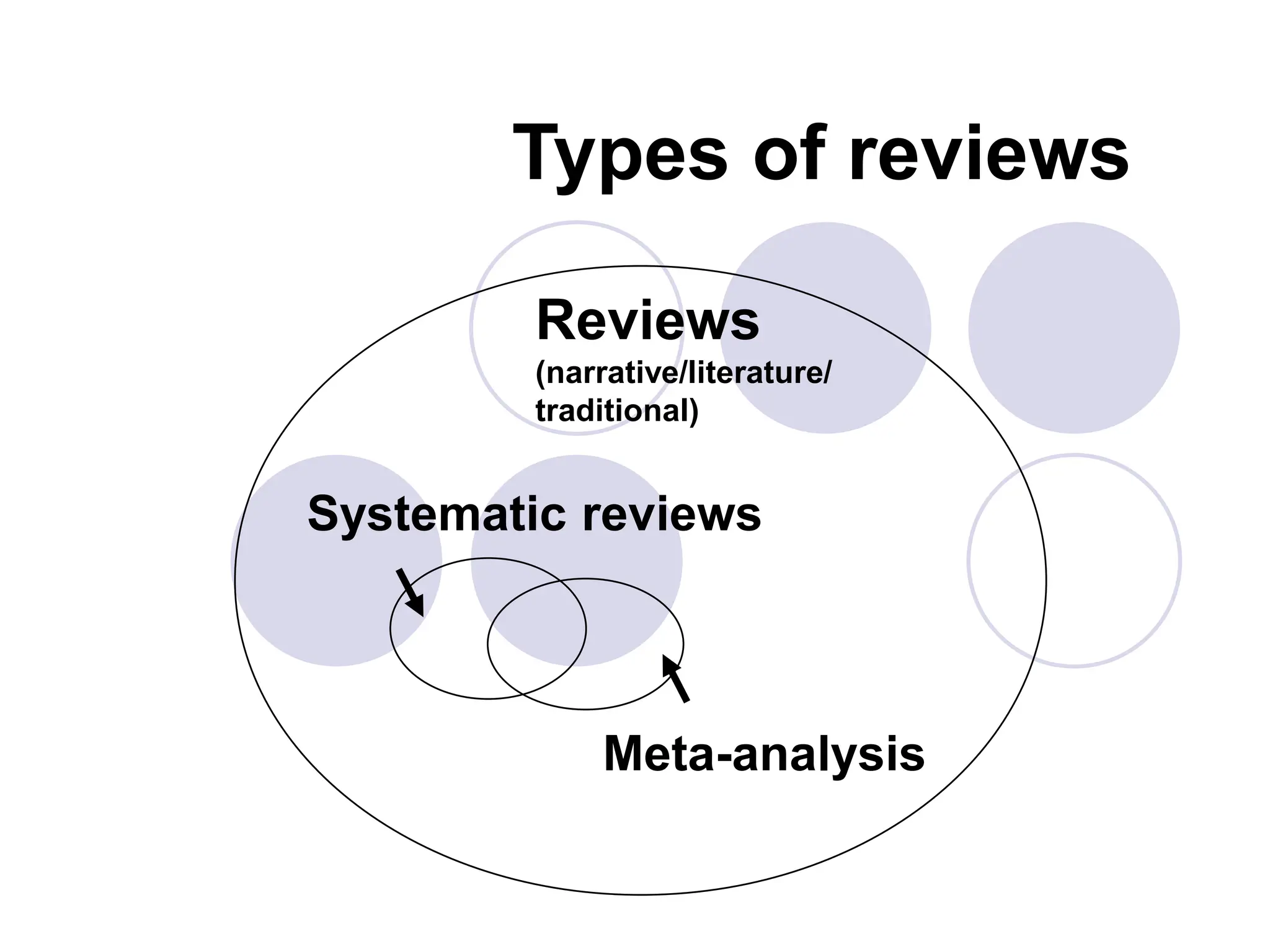
Systematic reviews provide a rigorous and unbiased summary of the evidence on a particular health issue or intervention. This document outlines key aspects of systematic reviews, including:
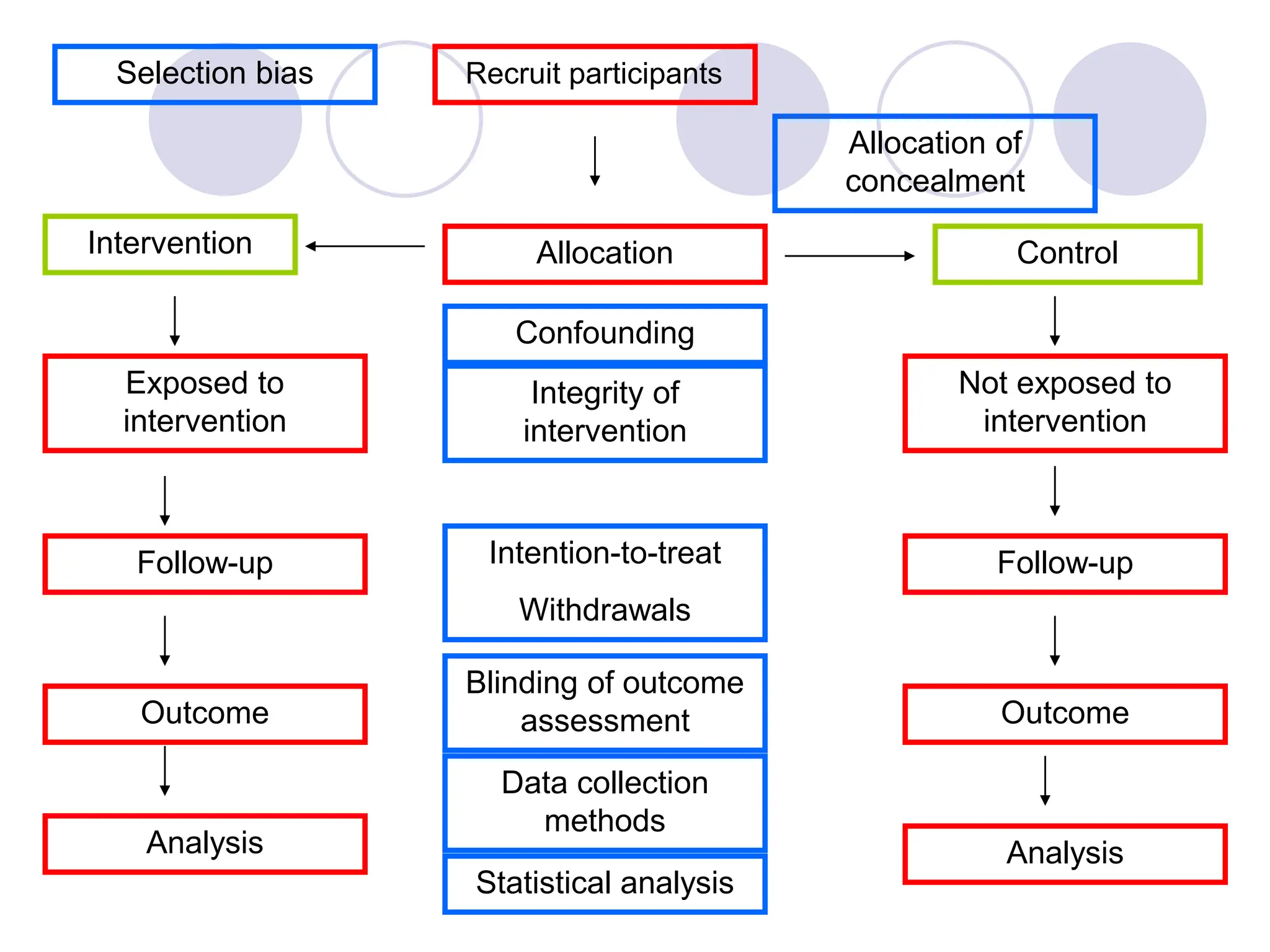
