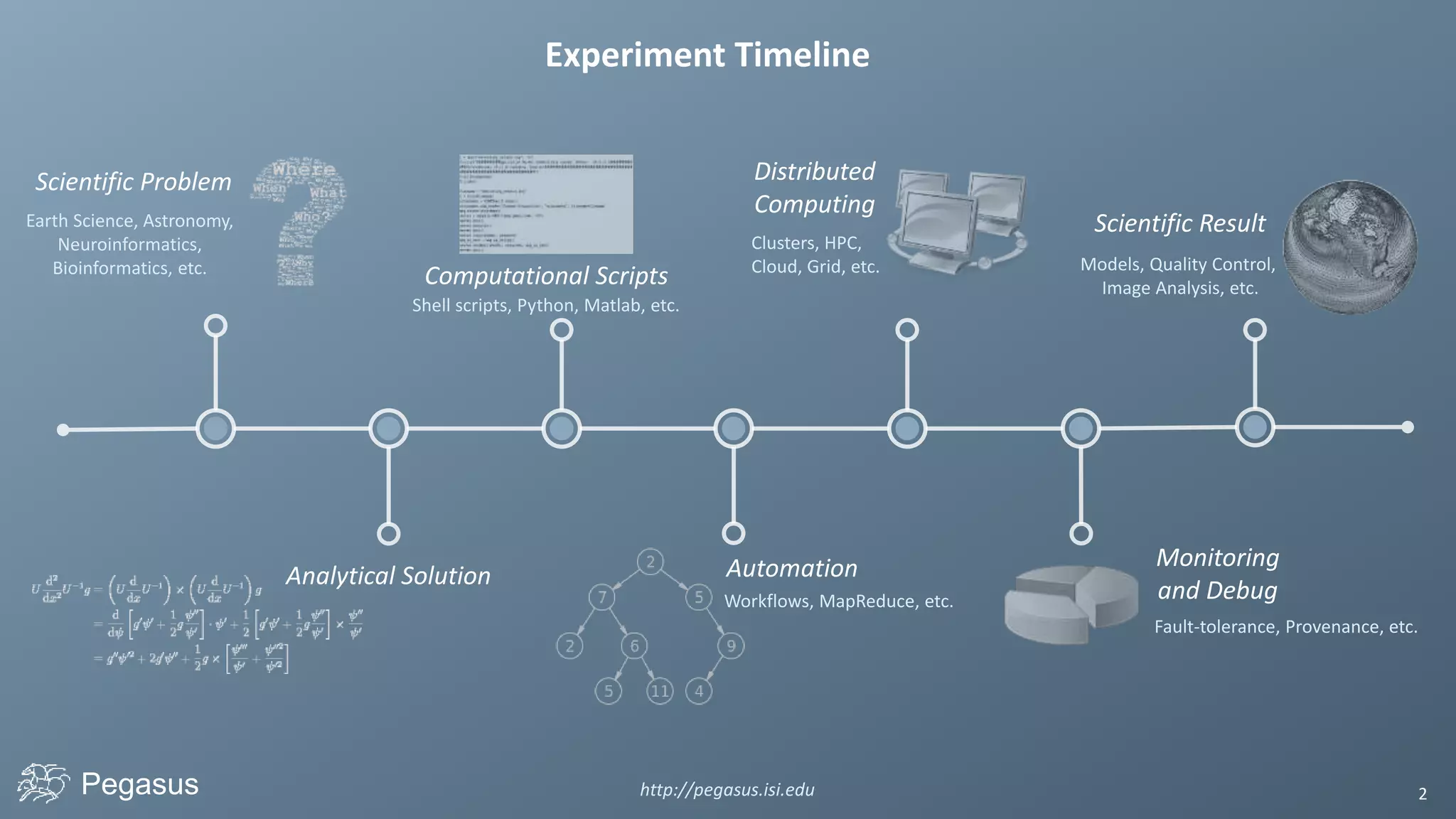
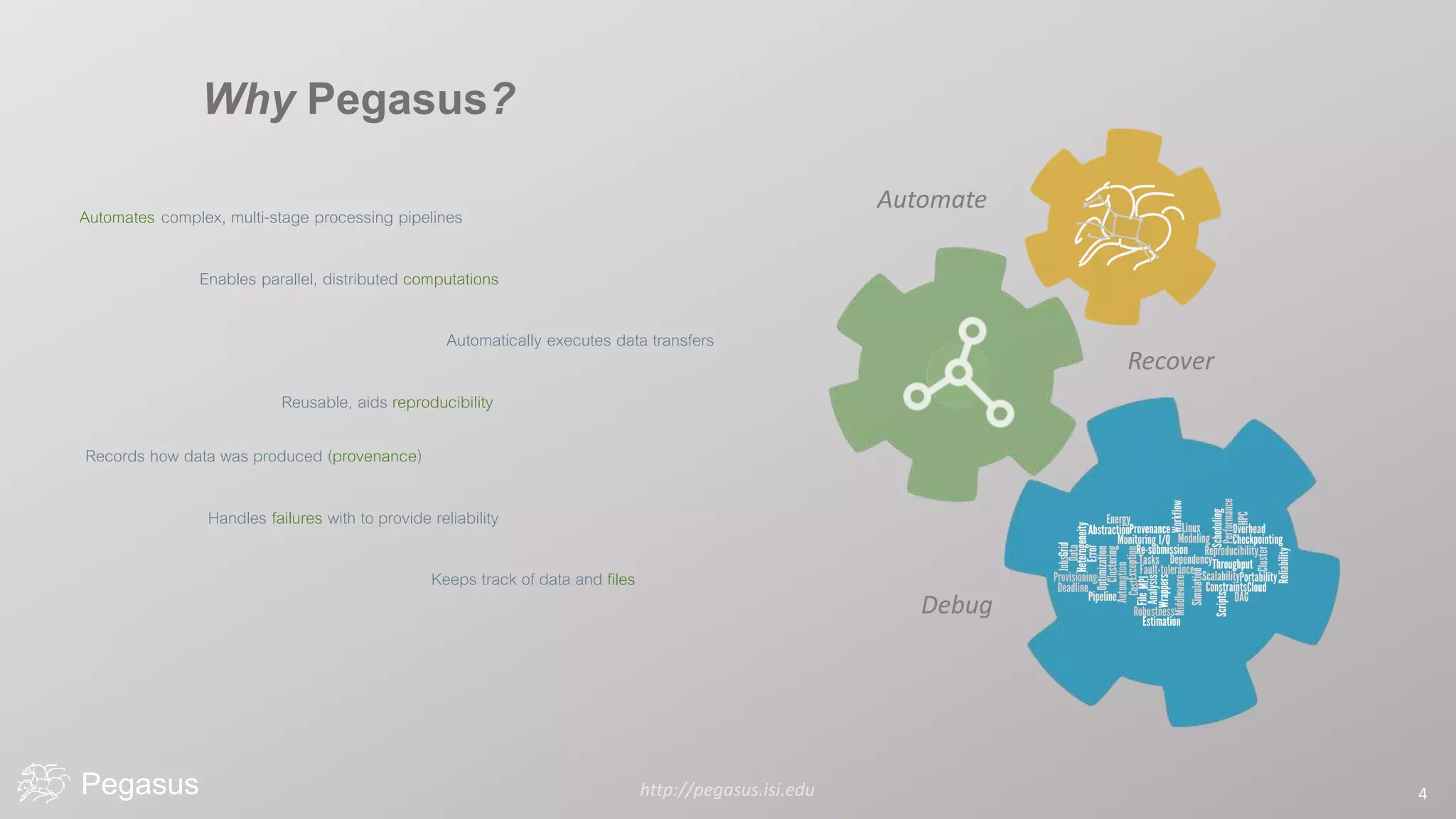
