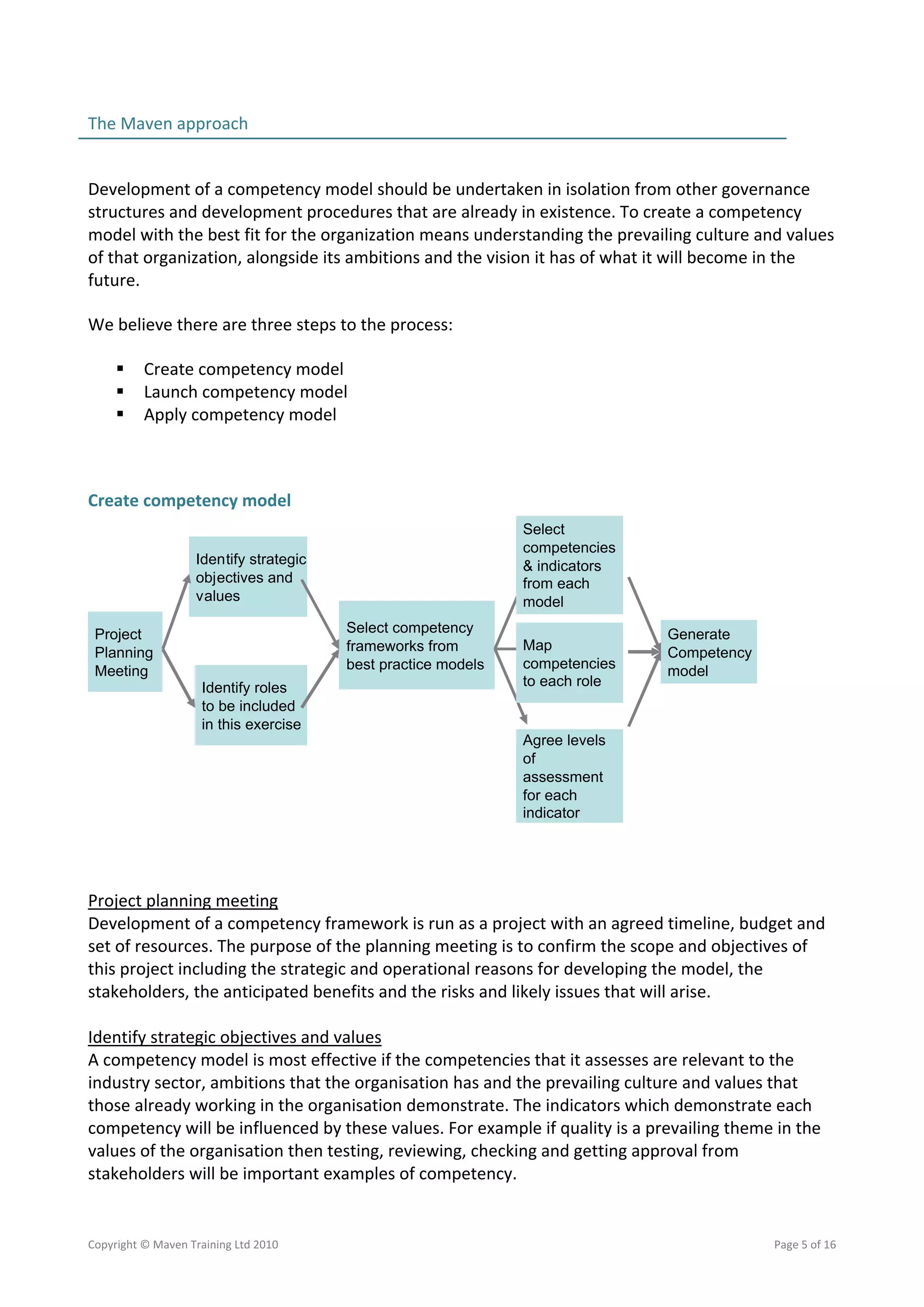
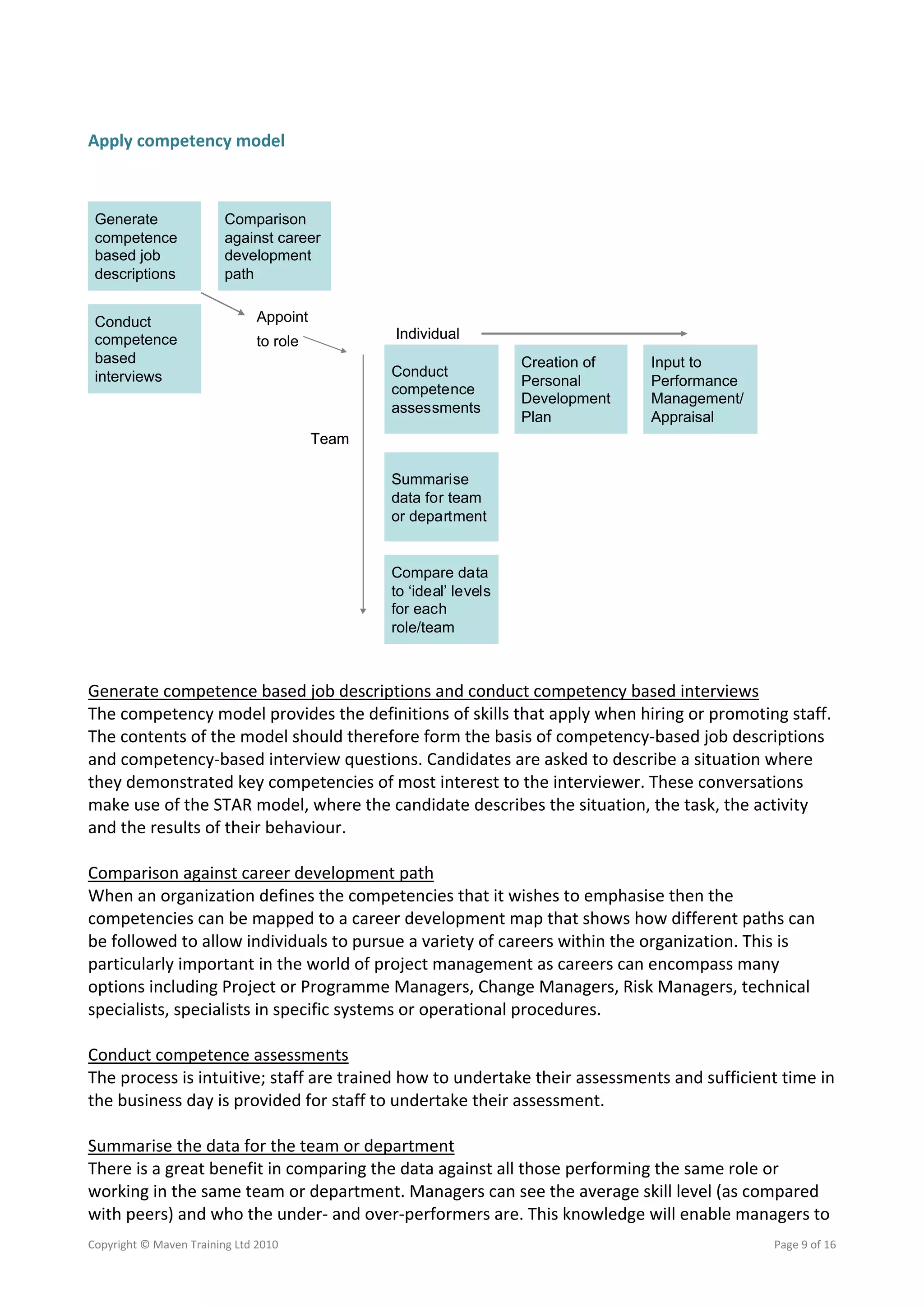
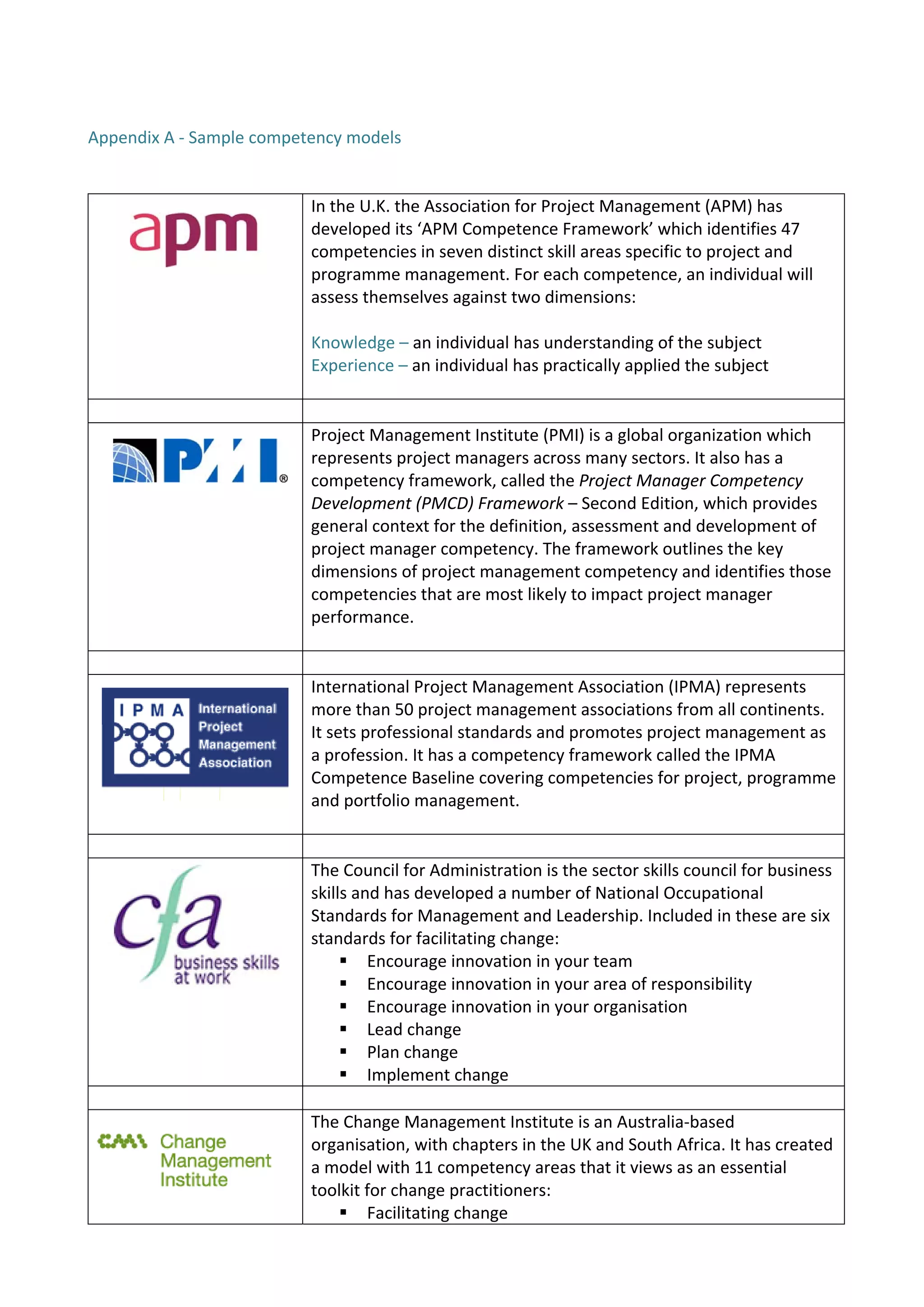
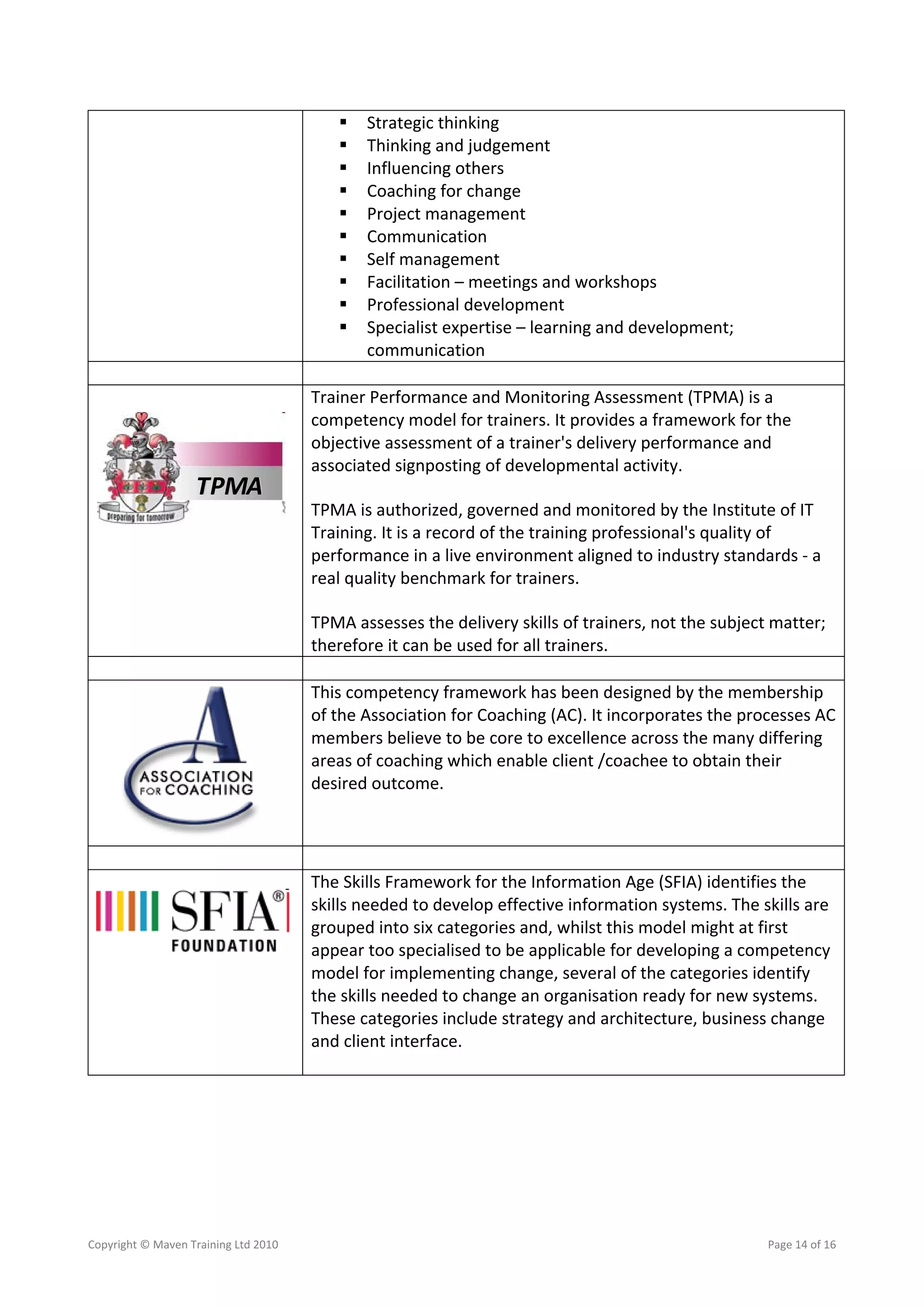
This document discusses building project management capability through competency assessments using Maven Training's approach. The three steps in Maven's approach are: 1) Create a competency model by identifying strategic objectives and values, selecting competencies and indicators from best practice models, and mapping competencies to roles. 2) Launch the competency model by generating the model and agreeing assessment levels. 3) Apply the competency model for recruitment, development, and aligning resources to initiatives. Developing a competency model tailored to an organization's culture can provide benefits like improved recruitment, development, and change implementation.