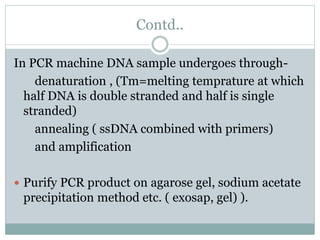
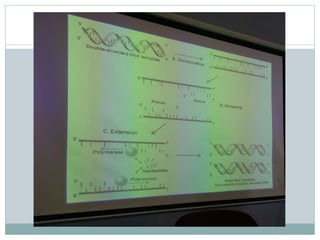
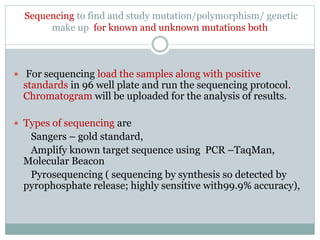
This document discusses the significance of pharmacogenomics in providing personalized medicine through diagnosis, prognosis, prediction, and treatment decisions. It covers the history of discoveries in genetics from Watson and Crick's DNA model to the identification of the human genome sequence. Key terms discussed include the differences between pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics, polymorphisms and mutations, coding and non-coding DNA regions. The effects of genetic mutations and polymorphisms on drug pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are also summarized.