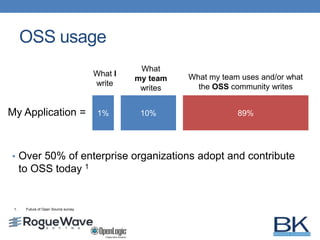
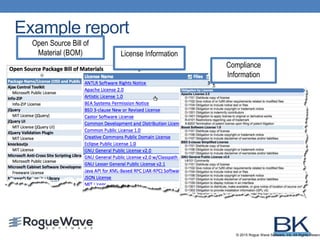
The document discusses the importance of conducting audits on open source software (OSS) to manage risks, including legal liabilities and security vulnerabilities. It outlines the processes for scanning OSS, analyzing the results, and creating compliance reports, alongside steps to mitigate future risks. It emphasizes the need for organizations to establish a robust OSS policy, utilize automated scanning tools, and remain vigilant about licensing obligations and security updates.