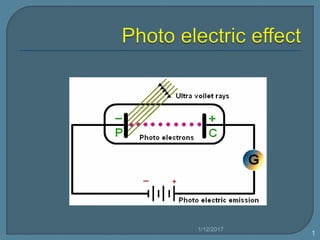
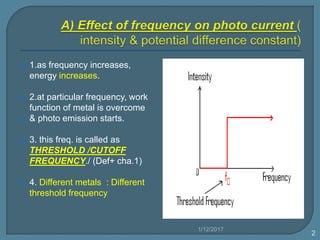
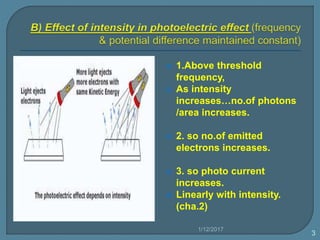
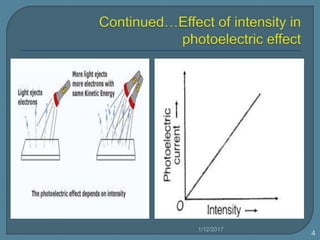
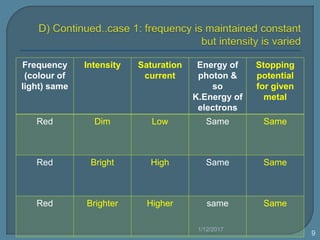
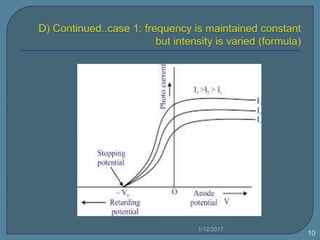
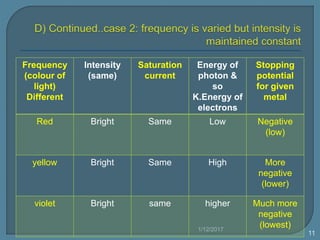
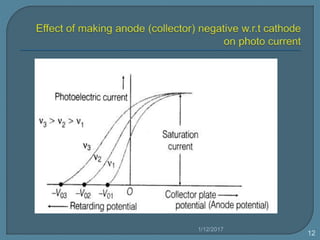
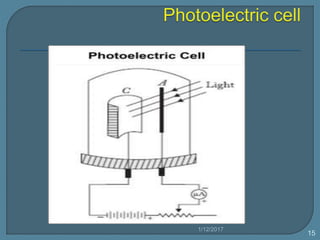
The document discusses the photoelectric effect and how various factors influence photoemission. It notes that:
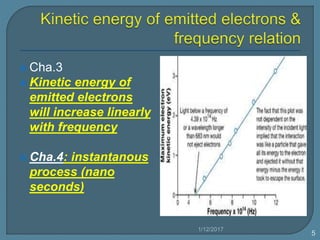
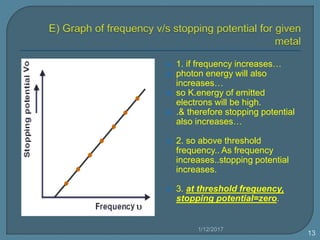
1) As frequency increases, the photon energy and kinetic energy of emitted electrons increases. The stopping potential also increases with higher frequencies.
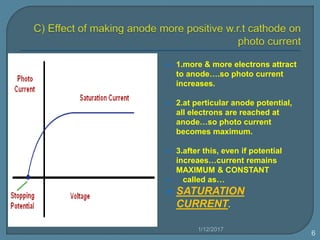
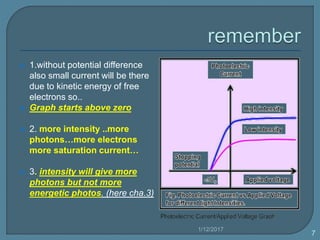
2) For a given metal, the saturation current increases with higher light intensities due to more photons and emitted electrons.
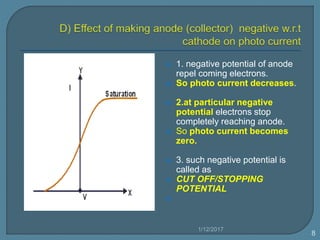
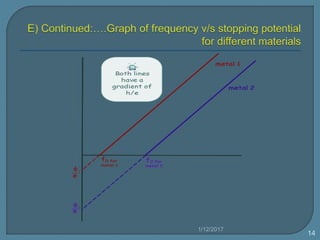
3) Different metals have different threshold frequencies above which photoemission occurs, and higher frequencies result in more negative stopping potentials.