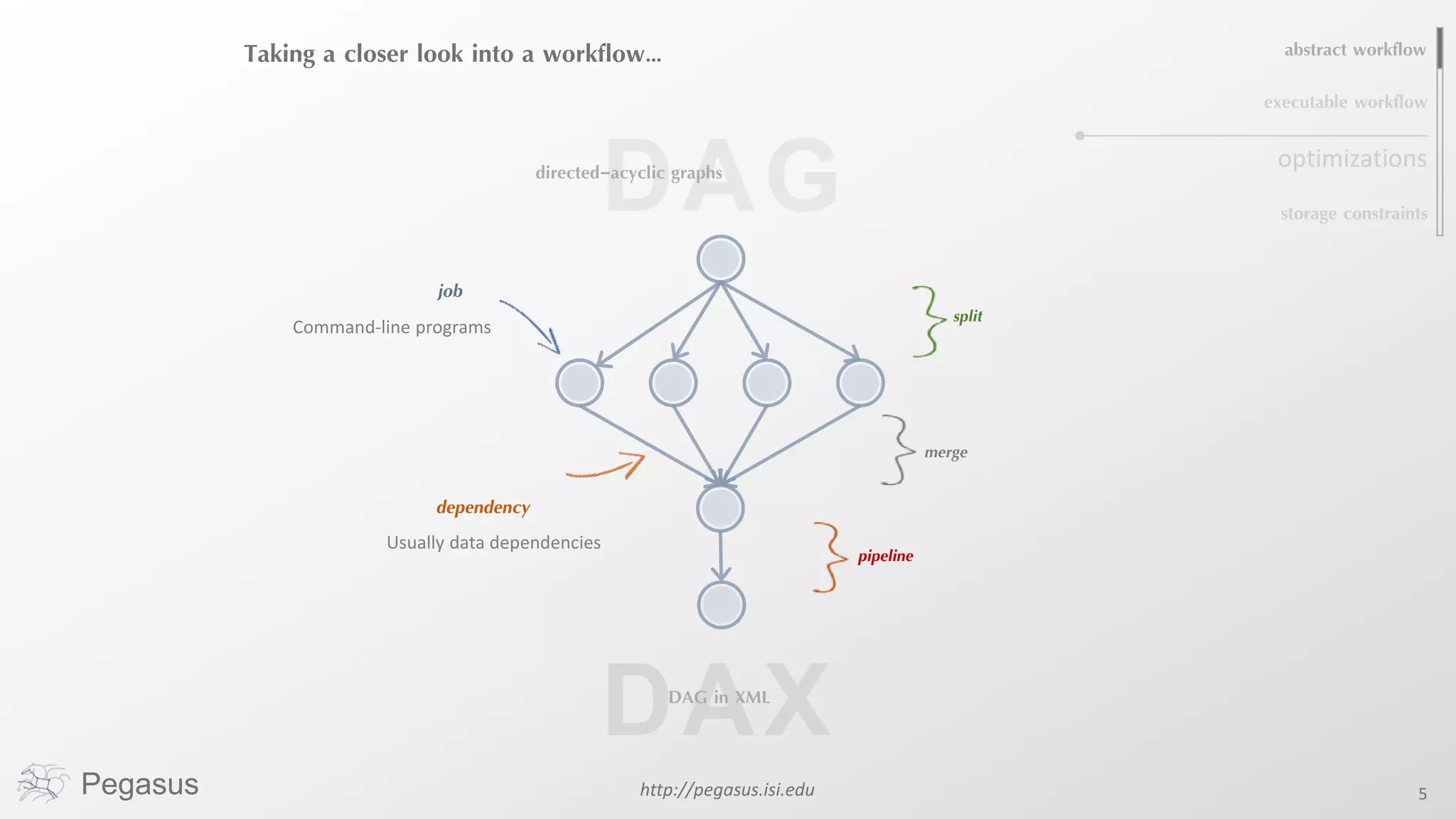
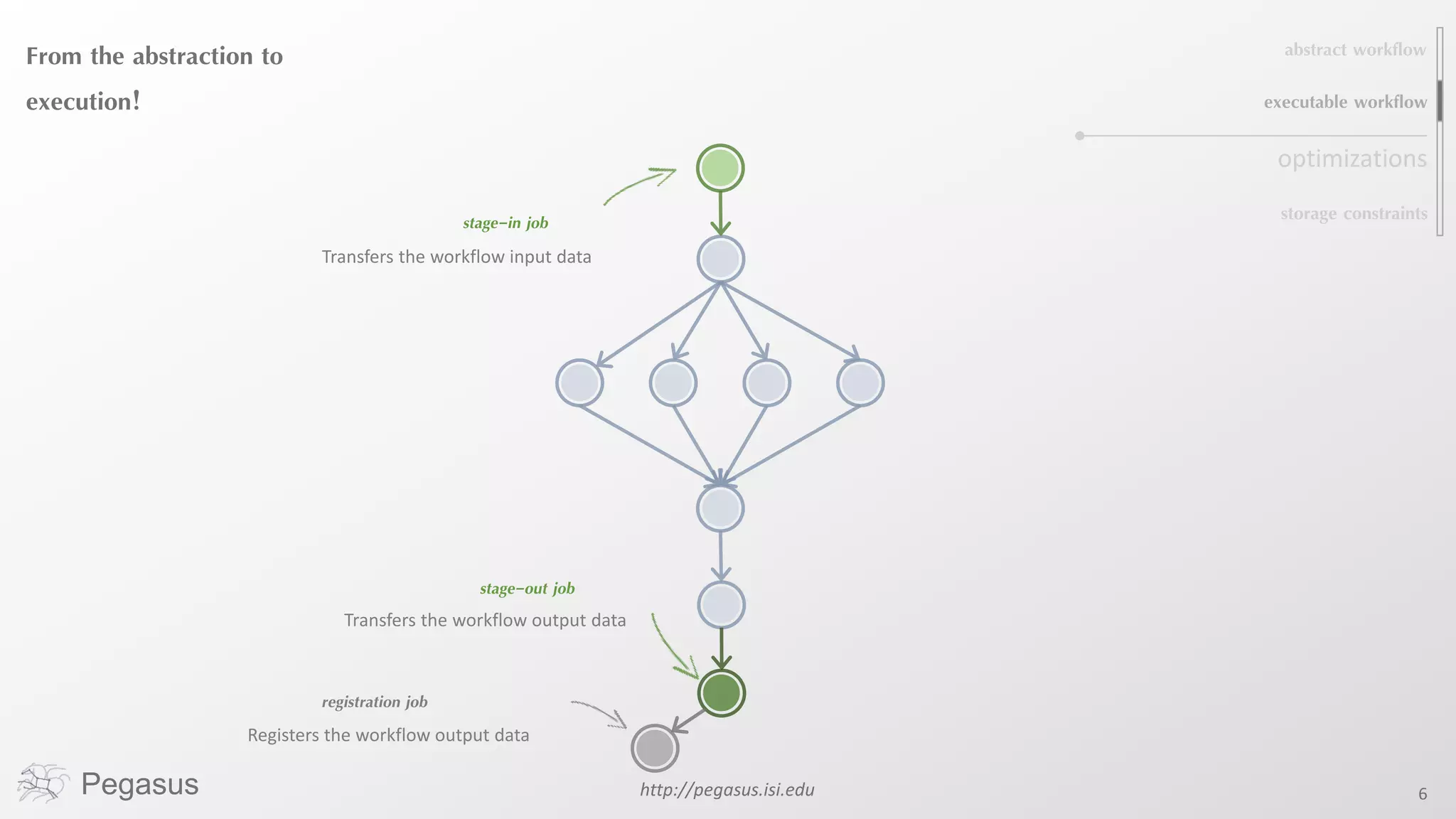
