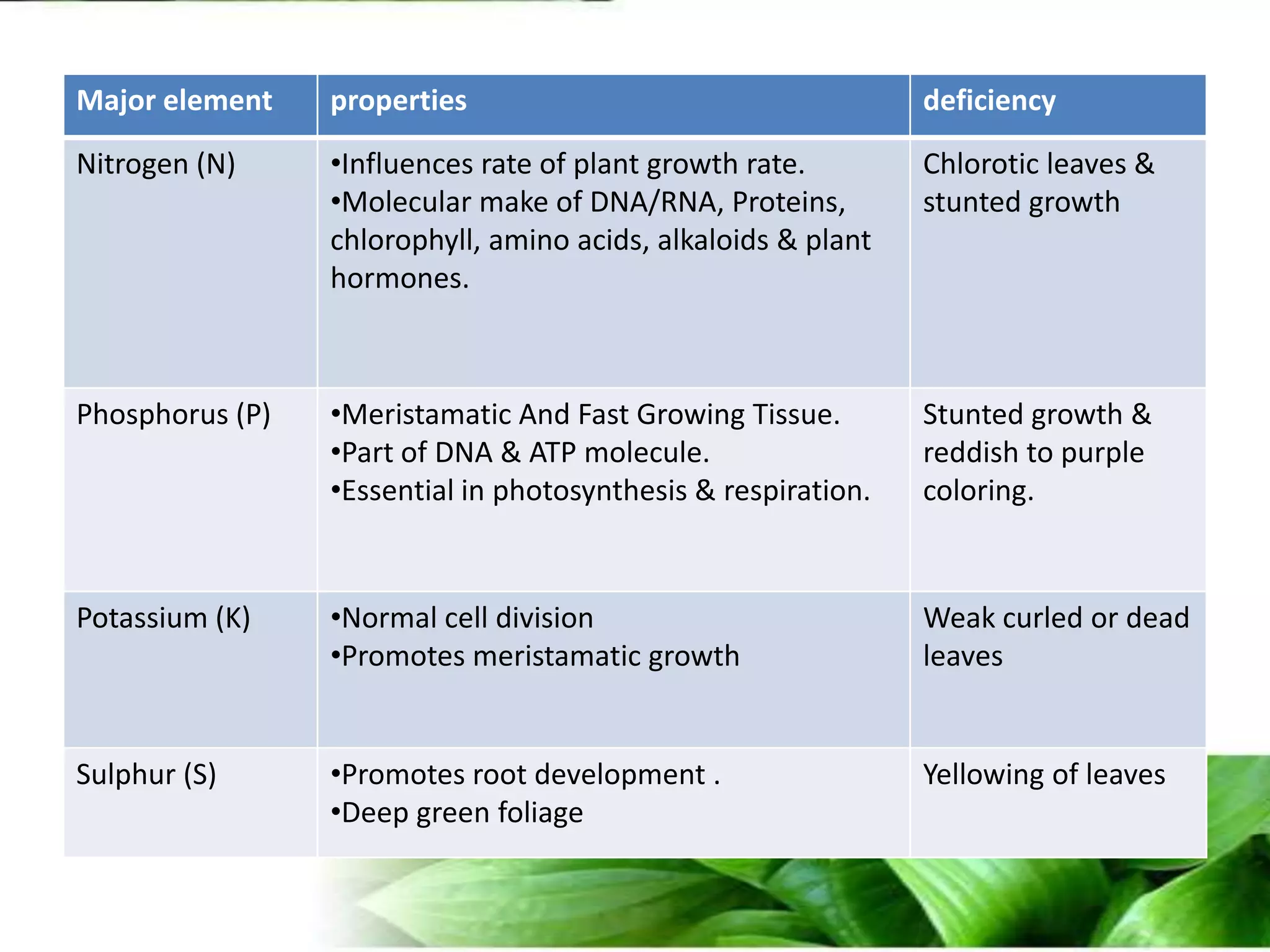
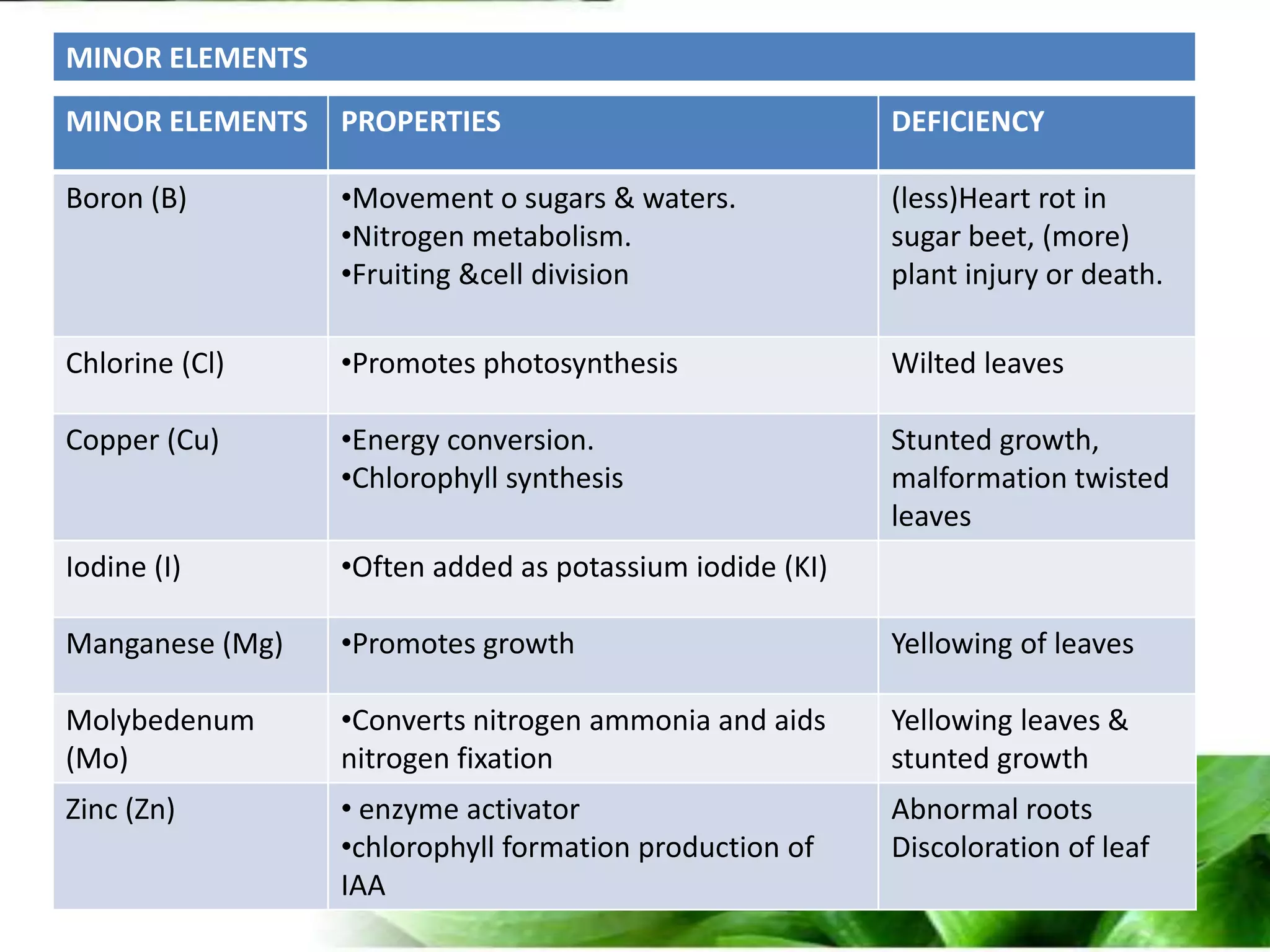
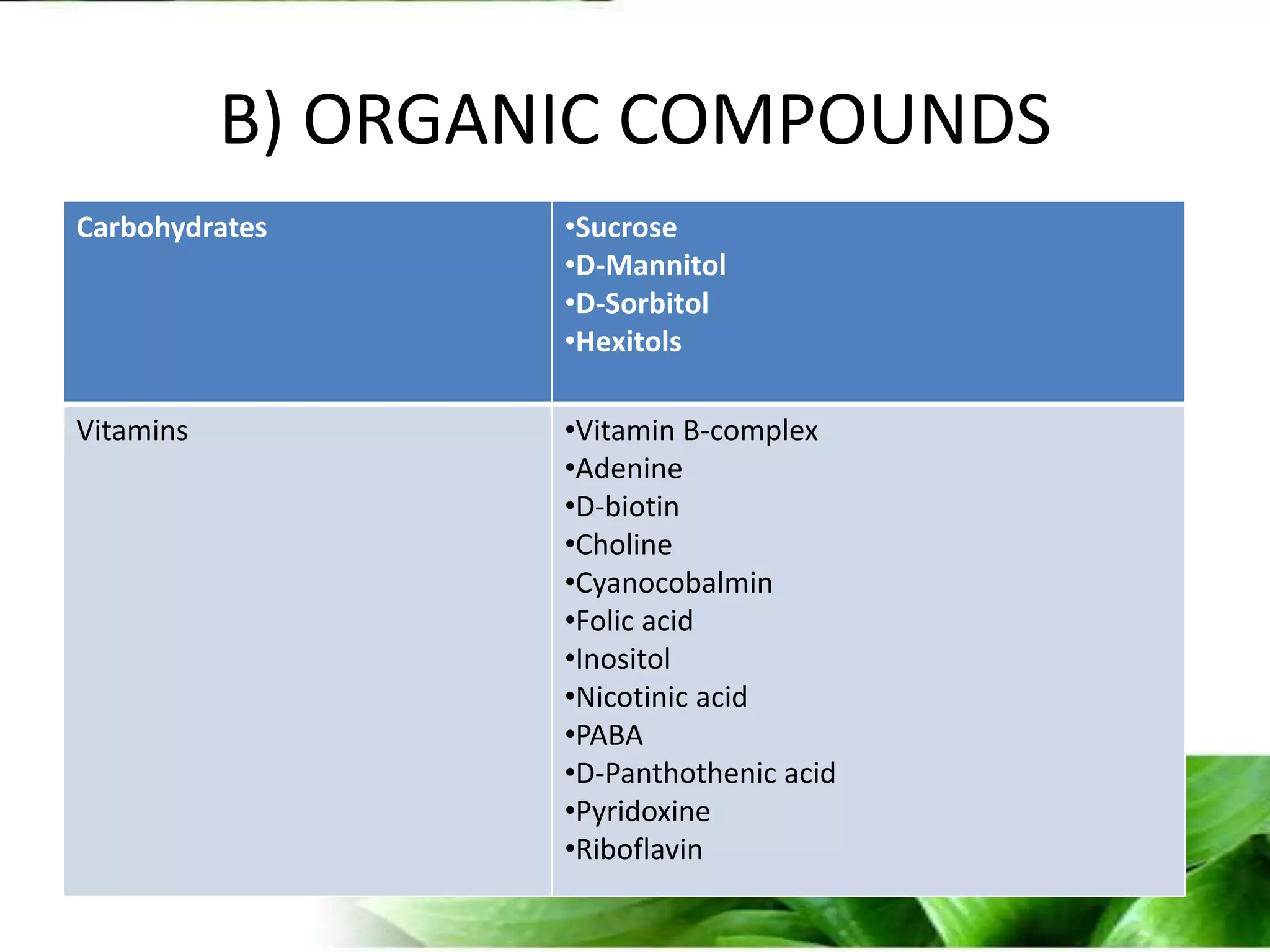
