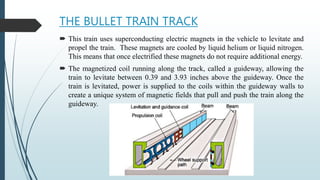
The document discusses India's plans for a high-speed rail or bullet train project connecting Mumbai and Ahmedabad. Key points include:
1) The 534km project will be India's first high-speed rail line and use magnetic levitation technology to enable train speeds up to 350km/hr.
2) Construction is set to begin in 2018 at an estimated cost of 97,636 crore with 81% funded by Japan.
3) The bullet train will reduce travel time between Mumbai and Ahmedabad from 7 hours to just over 2 hours.