- Systematic reviews follow a structured process to minimize bias, including formulating a clear question, conducting a comprehensive search, and critically appraising and synthesizing the evidence.
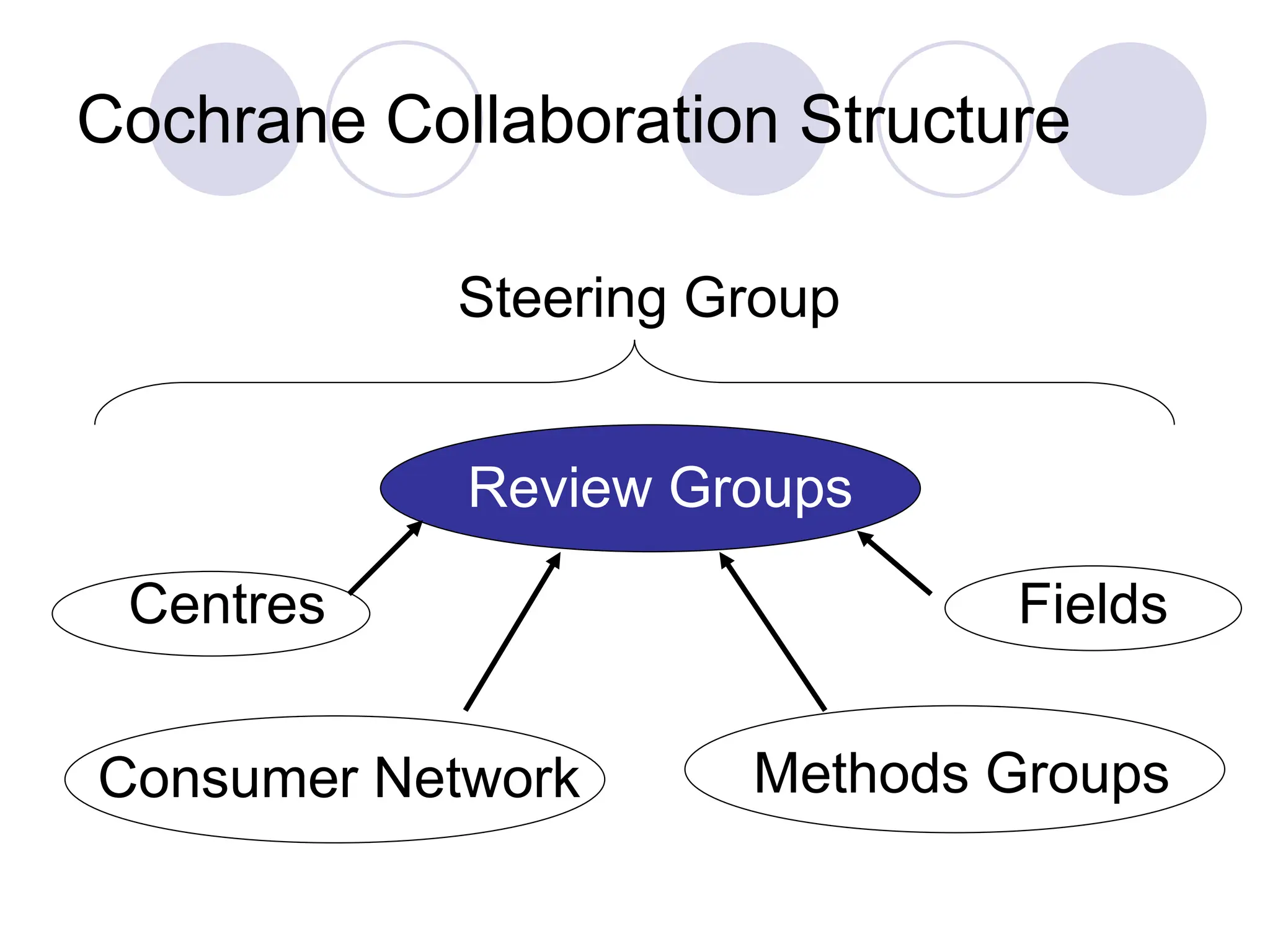