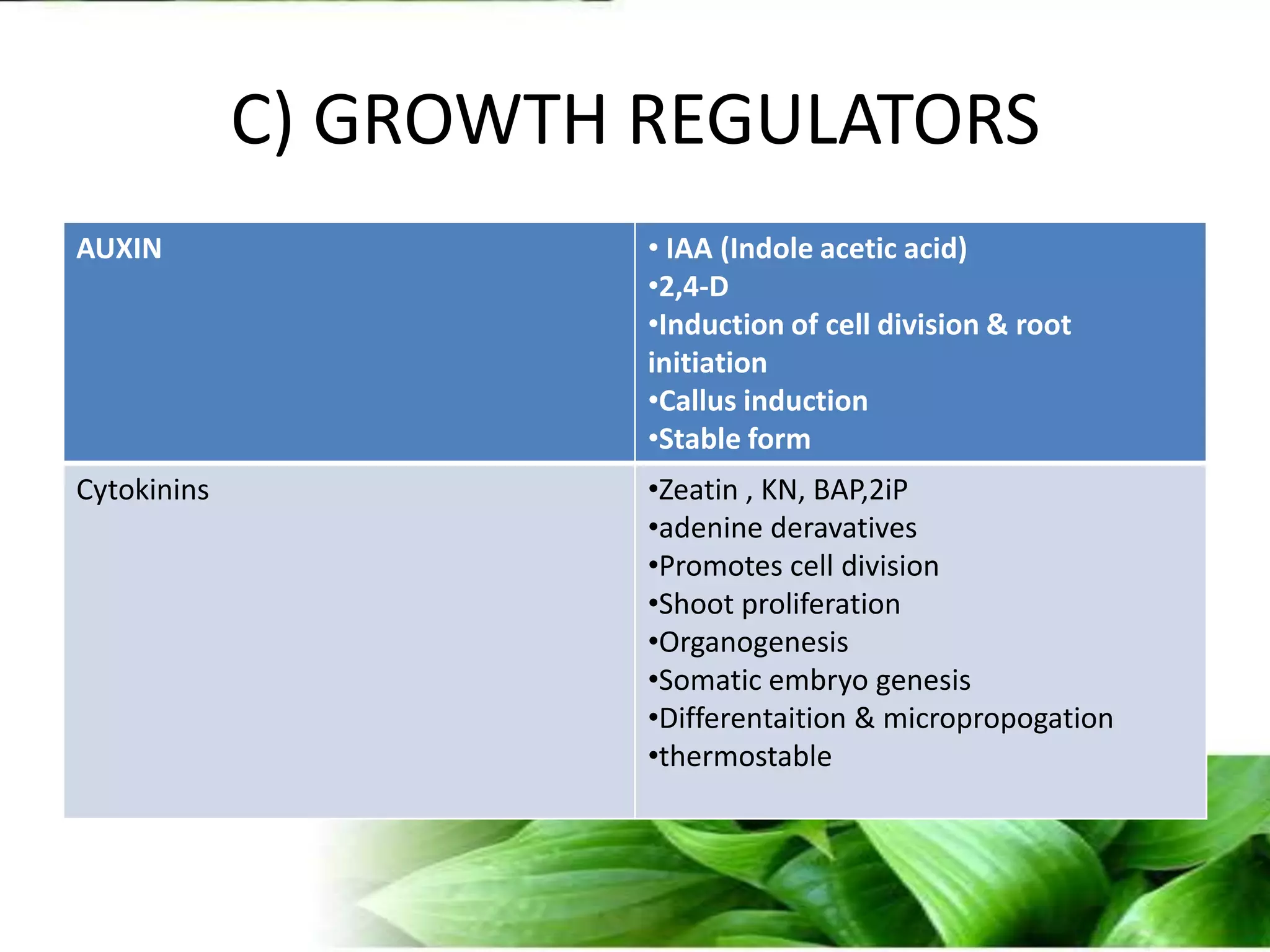
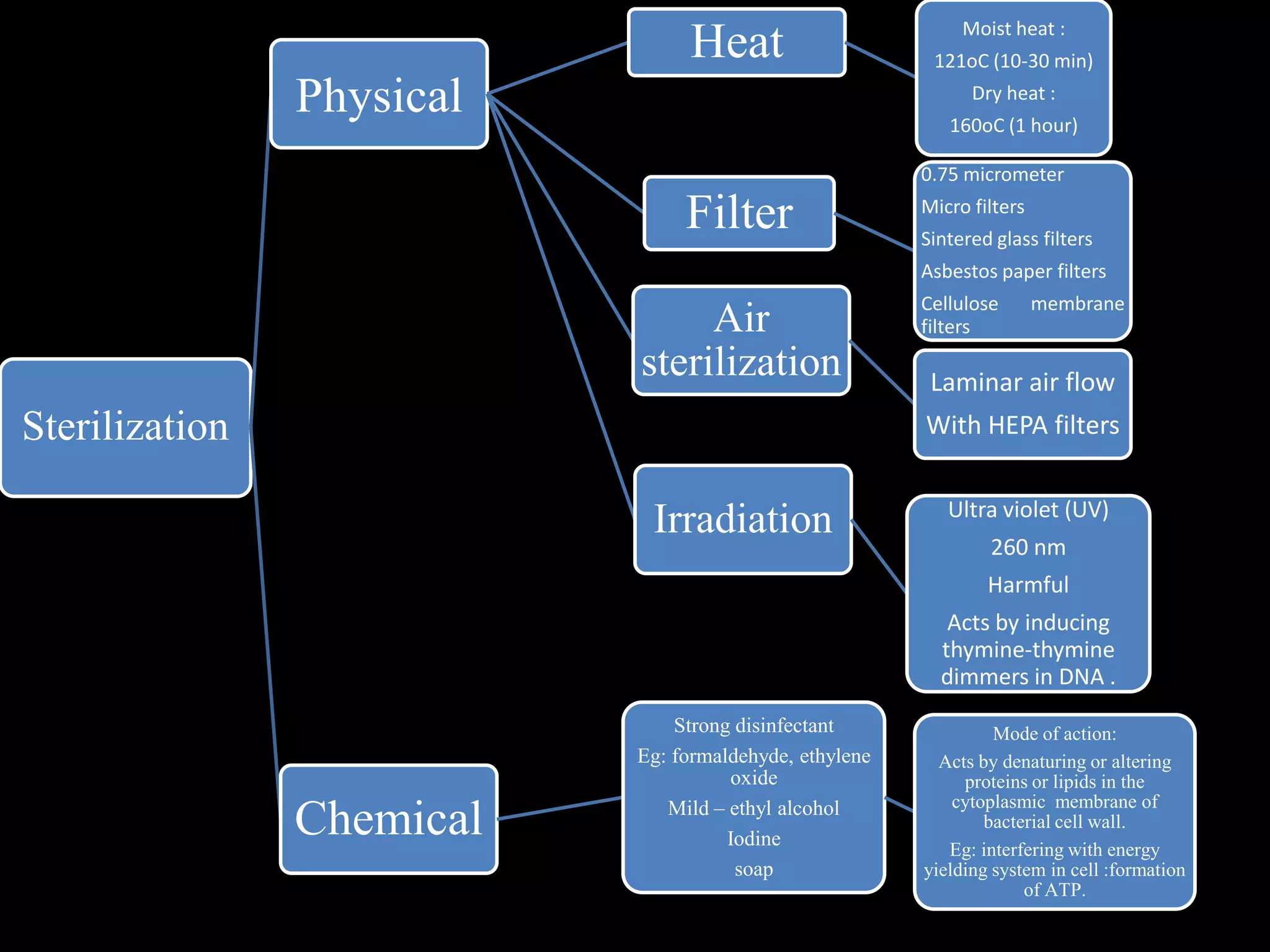
The document provides an overview of plant biotechnology, focusing on cell theory, plant tissue culture techniques including callus tissue formation and organogenesis, and the principles of plant growth and regeneration. It details the composition of culture media, aseptic techniques for sterilization, and the necessary laboratory equipment for tissue culture experiments. Key concepts discussed include totipotency, the nutritional needs of callus, and the environmental factors affecting plant growth.