- A peripheral smear (PS) provides important diagnostic information about red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and any hemoparasites present.
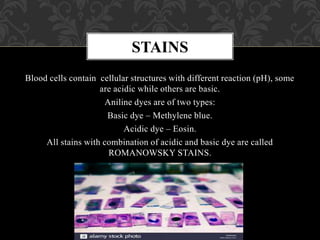
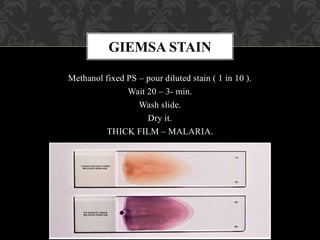
- Romanowsky stains like Leishman and Giemsa stains are commonly used because they differentially stain cellular components through a combination of basic and acidic dyes.
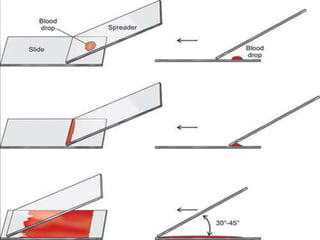
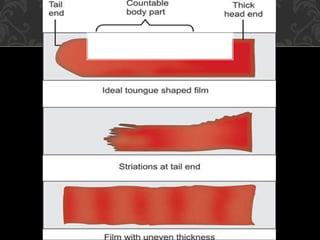
- To perform a peripheral smear, a small blood sample is spread in a thin layer on a slide and allowed to dry before being stained using a Romanowsky stain and examined under a microscope.