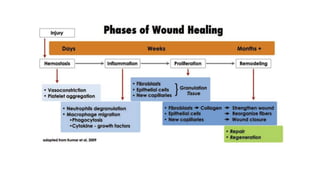
- Periapical wound healing is the host's programmed immunoinflammatory defense mechanism in response to infection or injury. It involves complex overlapping stages including inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling.
- The primary difference between healing after surgery and nonsurgical root canal treatment is that surgery requires blood clot formation and may result in faster healing dynamics. After successful nonsurgical root canal treatment, periapical inflammatory tissues will be eliminated mainly by phagocytic debridement.
- Healing involves osseous healing of trabecular and cortical bone as well as dentoalveolar healing resulting in repair or regeneration of the apical attachment apparatus. Various factors like age, tooth position, and root canal filling material can
























![• In 1974, platelets regenerative potentiality was introduced, and Ross et al.,[3] were first to describe a
growth factor from platelets. After activation of the platelets which are trapped within fibrin matrix,
growth factors released and stimulate the mitogenic response in the bone periosteum during normal wound
healing for repair of the bone.[4] Better understanding of physiologic properties of platelets in wound
healing since last two decades led to increase its therapeutic applications in the various forms showing
varying results.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-26-320.jpg)


![• Simonpieri et al. 2009 Jun In vivo PRF membranes are particularlyhelpful for periosteum healing and maturation.The thick peri-implantgingival is
as a result of several healing phases on a PRF membrane layer
• Simon et al. 2009 May Animal study PRFM alone may be the best graft for ridge preservationprocedures
• Simonpieri et al. [13] 2009 Apr In vivo PRF membranesprotects the surgical site,promotes soft tissuehealing,and when itsfragmentsmixed with
graft materialit functions as a “biologicalconnector”
• Magremanne et al. 2009 Apr Case report PRF may induce healing of non-reossifiedcystic cavity by supplying local growth factors
• Aroca et al. [19] 2009 Feb In vivo Modified coronally advanced flap (MCAF)is a predictable treatmentfor multipleadjacent Miller Class I or II
recession-typedefects. The addition of a PRF membrane positioned under the MCAFprovided inferiorroot coverage, but an additionalgain in
gingival/mucosalthickness (GTH)at 6 months compared to conventional therapy
• Anilkumaret al. [17] 2009 Jan Case report Describedlaterallydisplaced flap technique with PRF membrane technique as a navel root coverage
approach for gingival recessionof the mandibular anterior teeth
• Diss et al. [85] 2008 May In vivo The bone-added osteotome sinus floor elevation(BAOSFE)procedure with PRF as grafting materialcan lead to an
endosinus bone gain
• Lundquist et al. [86] 2008 May Review PRF provides sustainedrelease and protection against proteolyticdegradation of endogenous fibrogenic
factorsimportantfor wound healing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-29-320.jpg)




















![• Healing of large cysts like well-defined radiolucencies following conservativeroot canal treatmenthas been reported.
• Although the cysticfluid contains cholesterolcrystals, weekly debridement and drying of the canals over a period of two to three weeks, followed by obturationhas
led to a completeresolutionof lesions by 12 to 15 months.
• Decompression technique
• The decompression techniqueinvolves placementof a drain into the lesion, regular irrigation,periodic length adjustment,and maintenanceof the drain, for various
periods of time.
• The drain could either be ‘I’ shaped pieces of rubber dam,polyethylene tube along with a stent, hollow tubes, a polyvinyl tubing,uction catheter[32] or a radiopaque
latex tubing.There is no standard protocol as to the length of time necessary to leave the drain. It may be different for different kinds, sizes or locationsof lesions.It
can vary between two days to five years. Daily irrigationof the lesion can be carried out by the patientthrough the lumen of the drain using 0.12% chlorhexidine.The
advantages of this techniqueare; it is a simpleprocedure, it minimizesthe risk of damaging adjacent vitalstructures,and is easily toleratedby the patient.
• However, several disadvantageshave also been noted; patientcomplianceis very essential,inflammationof the alveolar mucosa, persistenceof the surgicaldefect at
site,development of an acute or chronic infection,displacementor submergence of the drainage tube
• Rees suggestsplacementof a small amount of red wax over the end of the drain to prevent ulcerationof the labialor buccal mucosa adjacentto the drain. The
decompression techniqueis contraindicatedin cases of large dental granulomas or any solid cellular lesion, assince there is an absence of a fluid-filledcavityto
decompress.Active nonsurgical decompression techniqueThis technique uses the Endo-eze vacuum system (Ultradent, Salt Lake, Utah) to create a negative pressure,
which resultsin the decompression of large periapicallesions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-50-320.jpg)

