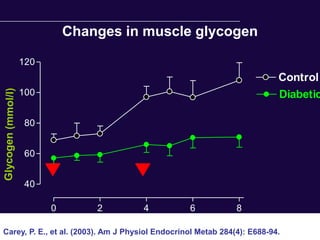
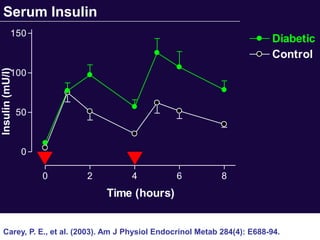
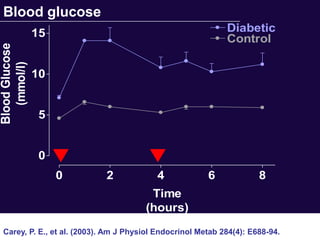
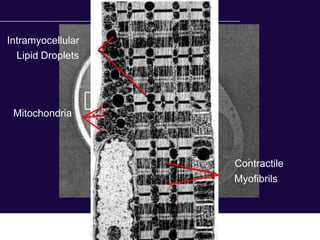
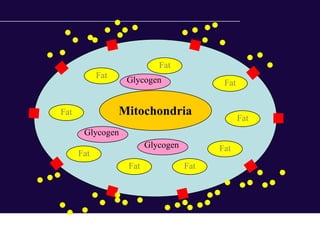
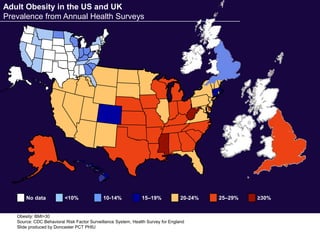
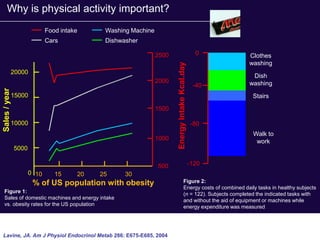
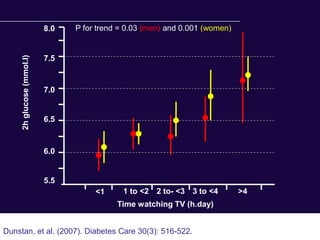
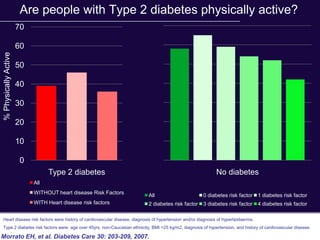
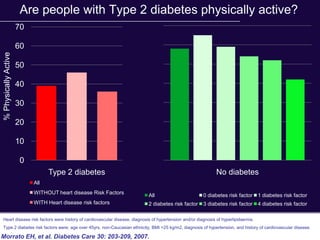
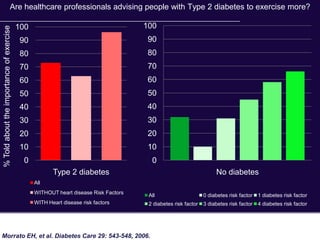
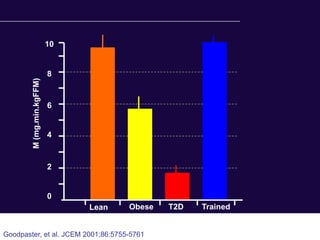
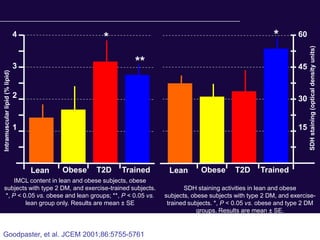
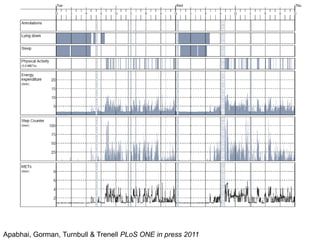
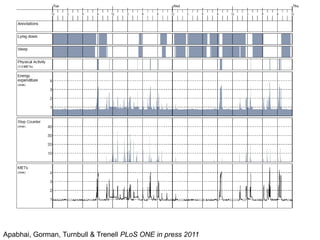
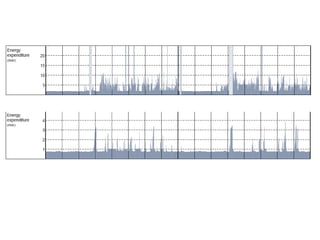
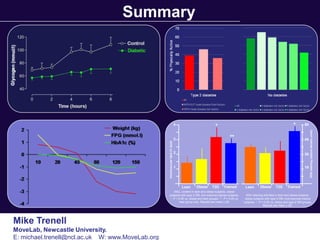
The document discusses the critical role of physical activity and exercise in managing type 2 diabetes, highlighting the relationship between physical fitness and glucose control. It notes that people with type 2 diabetes are generally less active, which can exacerbate their condition, and emphasizes the need for healthcare professionals to encourage exercise among these individuals. Overall, reversing physical inactivity could be a powerful therapeutic strategy for improving health outcomes in those with type 2 diabetes.