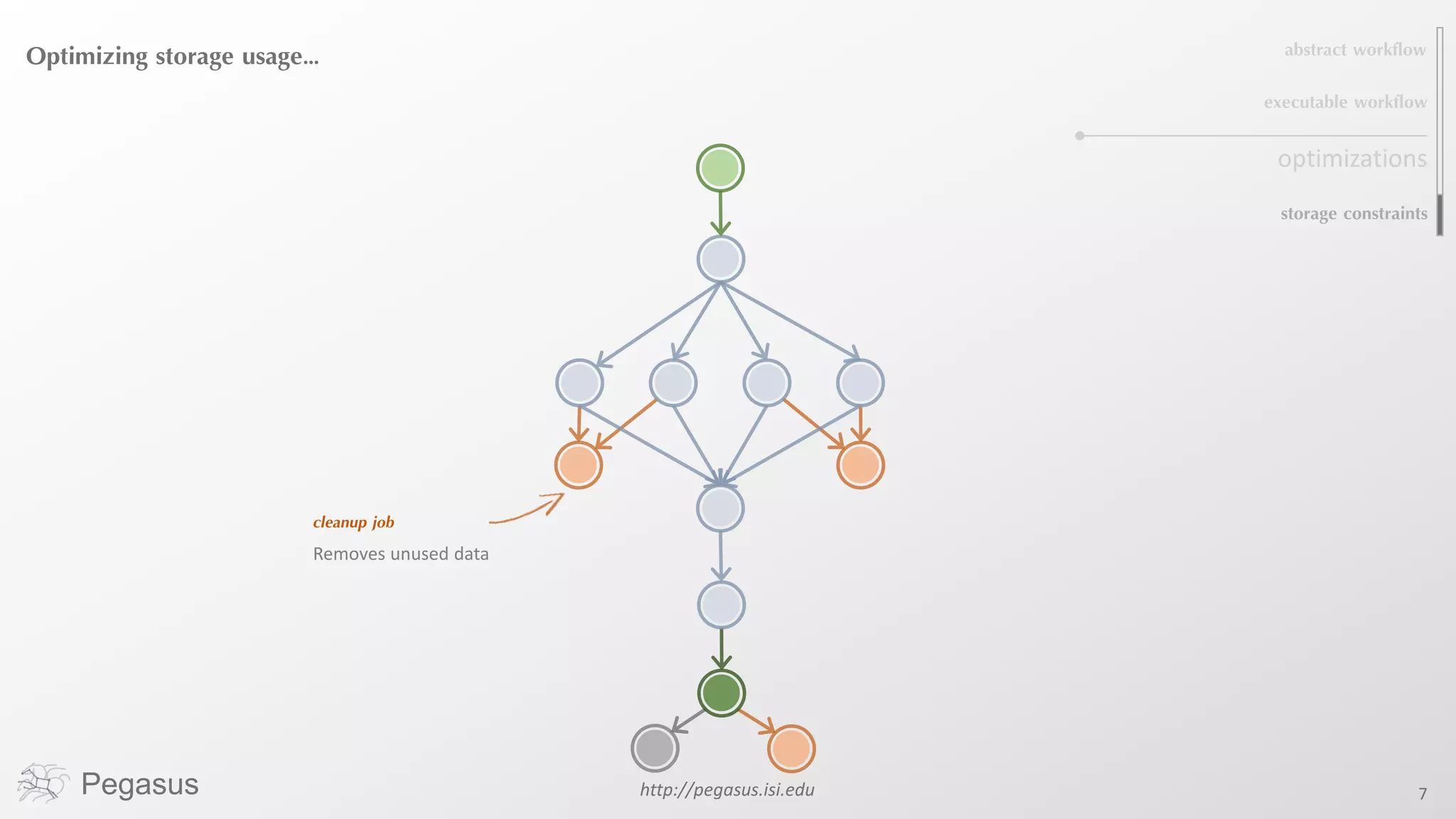
