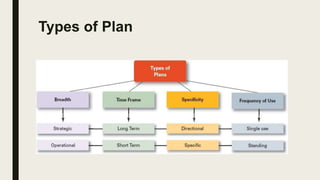
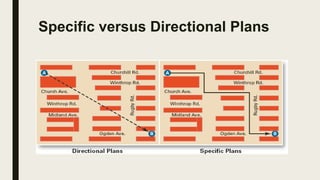
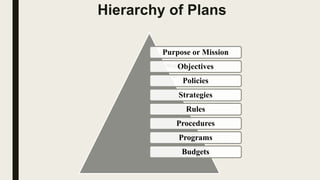
The document outlines the concept of planning as a primary managerial activity, detailing its purposes and types, including informal and formal planning. It defines various planning elements such as goals, plans, and the different types like strategic, operational, long-term, and short-term plans. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of policies, strategies, procedures, rules, programs, and budgets in the planning process, underscoring collaborative involvement from organizational members.