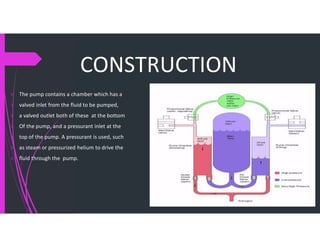
This document summarizes a pistonless pump designed for rocket fuel. It introduces the pistonless pump as an alternative to turbo pumps that is simpler, cheaper, and lighter. The summary describes how the pistonless pump works using pressurized gas to cycle fuel through two chambers alternately without any moving pistons. Advantages are listed as low cost, weight, and few moving parts compared to turbo pumps. Applications mentioned include use in deep space exploration missions.