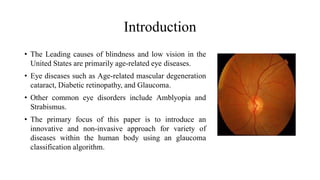
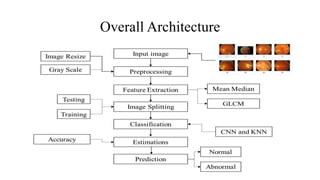
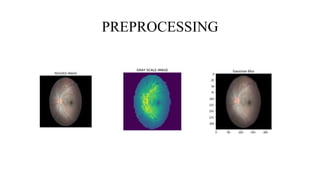
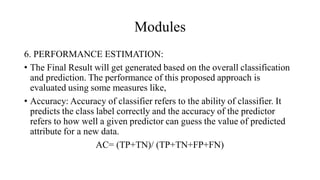
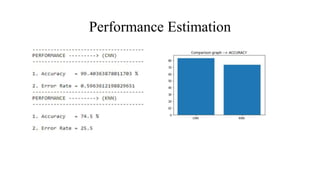
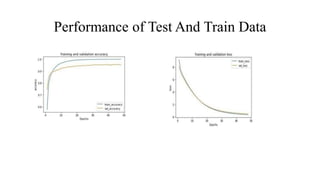
The document presents a deep learning approach for glaucoma disease classification, focusing on improving detection accuracy through innovative feature extraction methods. It discusses existing challenges in screening systems and introduces a new methodology that includes data collection, image preprocessing, and classification using machine learning algorithms. Future enhancements aim to expand the application of deep learning in ophthalmology, targeting additional eye conditions.