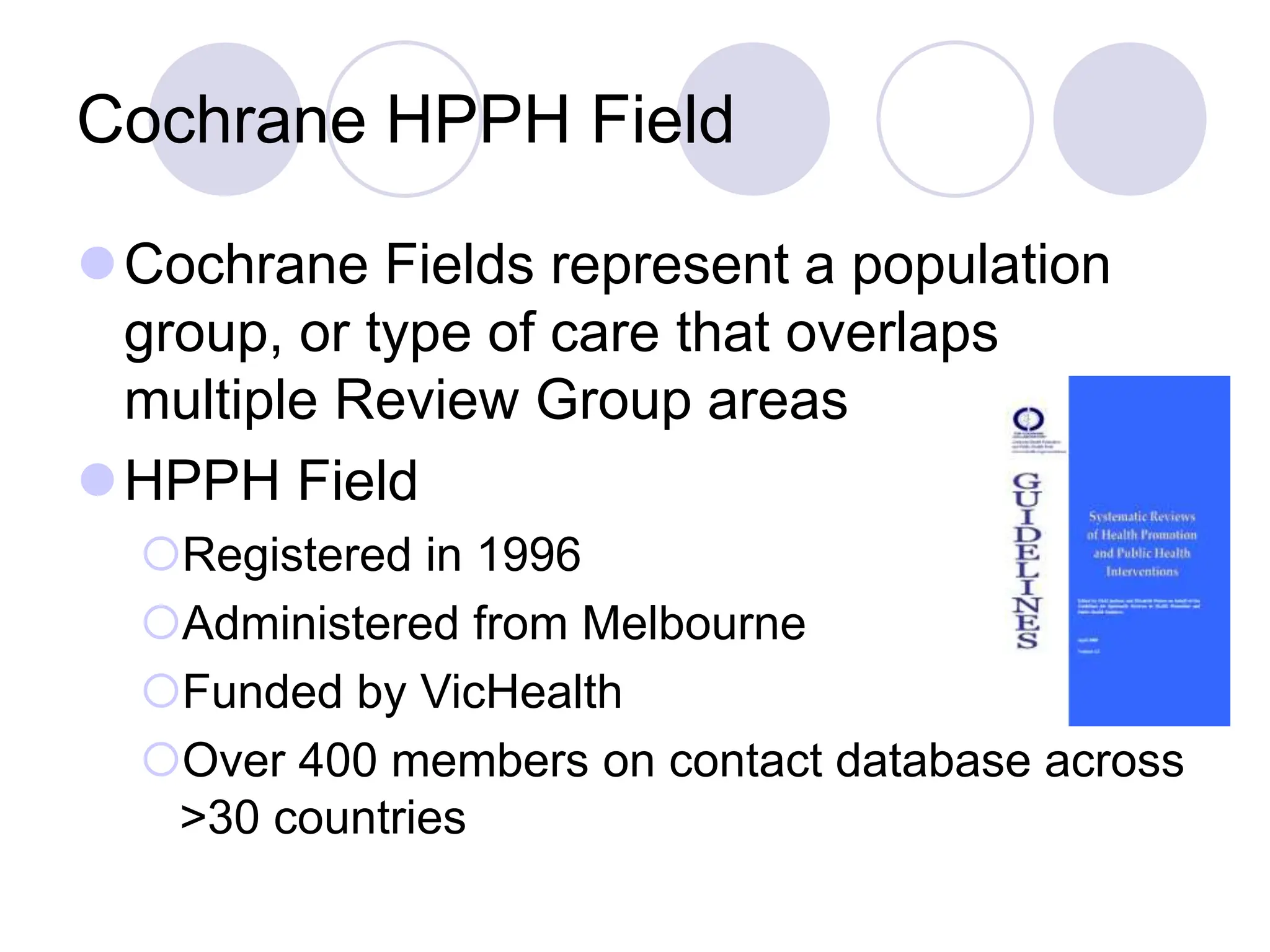
- The Cochrane Collaboration produces high-quality systematic reviews to inform health policy and practice. The Cochrane Health Promotion & Public Health Field represents the needs of health promotion and public health within Cochrane.
