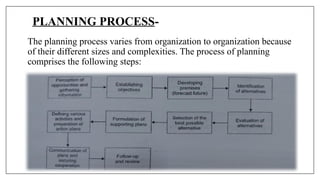
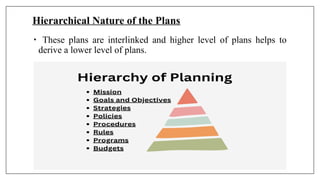
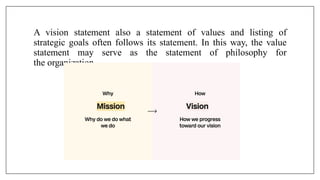
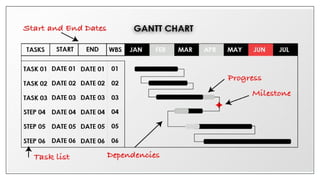
The document outlines the planning process in nursing management, emphasizing its crucial role in setting objectives, coordinating activities, and ensuring resource efficiency. It details the principles and importance of planning, as well as the steps involved in formulating and implementing effective plans, using tools like the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT). Key concepts include minimizing uncertainty, enhancing creativity, and improving organizational effectiveness through structured planning methods.