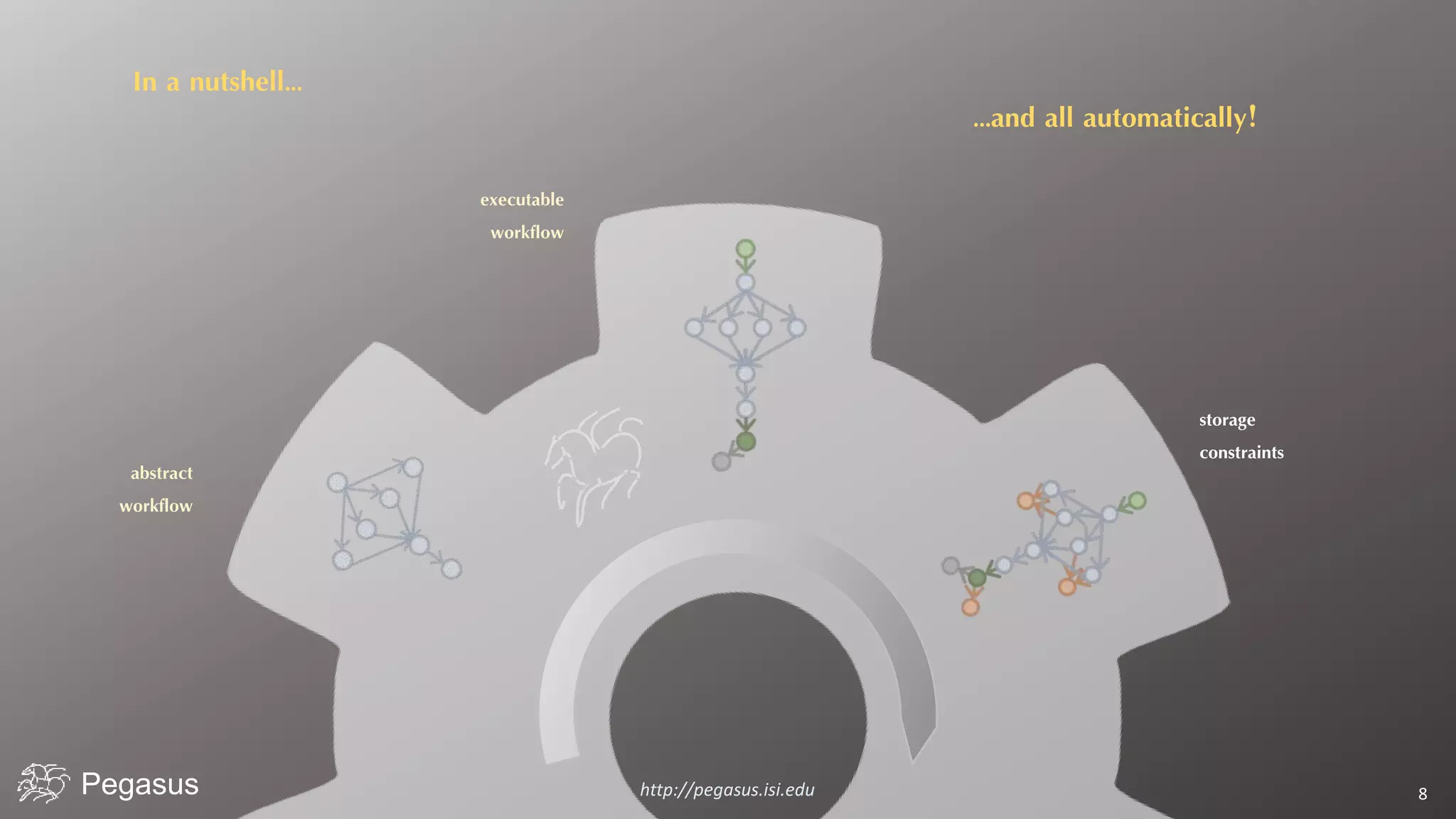
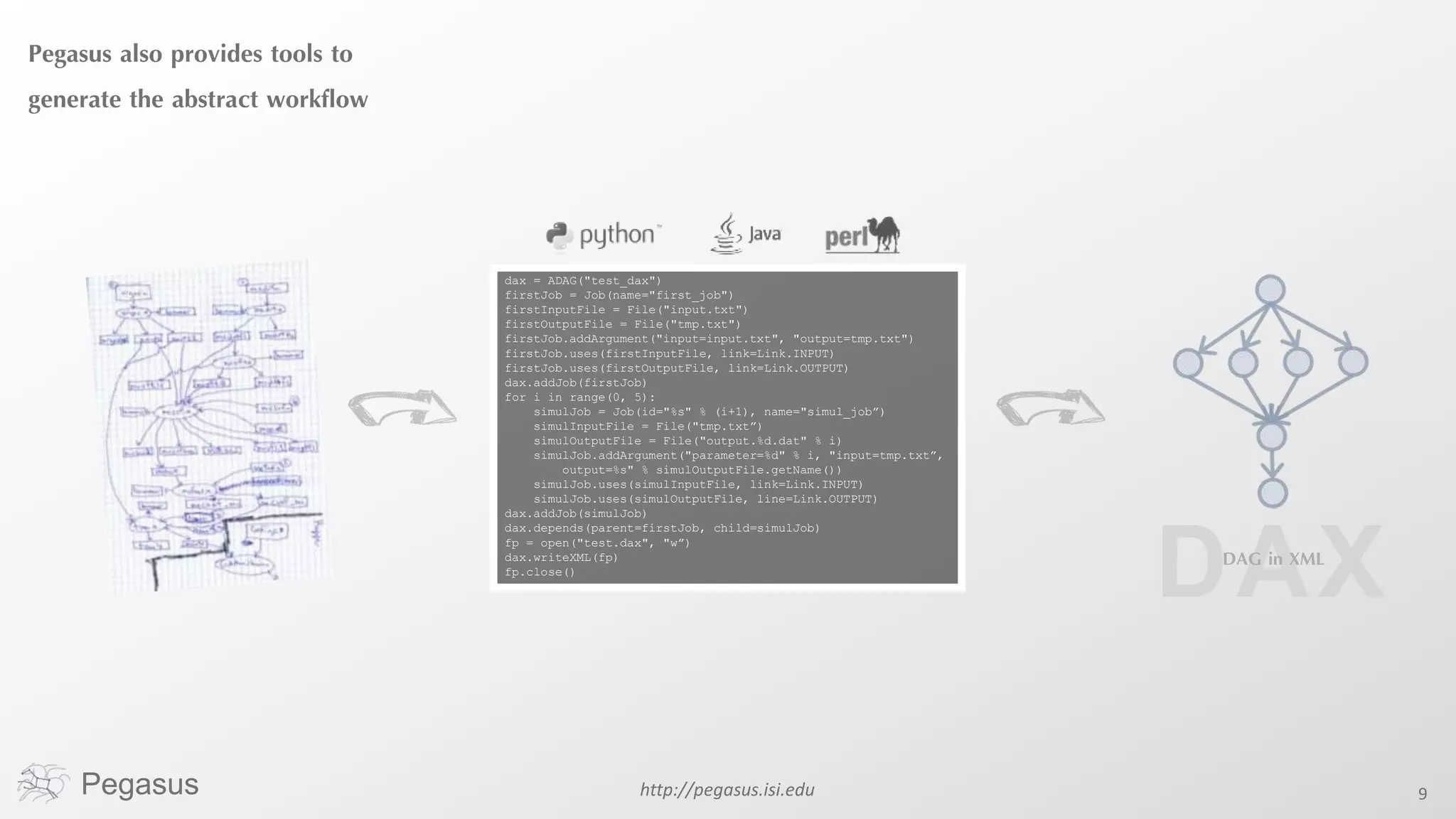