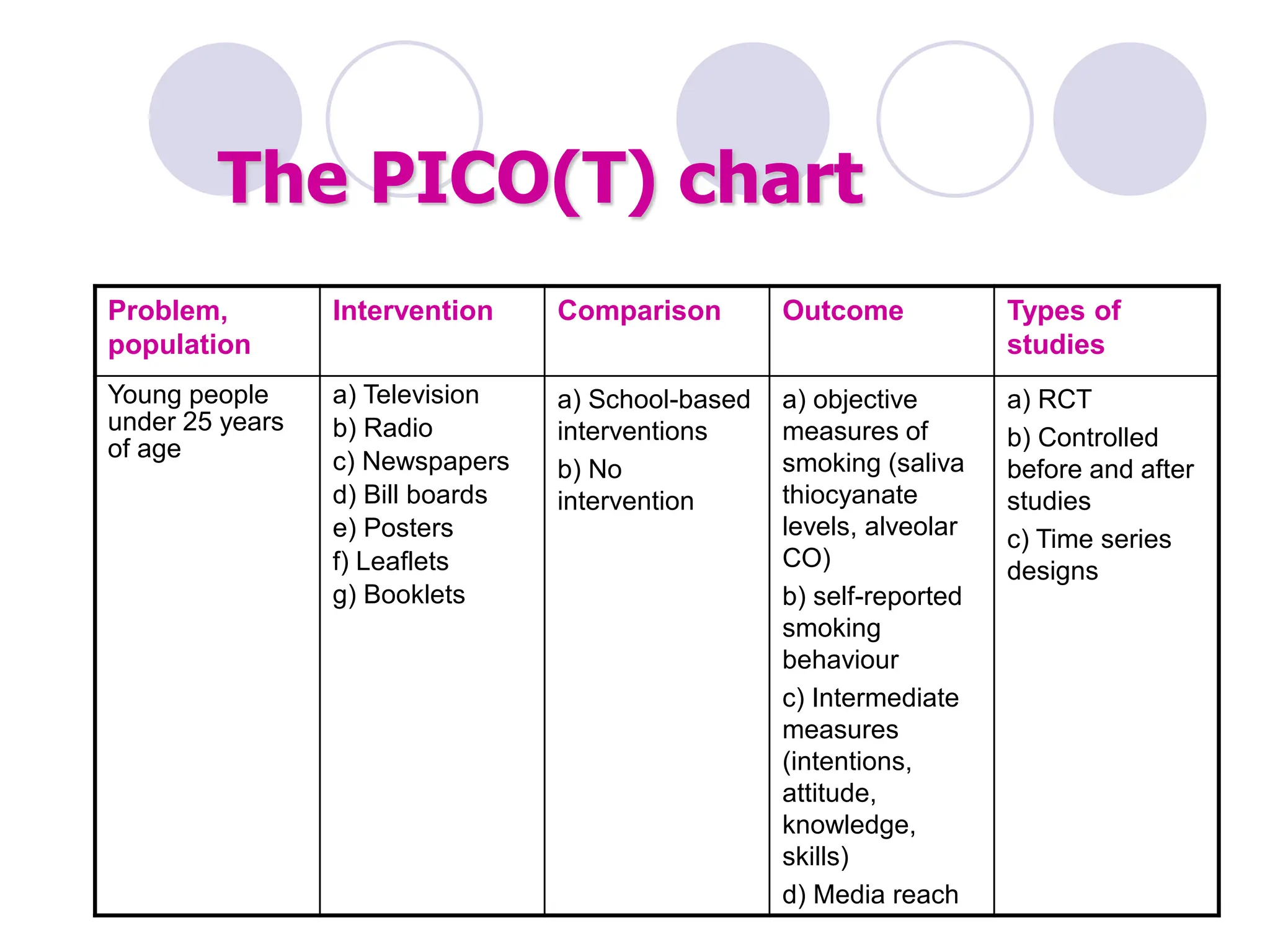
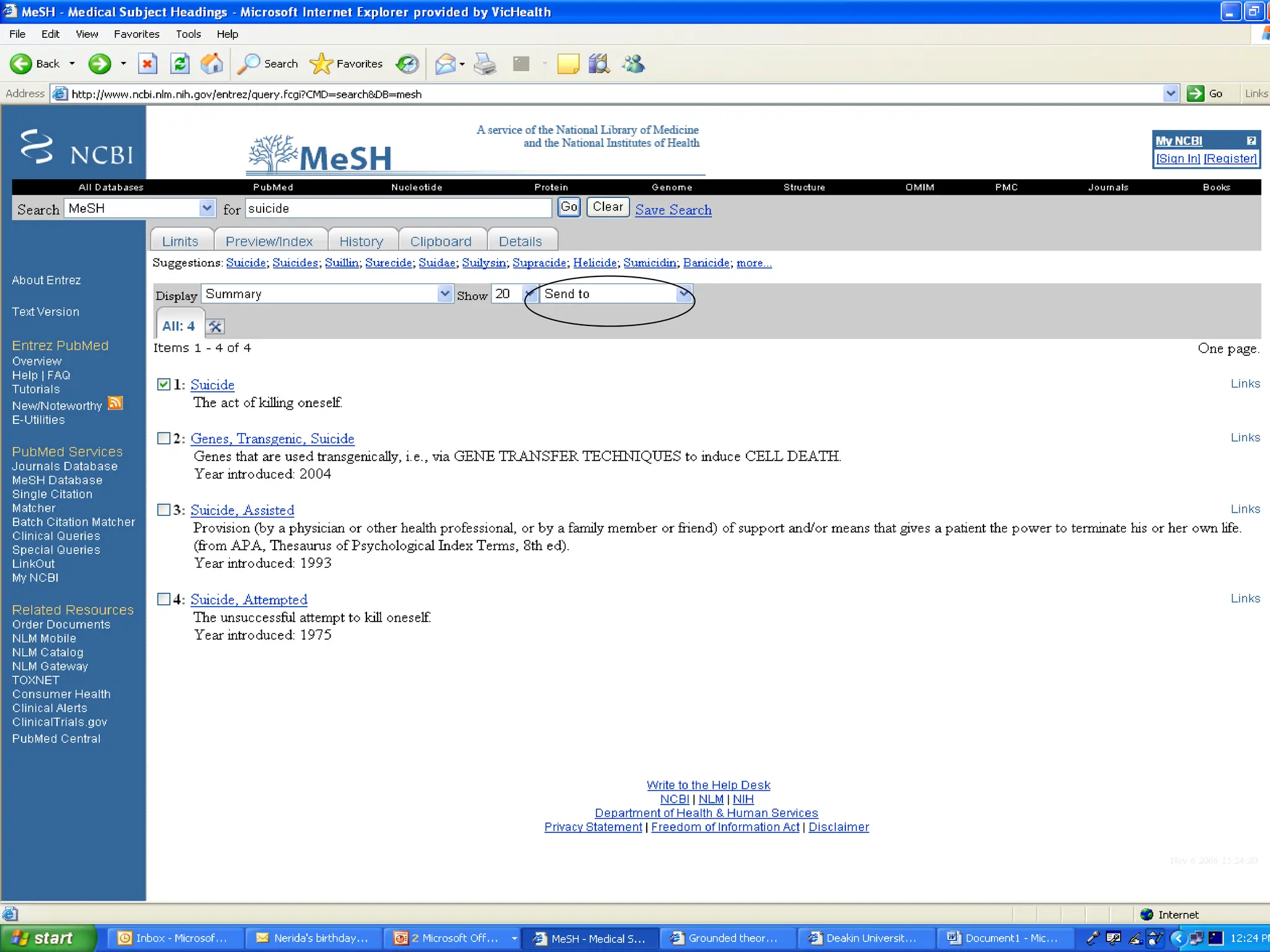
