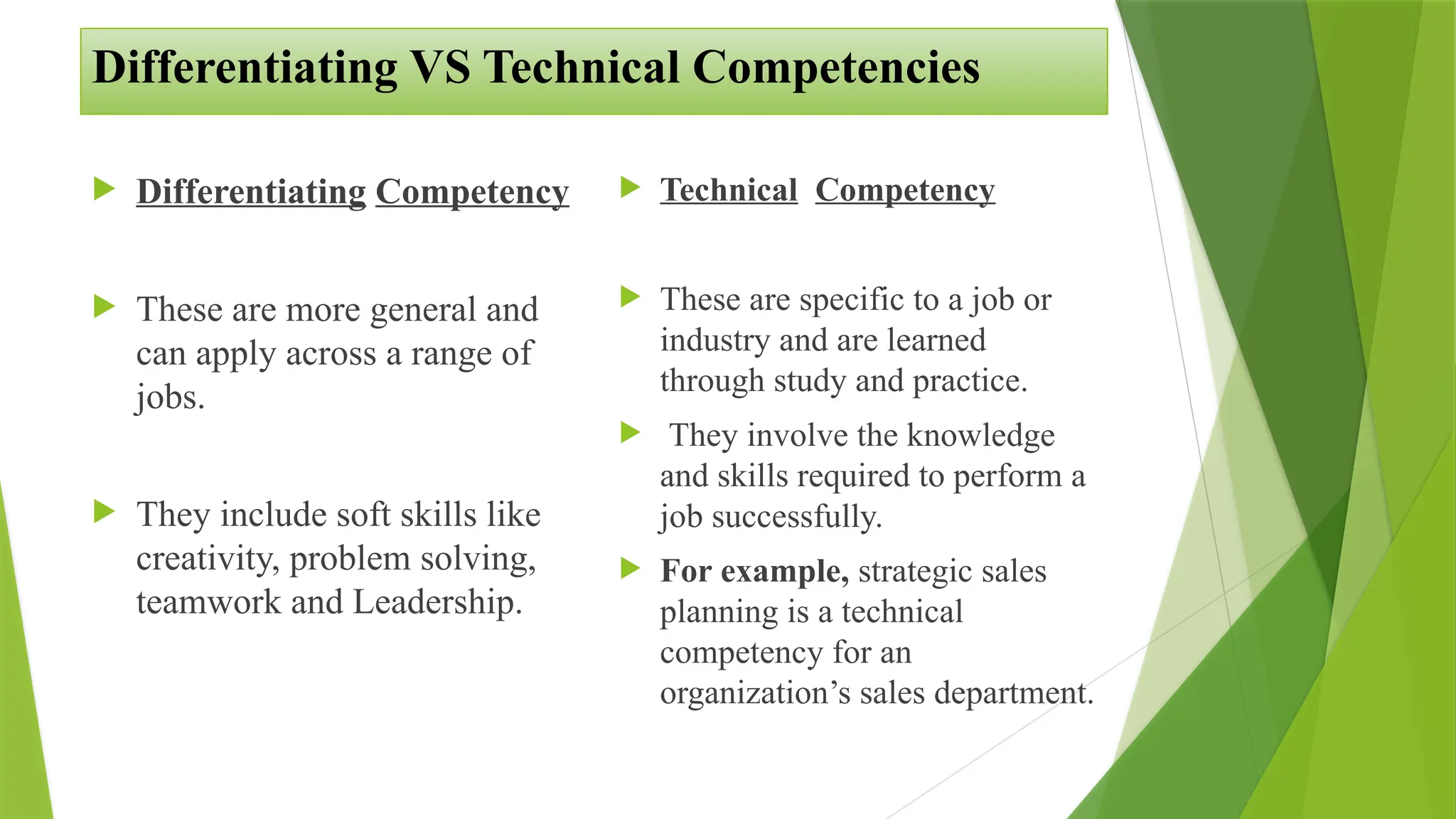
The document outlines the significance of a competency framework in HR for identifying and developing employee skills, enhancing talent management, and supporting career development. It delineates different types of competencies, including core, technical, and behavioral, and emphasizes the need for a systematic approach in developing, implementing, and validating the framework. The conclusion highlights the benefits for organizations and employees in fostering clearer performance expectations and professional growth.