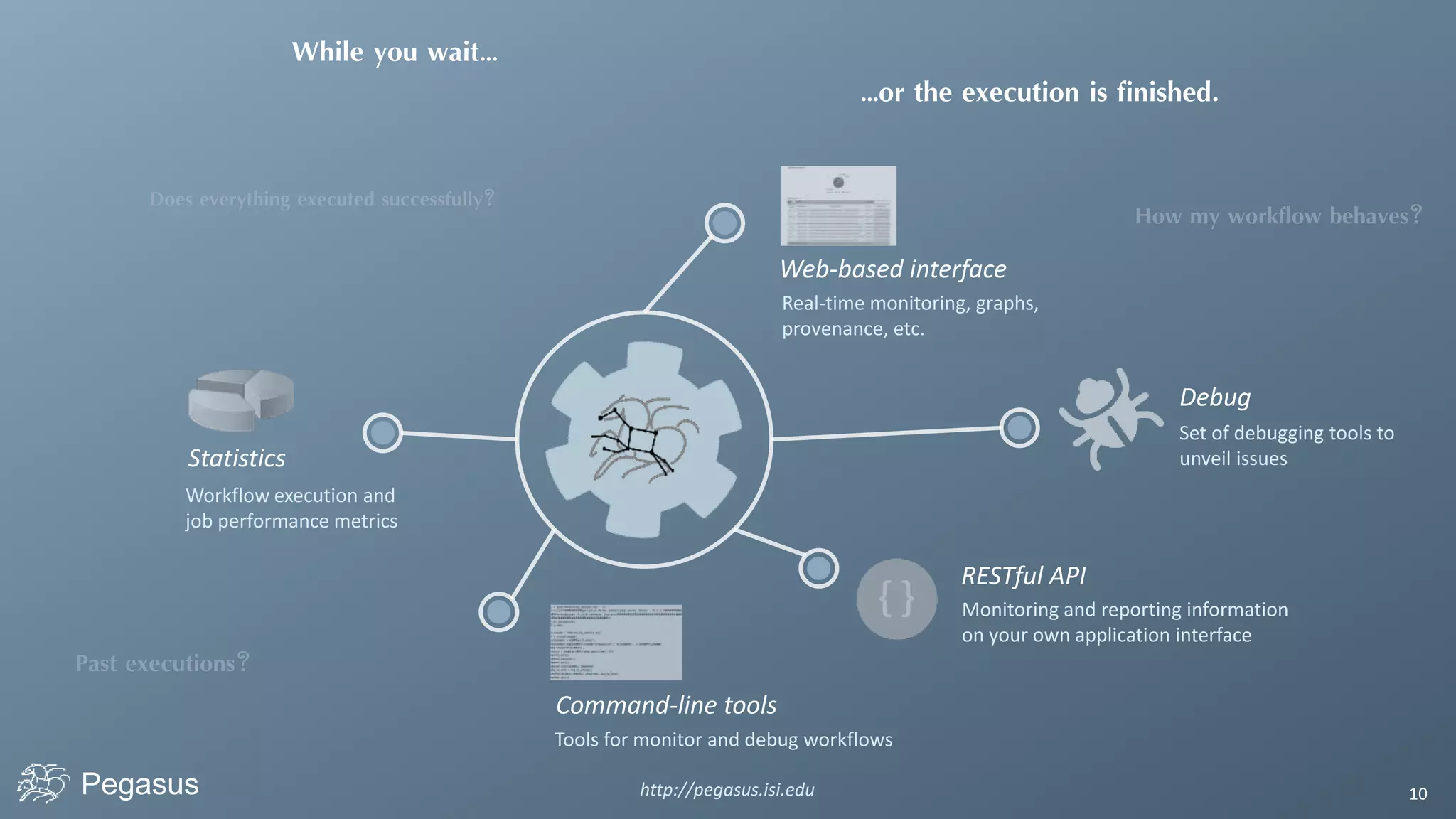
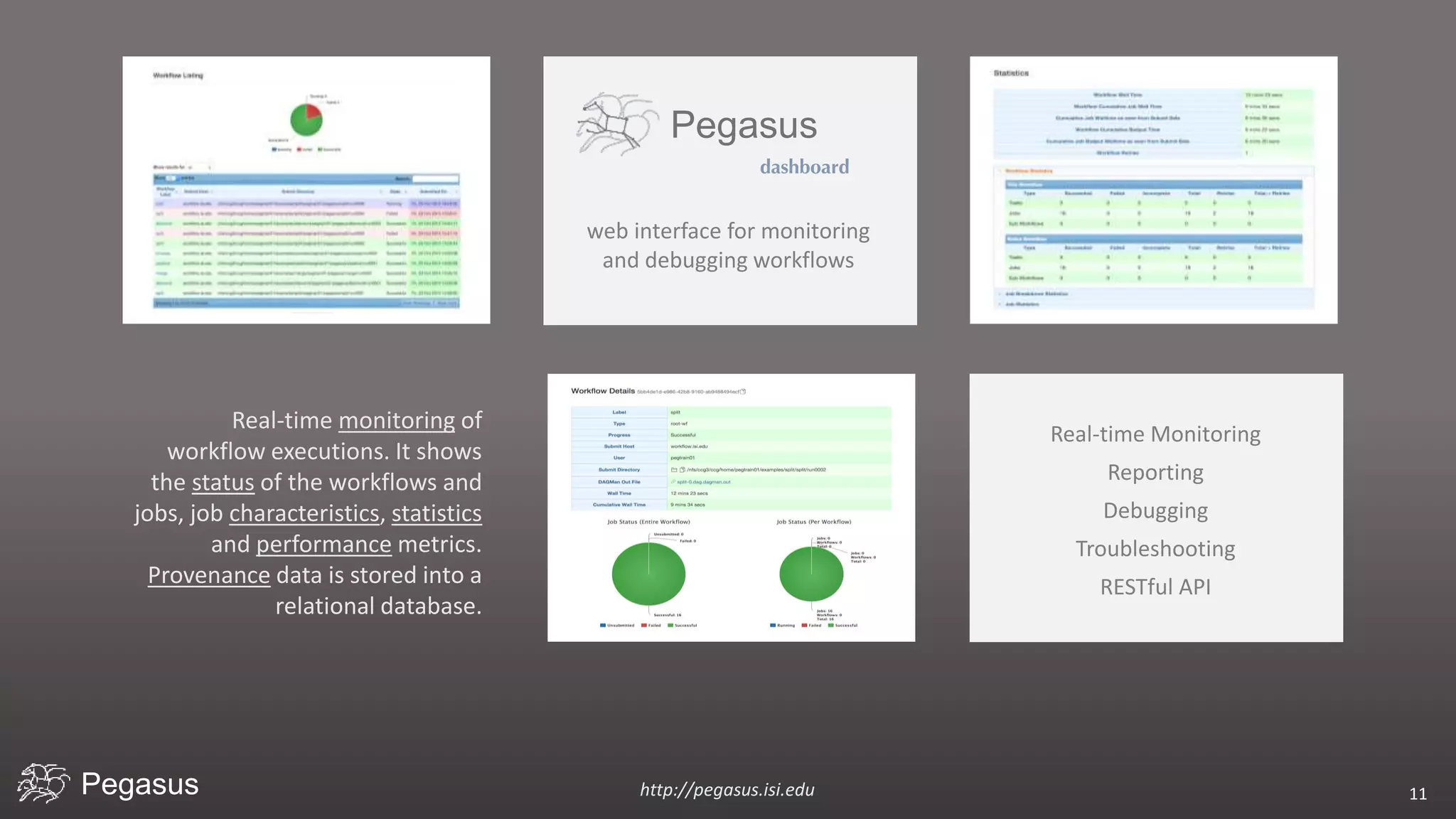
