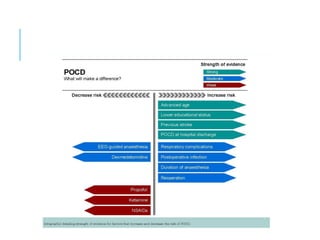
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a common and often underdiagnosed condition affecting elderly patients, characterized by cognitive decline after surgery, particularly following major operations like cardiac and orthopedic surgeries. The condition is linked to neuroinflammation, anesthesia effects, and patient-specific risk factors such as age and pre-existing health issues. Preventative strategies include preoperative cognitive screenings and careful management of anesthesia, while post-surgical care involves cognitive rehabilitation and a multidisciplinary approach to patient support.