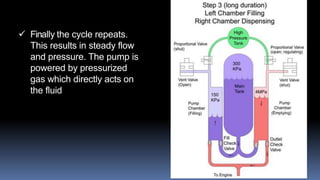
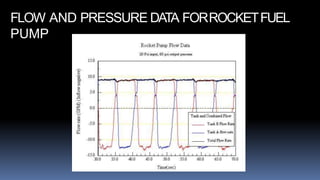
This seminar report summarizes a presentation on a pistonless pump developed by NASA as an alternative to turbo pumps for rocket fuel. Pistonless pumps have no moving parts besides chamber valves, providing increased flexibility and reliability compared to turbo pumps. Turbo pumps are heavy, complex, inefficient, and failure-prone. In contrast, pistonless pumps have fewer parts, higher efficiency, are simpler to design and manufacture, and have built-in redundancy. The report describes the working of the dual pistonless pump, which alternately pressurizes and refills two chambers to provide steady fuel flow and pressure. Data is presented showing its potential to significantly reduce the cost and improve reliability of rocket fuel pumps.