![• Different synthetic ways have been utilized to prepare nano-sizedapatite crystals.Yet, preparationof actualbiomimetic
nanocrystallineapatites might be considered as a scientific and technologicalchallenge.
• Thus, the large surface-tovolume ratio, the existenceof a surface hydrated layer, and non-apatiticin nature are important in
the formation procedureof a solution. This layer is bound to disappear progressivelyas the stable apatite domains(in the core
of the crystals) improve with time. Possessing a great ionic mobility, ion exchangeand adsorption capacities allows for
participationof this hydratedlayer in the interactionwith macromolecules .
• Effectsof n-HA on epithelial cells Kawai and colleaguesstated that n-HA might have a therapeutic effect on periodontal
epithelium. Therefore, they conjectured thathealing processof open wound by contractioneffect could be increasedthrough
intravenous calcium-based nanoparticles.Role of n-HA in differentiationand proliferationof periodontal ligament (PDL)
cells
• Kanaya and co-workers [14] observed n-HA could stimulate differentiationof PDL cells, mediatedby mechanosensitive
signalling pathway and expressionof BMP-2. Besides, Yang et al. [15] conductedan animal study through which they found
n-HA could be used as a coating onsilk scaffolds. Thus, they pointed out that n-HAcoated silk scaffoldsmight be potentially
good biomaterialsfor regeneratingperiodontaltissue. Along with the above-mentionedstudies, there are several research
articlesin the extant literature that emphasize n-HA effects on different cells in the periodontium.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-52-320.jpg)
![• Fibroblast Based on the results of a study by Saleh et al. , it was proven that silver n-HA could enhance fibroblast cell maturation and
proliferation. This could eventually result in connective tissue regeneration. In contrast, n-HA was found to be much more
biocompatible than silver nanomaterial in a study of evaluating the biocompatibility of silver and n-HA on fibroblast cells by Shahoon et
al..
• An in vitro study by Sun and colleagues revealed that n-HA could increase proliferation and differentiation of PDL fibroblast cells in
comparison to dense hydroxyapatite. Additionally, it was pointed out that n-HA was more biocompatible than dense HA.
• Osteoblast Shnettler et al. found that n-HA could bind to the bone and stimulate the osteoblasts in the early stage of periodontal defect
repair. This can lead to bone formation. Similar results were found in a study by Thian and co-workers .
• Moreover, Pilloni et al. proved that n-HA can increase the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. In a report by Webster et al.
greater protein adsorption and osteoblastic cells adhesion on n-HA were shown. Liu et al. [23] found that n-HA could stimulate binding
and proliferation of osteoblast-like MG-63 cells. It was proven that n-HA exhibits biocompatibility and minimal toxic effect on
osteoblast cells in studies by Motskin et al.
• Hsieh et al. , and Zhao et al. . Osteoclast In a study by Detsch et al. it was shown that n-HA with low or no carbonate content can
enhance the differentiation of osteoclast-like cells. This can result in having a great number of osteoclast cells on the material compared
to carbonate-rich group. Activated osteoclast recruited mesenchymal cells from the bone marrow to differentiate them into osteoblasts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-53-320.jpg)