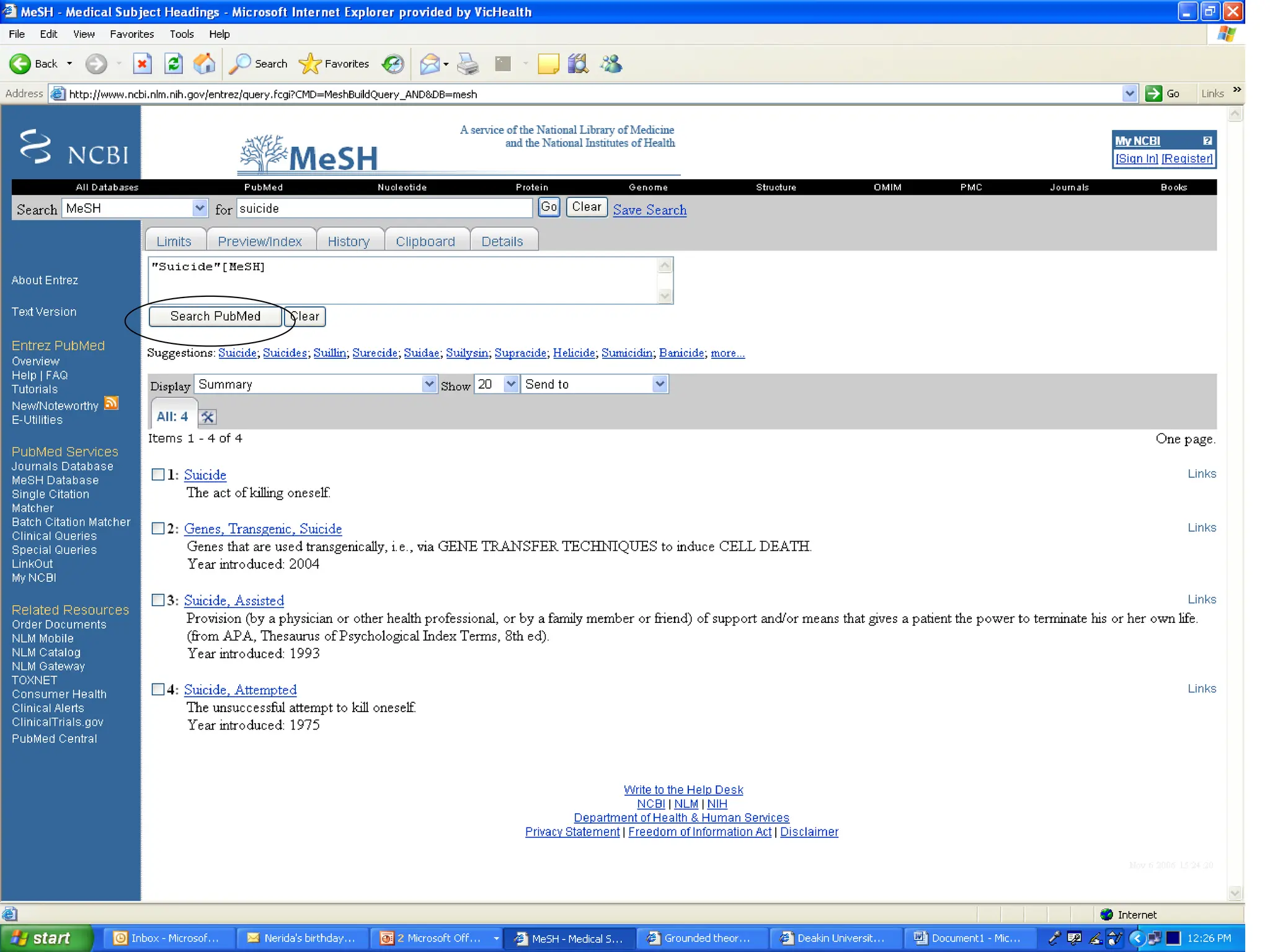
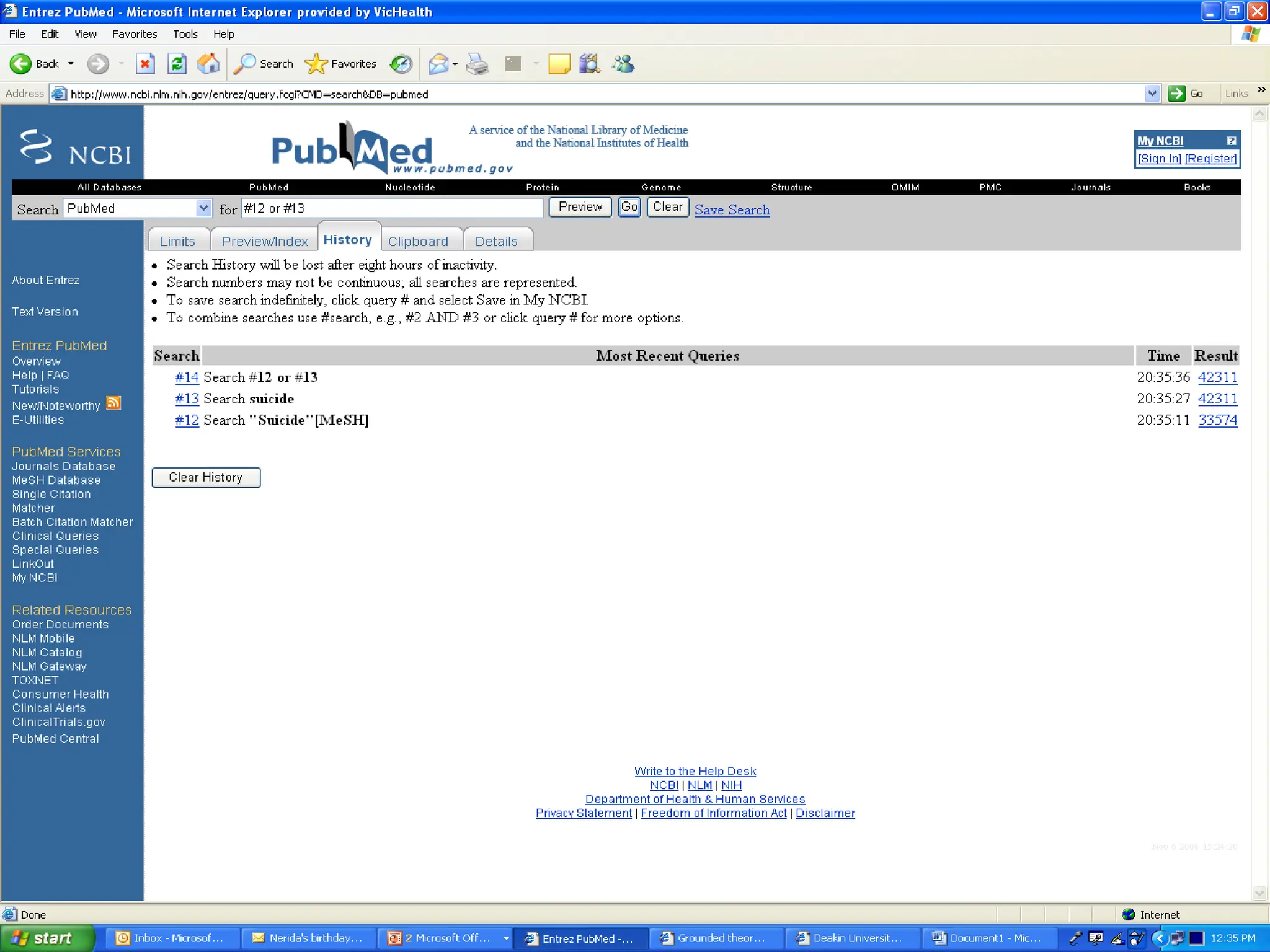
