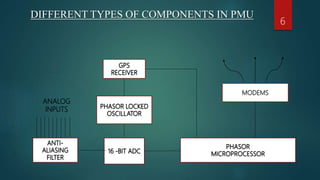
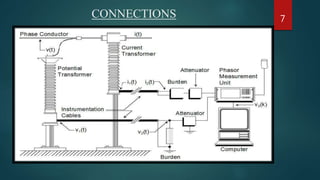
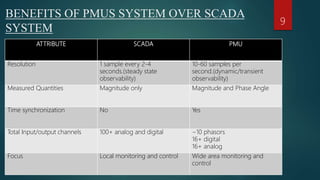
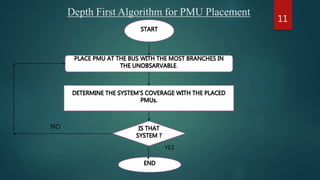
This document presents a seminar on phasor measurement units (PMUs) and their applications in improving power system monitoring and control, especially over traditional SCADA systems. It discusses the functionality of PMUs, their benefits, challenges faced in their implementation, and potential future applications in power system protection. The concluding remarks emphasize the importance of synchronized phasor measurements in enhancing system observability and operational efficiency.