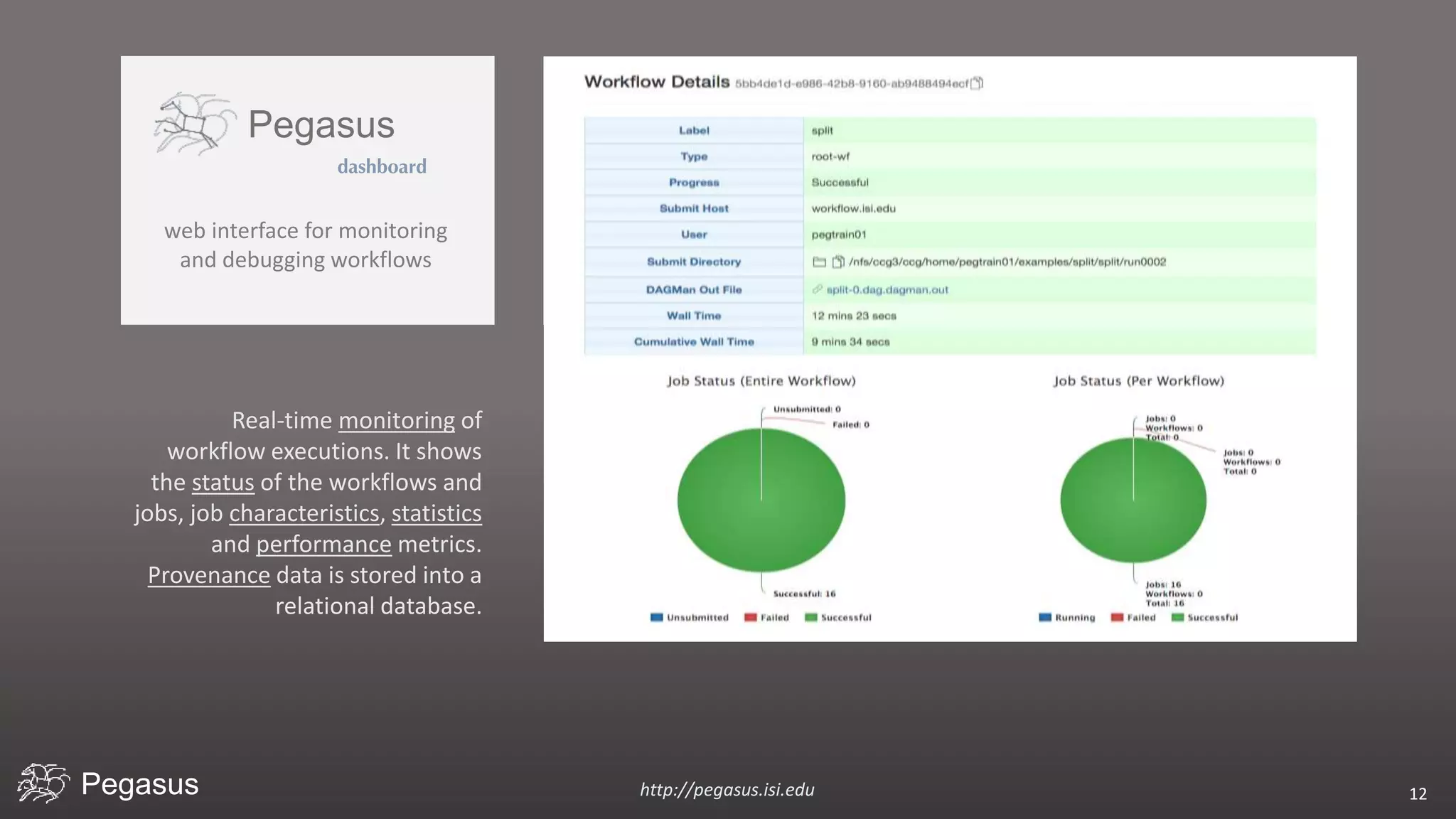