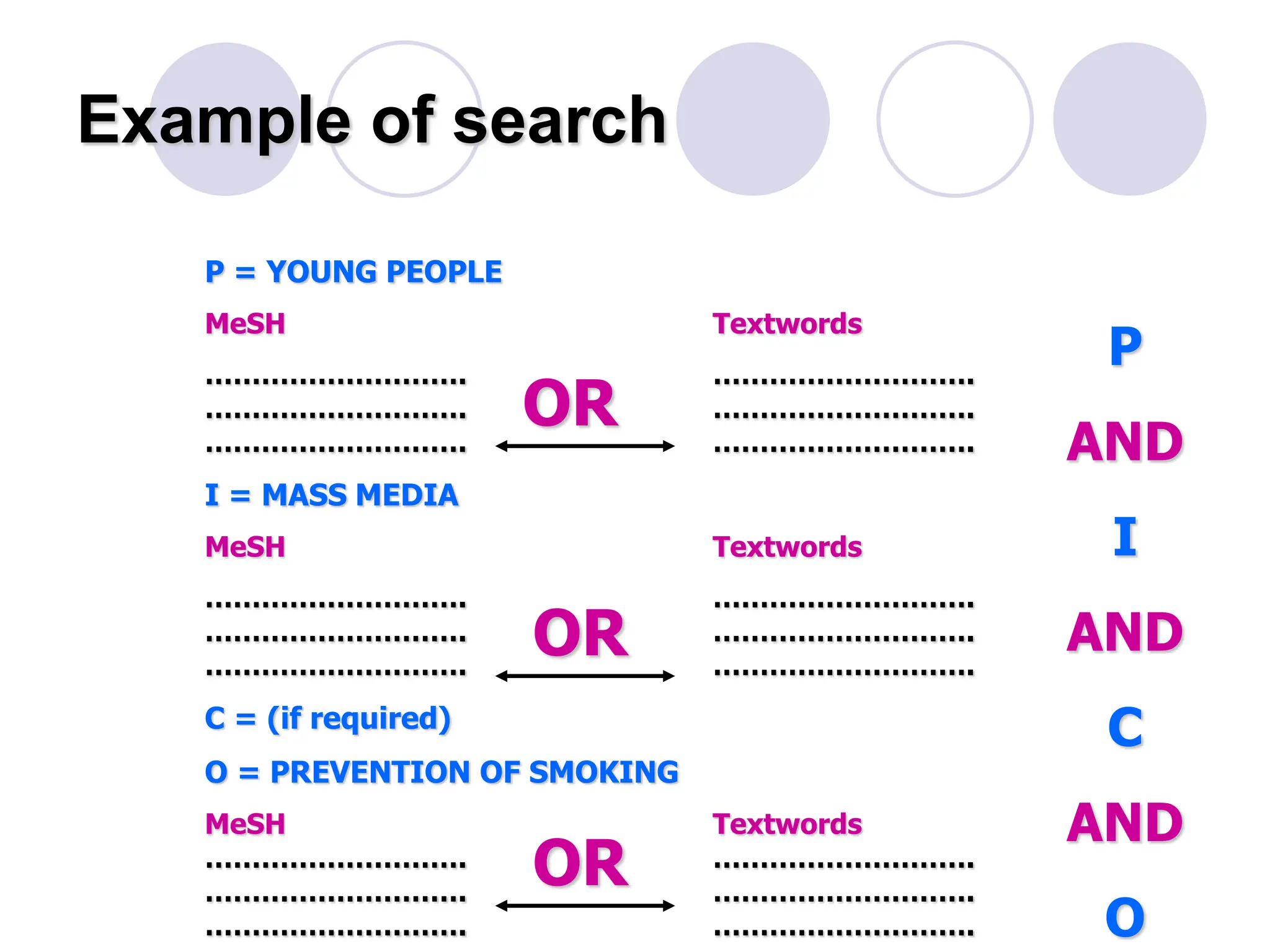
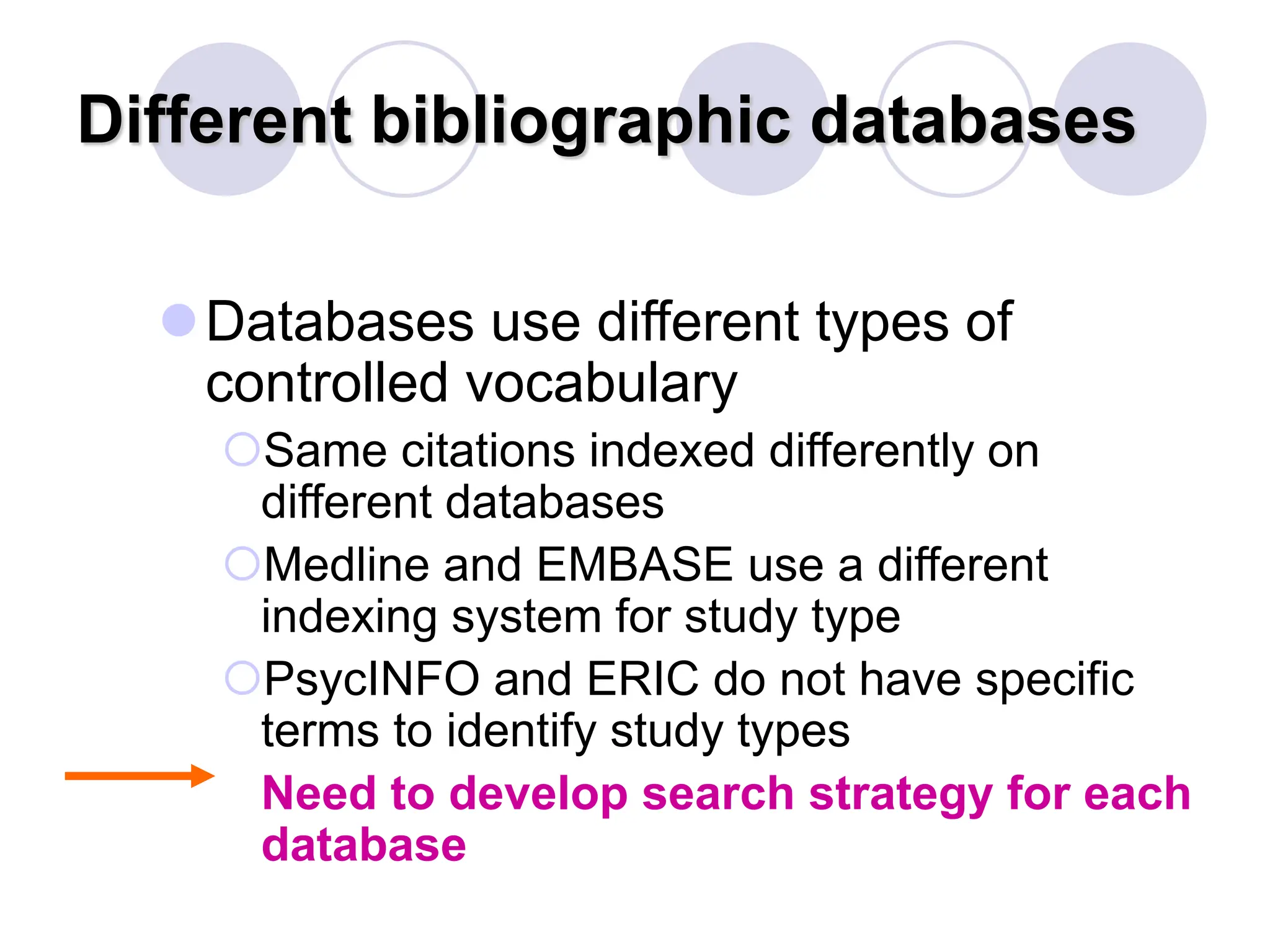
- Conducting a good systematic review requires asking a focused and answerable question using the PICO framework, performing a comprehensive search across multiple databases and sources, and documenting