![• A 33-years-oldfemale patientreported to the Department of ConservativeDentistry and Endodontics with a chief complaint
of swelling on the inner surface of gum region in relation to upper front teeth for the past 10 days. Swelling was initially
small, then gradually progressed and was associatedwith discomfort while taking food.
• Clinical examinationrevealedEllis Class IV fracture in 21 with a swelling of 2.5 cm × 2 cm size seen over the palatal
mucosa in relationto 21, 22, and 23 [Figure 1a]. Tendernesswas felt on palpation overthe apical mucosa in relationto 21,
22, and 23. These three teeth were sensitiveto percussion tests.
• Pulp sensitivity tests revealed that 11, 21, 22, and 23 were nonvital. Preoperative intraoral periapical radiograph of 21, 22,
and 23 reveals presenceof large irregularperiapicalradiolucency(3 cm × 2 cm in size) at the apex of 21, 22, and 23 [Figure
2a and b]. This case was planned forconventional root canal treatment followed by periapical surgery.The root canal
treatment was performed using step back technique till anapical size of #50, # 55, #45, and #60 in relationto teeth 11, 21,
22, and 23, respectively.
• .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-55-320.jpg)
![• Sodium hypochlorite (5.25%) solution (Prime Dental Products Pvt. Ltd., Thane, India) was used to irrigate
the canals during the canal preparation. Nearly 2% chlorhexidine solution (ICPA Health Products Ltd,
India) was used as the final irrigant after biomechanical preparation. The root canal treatment was
performed in three visits, and calcium hydroxide was used as the intracanal medicament. The root canals
were obturated using gutta-percha (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) and AH 26 sealer
(Dentsply DeTrey GmbH, Philadelphia, USA) by lateral compaction technique
• Before planning for the surgical procedure, patient’s platelet count (4 lakh/mm3 ), hemoglobin (12 g/dl),
bleeding time (2.5 min), and clotting time (4.5 min) were assessed and found to be within normal limits.
Informed consent was obtained from the patient. Under local anesthesia (1:200,000 adrenaline, DJ Lab,
India), a full thickness mucoperiosteal flap was reflected by a sulcular incision starting from the distal
aspect of the tooth 12 to distal aspect of the tooth 25 [Figure 2a]. A large periapical defect was seen with
complete loss of labial cortical plate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-56-320.jpg)
![• .
• The lesion measured 2.5 cm, 2 cm, and 2 cm correspondingto the length, width, and depth of the lesion. Tissue curettage
was done at the defect site followed by thorough irrigationusing sterile salinesolution [Figure 2b and c]. Using #702 tapered
fissure bur (SS White Burs), root end resectionwas performed in teeth 11, 21, 22, and 23 [Figure 2d]. Root end cavity of 3
mm depth was prepared with diamond-coatedultrasonicsurgical tip S12 90ND (Satelec/Acteon,Merignac, France) at high-
power setting of ultrasonic device.White mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) (ProRoot MTA; Dentsply, Tulsa, USA) was
used as the root end filling material. A volume of 10 mL of blood was drawn from the patient’s antecubitalvein and
centrifuged (REMI centrifuge machine Model R-8c with 15 mL swing out head) for 10 min under 3000 revolutions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-57-320.jpg)
![• 400 g) per minute to obtain the PRF. The resultant product consisted of the following three layers: • A cellular
plateletpoor plasma at the top of the tube • Fibrin clot (PRF) in the middle of the tube and • Red blood corpuscles
at the bottom of the tube. PRF was carried and packed into the defect to the level of defect walls
• Flap stabilization was done followed by suturing using 3-0 black silk suture material (Sutures India Pvt. Ltd,
Karnataka,India). Analgesicsand antibioticswere prescribed,and the patient was advised to use 0.2%
chlorhexidine mouthwash for a week. Suture removal was done 1 week later and the healing was satisfactory.
• Patientwas reviewed at 3 months [Figure 3a and b] and 12 months [Figure 3c] during which there were no
symptoms of pain, inflammation, or discomfort.These follow-up visitsincluded routine intraoral, radiographic
examinations,and professionalplaque control. Radiographically, periapicalbone regenerationwas evident at the
end of 12 months [](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-58-320.jpg)
![• Discussion Orthograde root canal therapy should be the first option for treatment ofall inflammatoryperiapicallesions which have
85% of success rate. Periapical surgery remains the last resort when orthogradetreatment failsor is not possible. After a surgical
procedure, healingusually occurs by repair or regeneration.
• The four critical factorsthat influence bone regeneration after theperiapicalsurgery are primary wound closure, angiogenesisas a
blood supply and source of undifferentiatedmesenchymalcells, space maintenance, and stabilityof the wound (PASS principle).
• The present case report evaluated theclinical efficacy ofPRF in the treatmentof intrabony defect. PRF is a matrix of autologous
fibrin with a large quantity ofplatelet and leukocyte cytokinesembeddedin it. As the network of fibrin disintegrates, the intrinsic
incorporation ofcytokineswithin the fibrin mesh allows their progressivereleaseover time (7–11 days). The main componentof
PRF is high concentrationof growth factors present in the plateletswhich are required for wound healing.[11-14]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phppt212021-210705141130/85/PERIAPICAL-WOUND-HEALING-59-320.jpg)