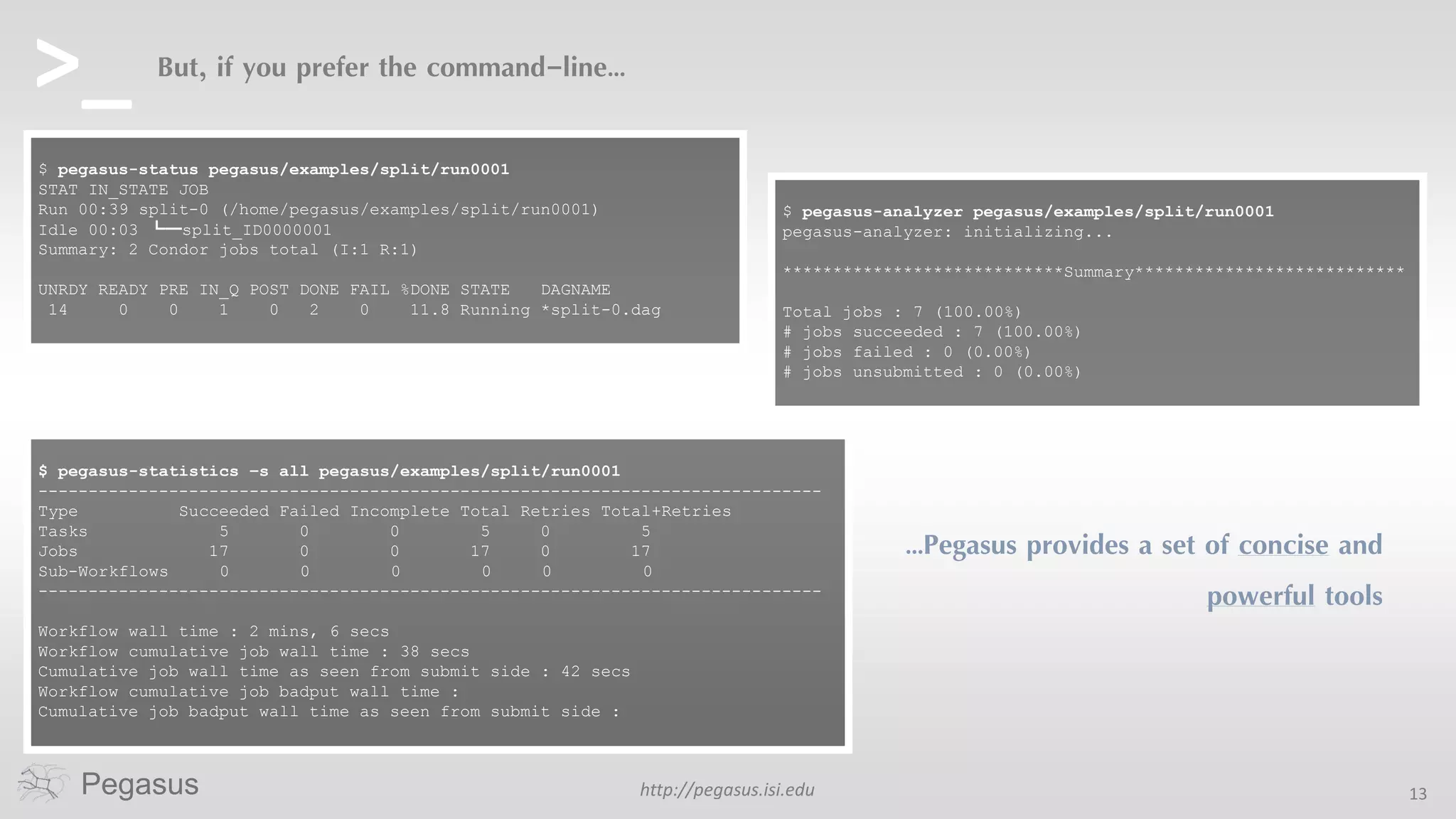
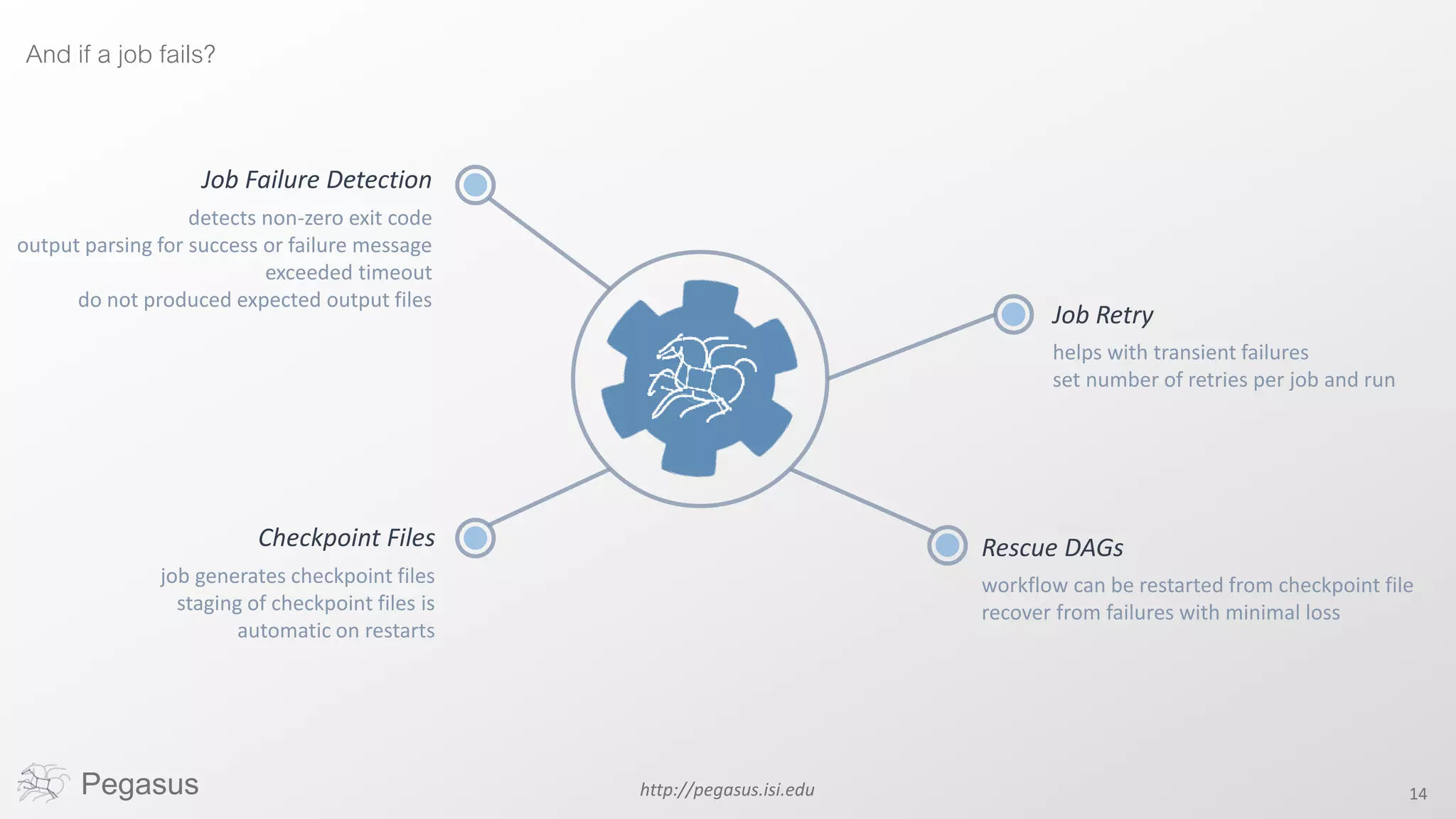
