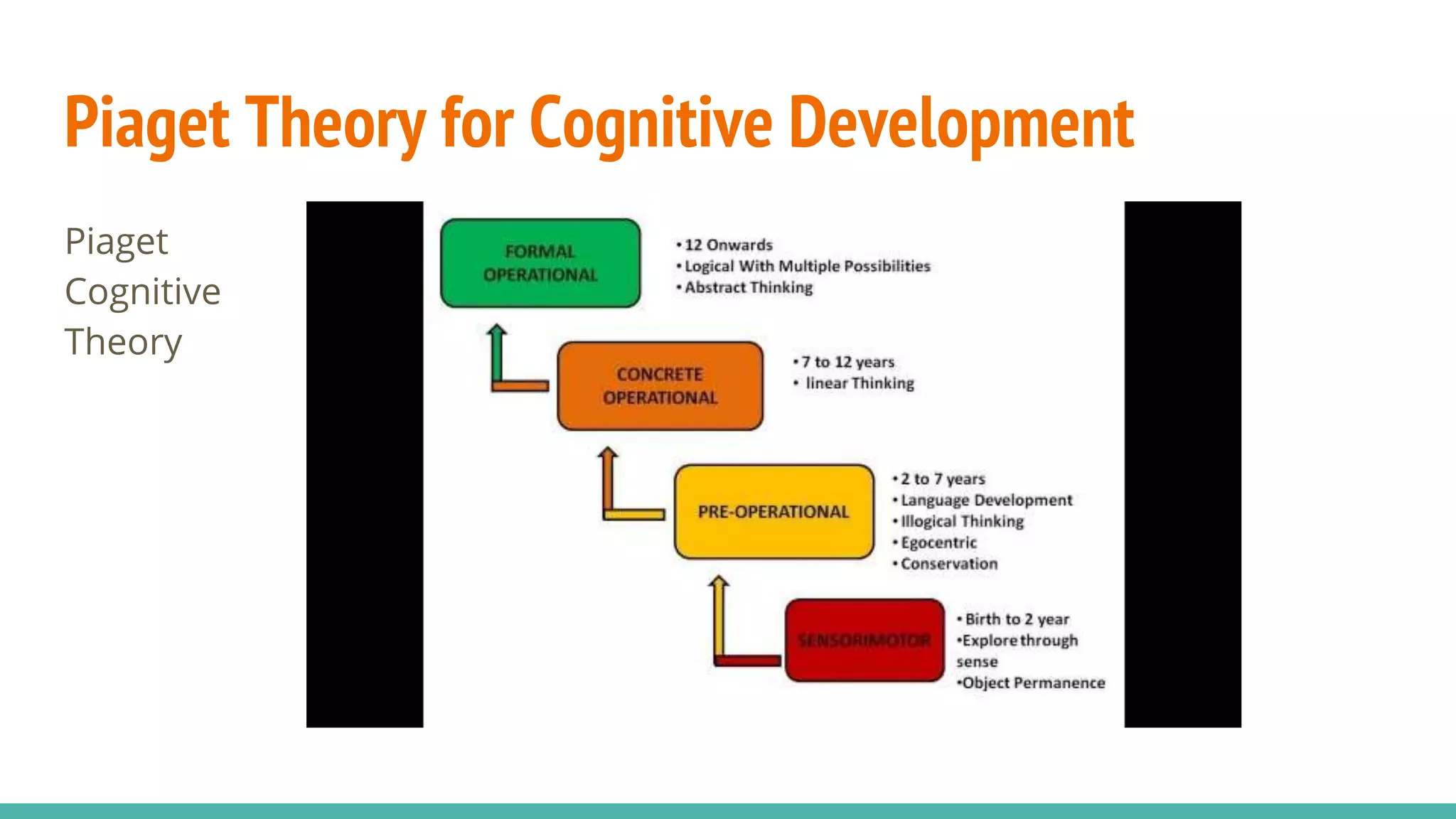
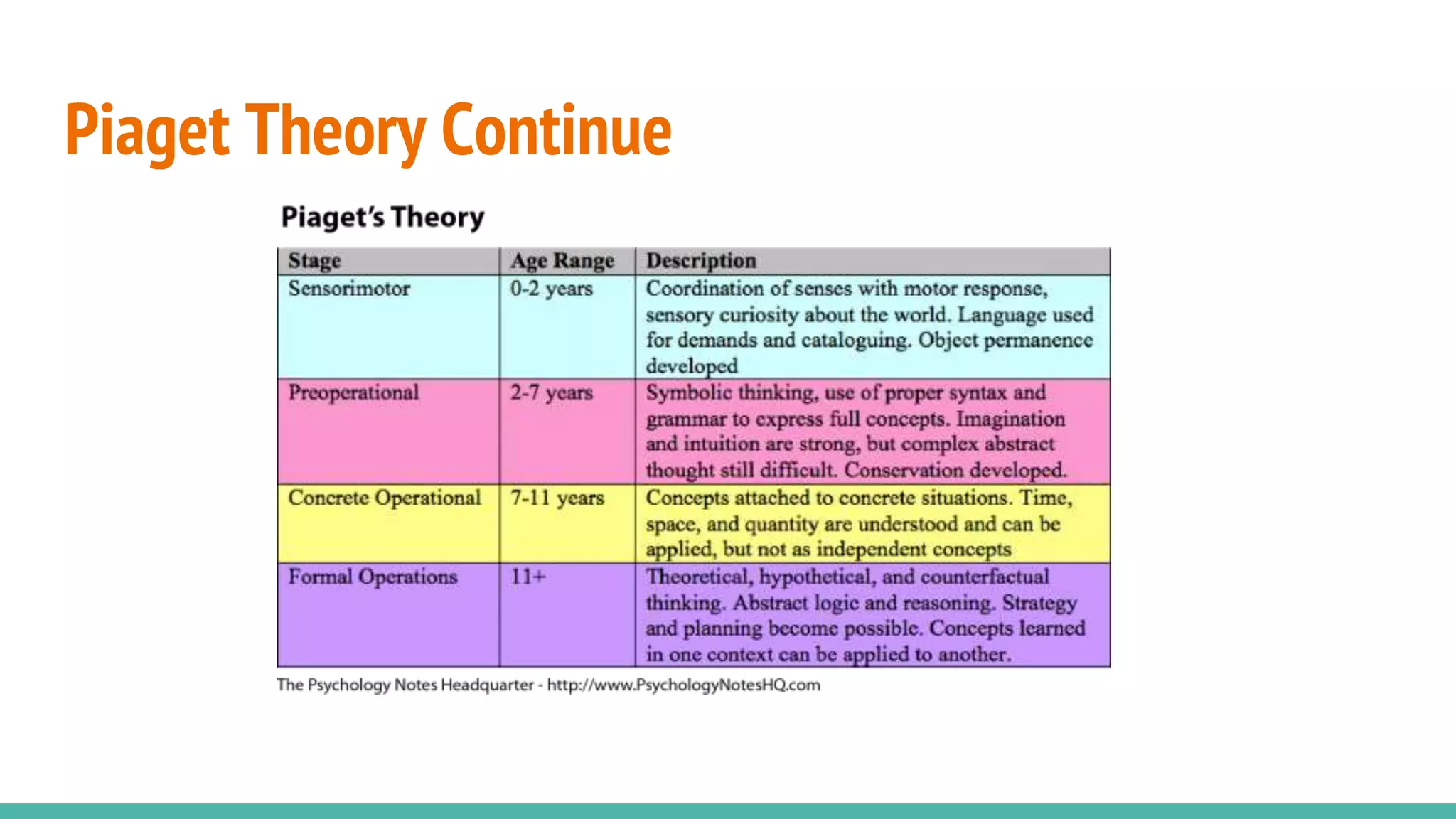
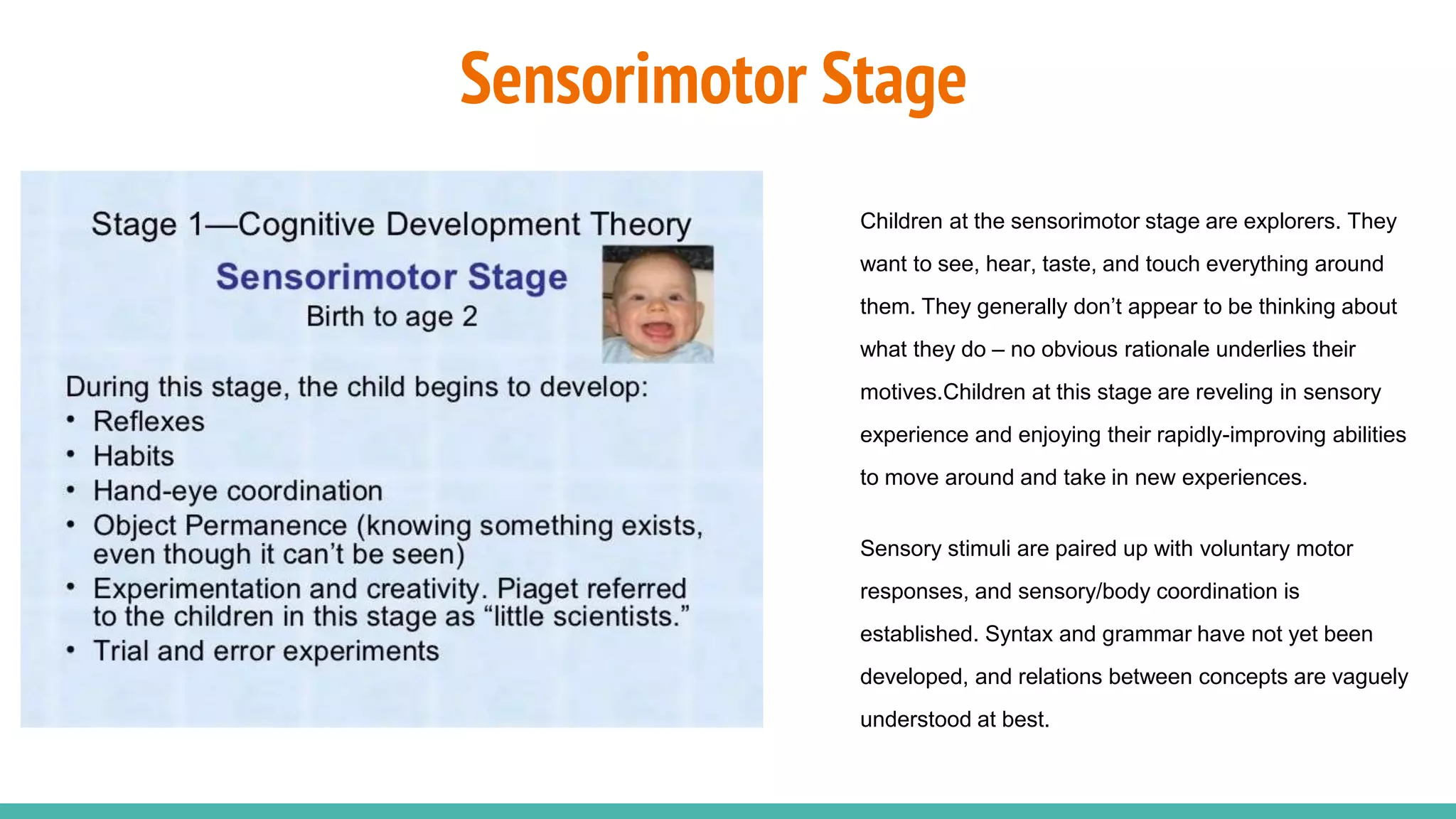
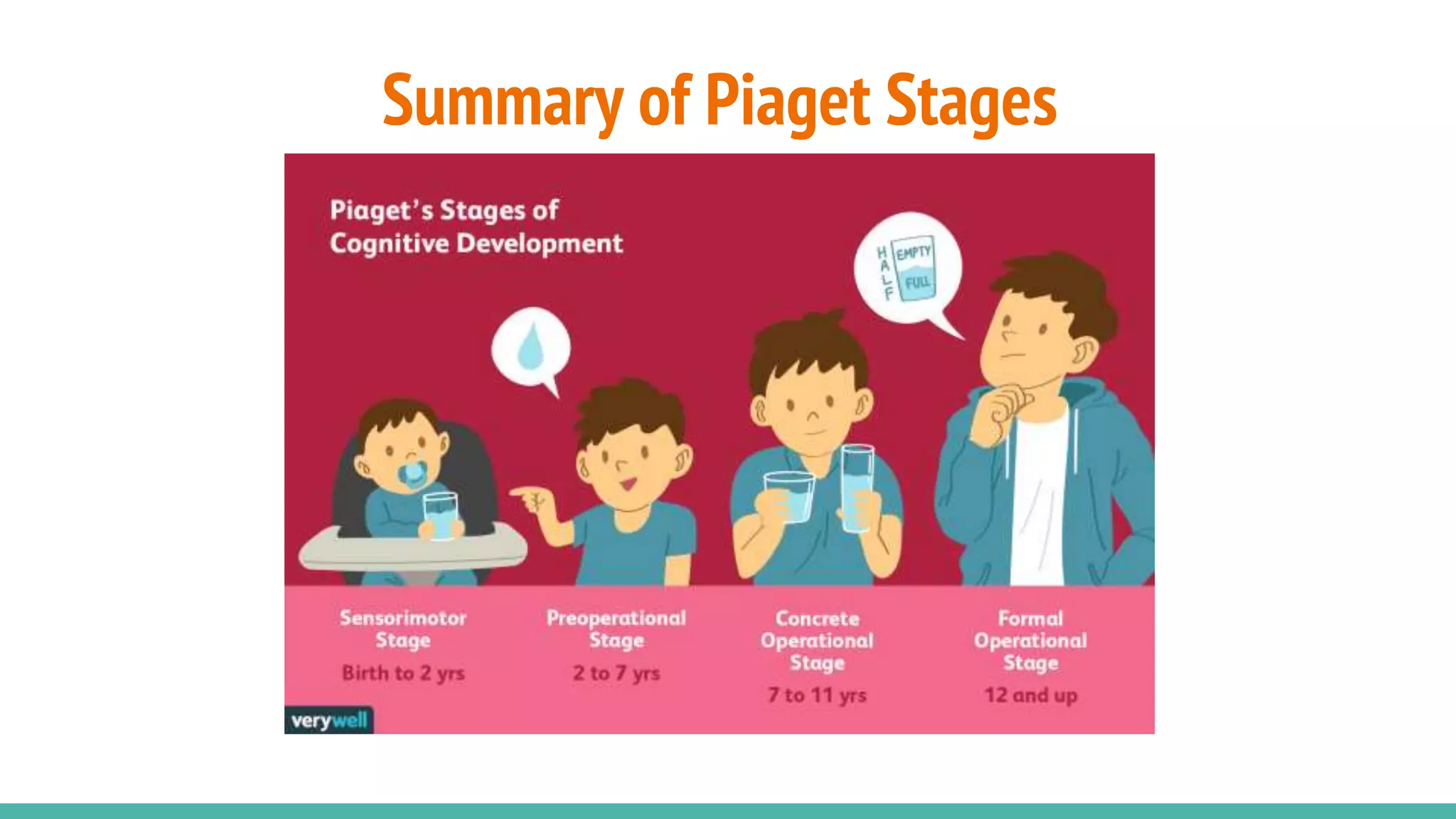
The document discusses cognitive development according to Piaget's model, detailing the stages from sensorimotor to formal operations and how children perceive morality. It explains that children initially view morality as dictated by authority before progressing to a more autonomous understanding of moral rules as social agreements. The document also addresses cognitive impairments, the influence of heredity and environment on development, and the importance of supportive caregiving in enhancing cognitive abilities.