This document lists and describes various clinical signs, symptoms, and findings that are associated with specific medical conditions. It includes over 50 entries that each define a sign through 1-3 findings, symptoms, or exam results and associate it with the relevant condition. The signs cover a wide range of body systems and diseases, including cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, neurological, and others.
![Allen's Test
Check patency of ulnar artery prior to placing
radial artery line or ABG
ACUTE MESENTERIC ISCHEMIC [AMI
Abdominal Pain is DISPROPORTIONATE to
any physical exam findings]
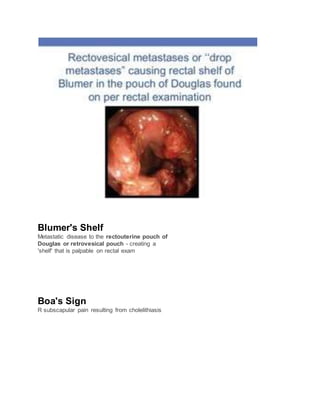
Ballance's Sign
DuLLness to percussion in the Left
flank/LLQ and Resonance to percussion in
the Right flank [the sounds are "im-Balanced"]
Seen with splenic rupture/hematoma](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjsigns-180627210612/85/Pj-signs-1-320.jpg)

![Borchardt's Triad
Seen with GASTRIC VOLVULUS:
1) Retching followed by no emesis
2) epigastric distention
3) inability to pass NG tube
Carcinoid Triad
Seen with CARCINOID syndrome:
1) Flushing
2) Diarrhea
3) right-sided heart failure (Right HF) [dependent
edema, liver, etc]
Charcot's Triad
Seen with CHOLANGITIS
1) Fever and chills
2) Jaundice
3) RUQ pain
Chvostek's sign
Twitching of facial muscles upon tapping the
facial nerve in pts w/ hypOcalcemia
["Chew-twitch sign"]
Courvoisier's Law](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjsigns-180627210612/85/Pj-signs-4-320.jpg)





![Kelly's sign
Visible peristalsis of the ureter in response to
squeezing or retraction
- Used to identify ureters during surgery
Laplace's law
Wall tension = pressure x radius [T=Pr]
- Thus, the colon perforates preferentially at
the cecum b/c of↑ radius and thus, wall
tension
McBurney's point
1/3 the distance from the ASIS to the umbilicus
on a line connecting the two [Appendicitis pain]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjsigns-180627210612/85/Pj-signs-10-320.jpg)



![Raccoon eyes
Bilateral black eyes due to basilar skull fracture
Reynold's Pentad
1) Fever and chills
2) jaundice
3) RUQ pain
[ 1-3 = Charcot'striad ] +
4) Mental status Δs, and
5) Shock or sepsis
Seen in patients w/ Supperative Cholangitis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjsigns-180627210612/85/Pj-signs-14-320.jpg)
![Rovsing's sign
Palpation of LLQ resulting in pain in RLQ; seen
in appendicitis
["Rovsing = Right sings when left is pressed"]
Romana's Sign
unilateral painless periorbital swelling associated with the acute stage of CHAGAS
DISEASE.
Saint's triad
1) Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
2) Hiatal hernia (GERD)
3) Diverticular disease (Gut & Butt)
Silk glove sign
Indirect hernia sac in the pediatric patient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjsigns-180627210612/85/Pj-signs-15-320.jpg)

![Valentino's sign
RLQ pain from a perforated peptic ulcer due to
succus/pus draining into the RLQ
Westermark's sign
Decreased pulmonary vasculature
markings on CXR in a pt w/ PE
[Wester-Mark = "Markings Wasting away"]
Whipple's Triad
Evidence for insulinoma:
1) Hypoglycemia < 50
2) CNS and vasomotor symptoms (syncope,
diaphoresis)
3) Relief of symptoms w/ administration of
glucose](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pjsigns-180627210612/85/Pj-signs-17-320.jpg)
