This document summarizes key information about pertussis (whooping cough):
- Pertussis is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis and is highly contagious through respiratory droplets. It most severely affects young infants and children.
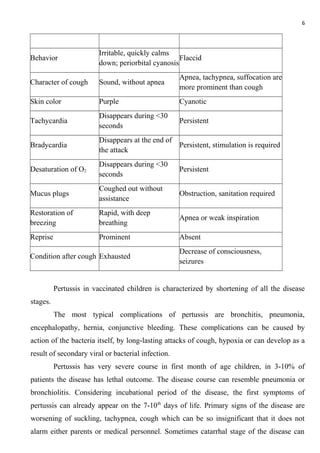
- Clinical symptoms progress through catarrhal, paroxysmal cough, and spastic cough stages, characterized by severe coughing fits and vomiting. Complications can include pneumonia, encephalopathy, and pulmonary hypertension.
- Diagnosis is based on clinical presentation and culture of B. pertussis from respiratory samples, though vaccination and prior infection do not provide lifelong immunity. Exclusion of contacts and antibiotic prophylaxis are effective prevention measures.