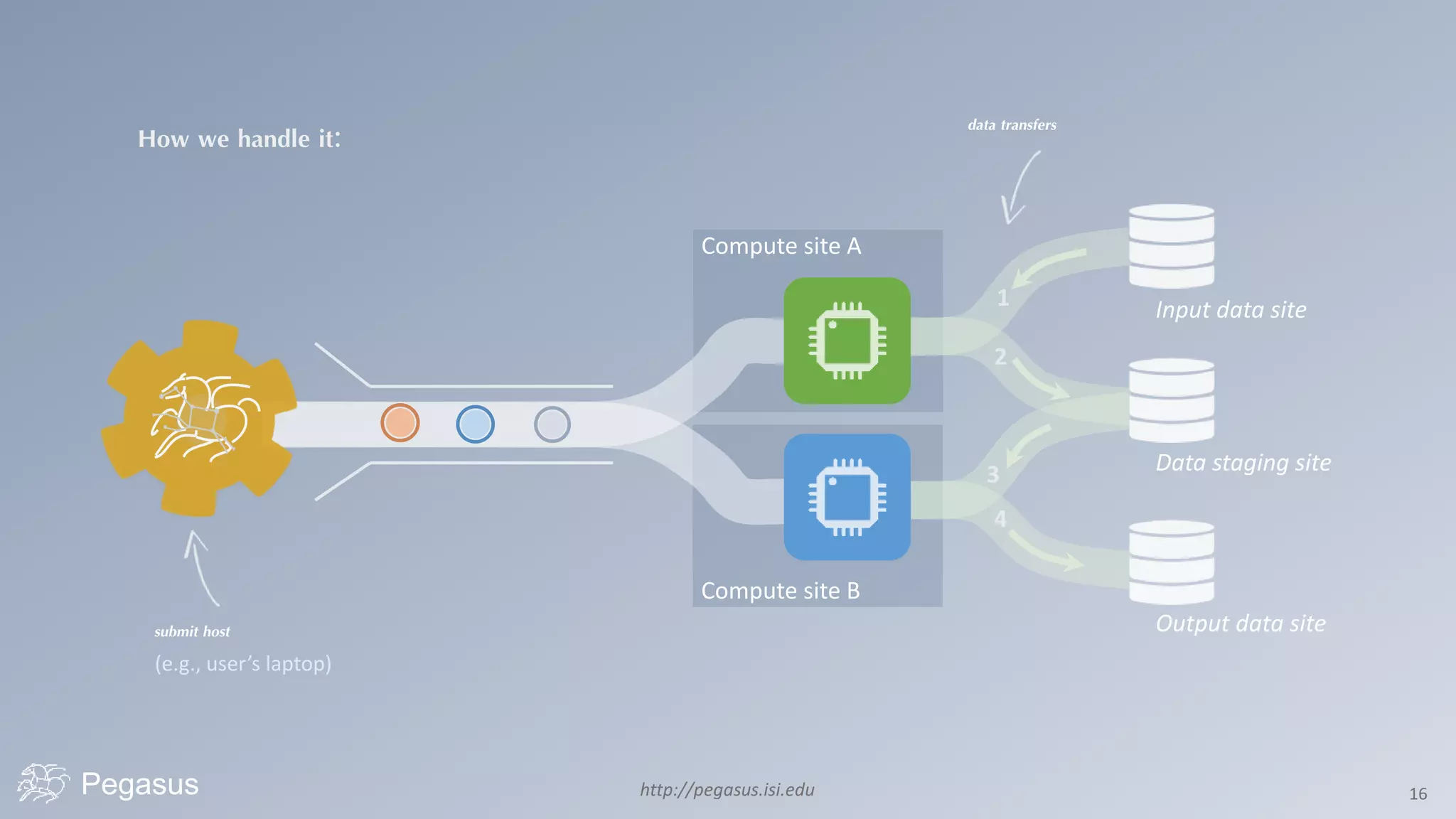
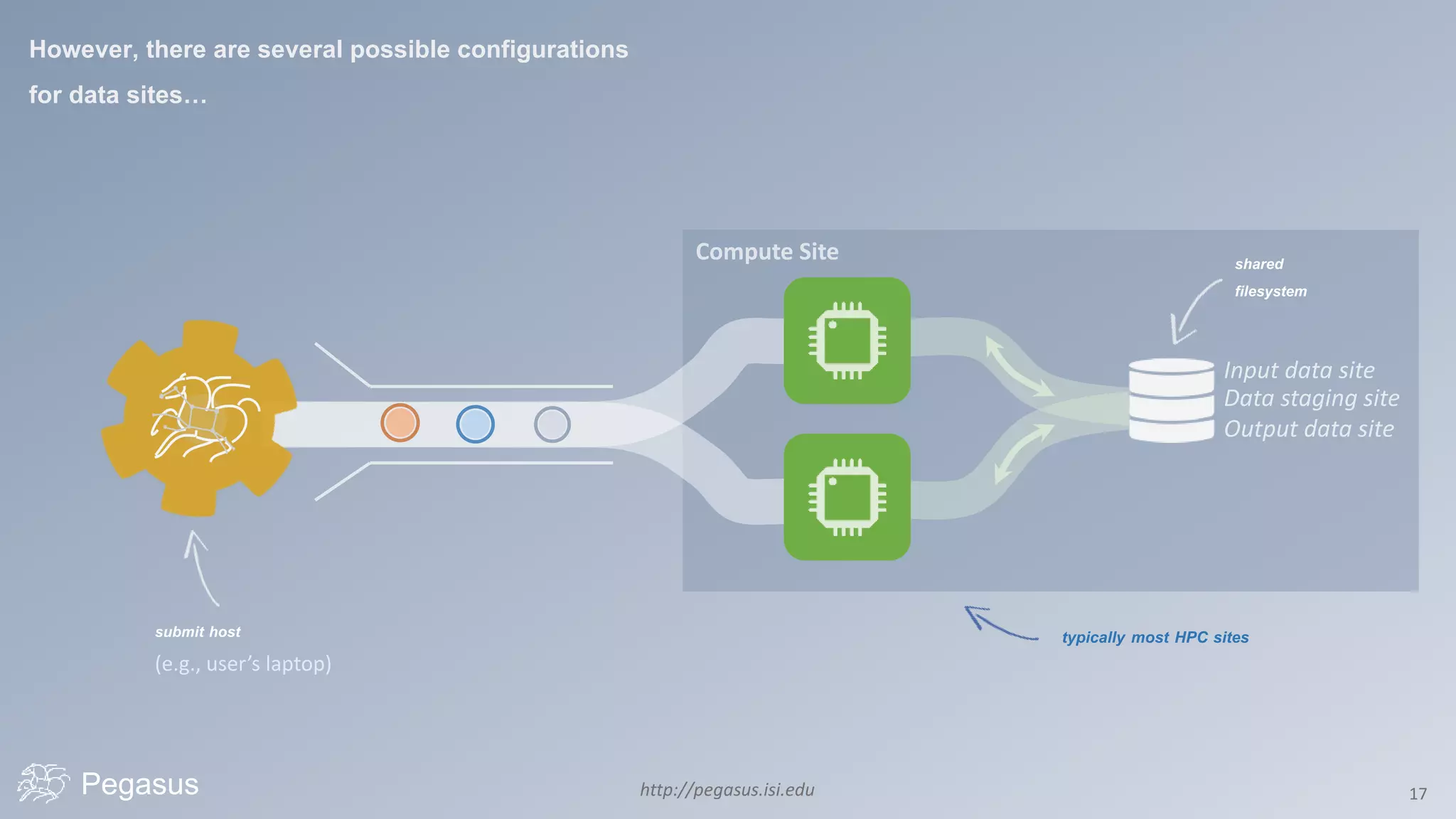
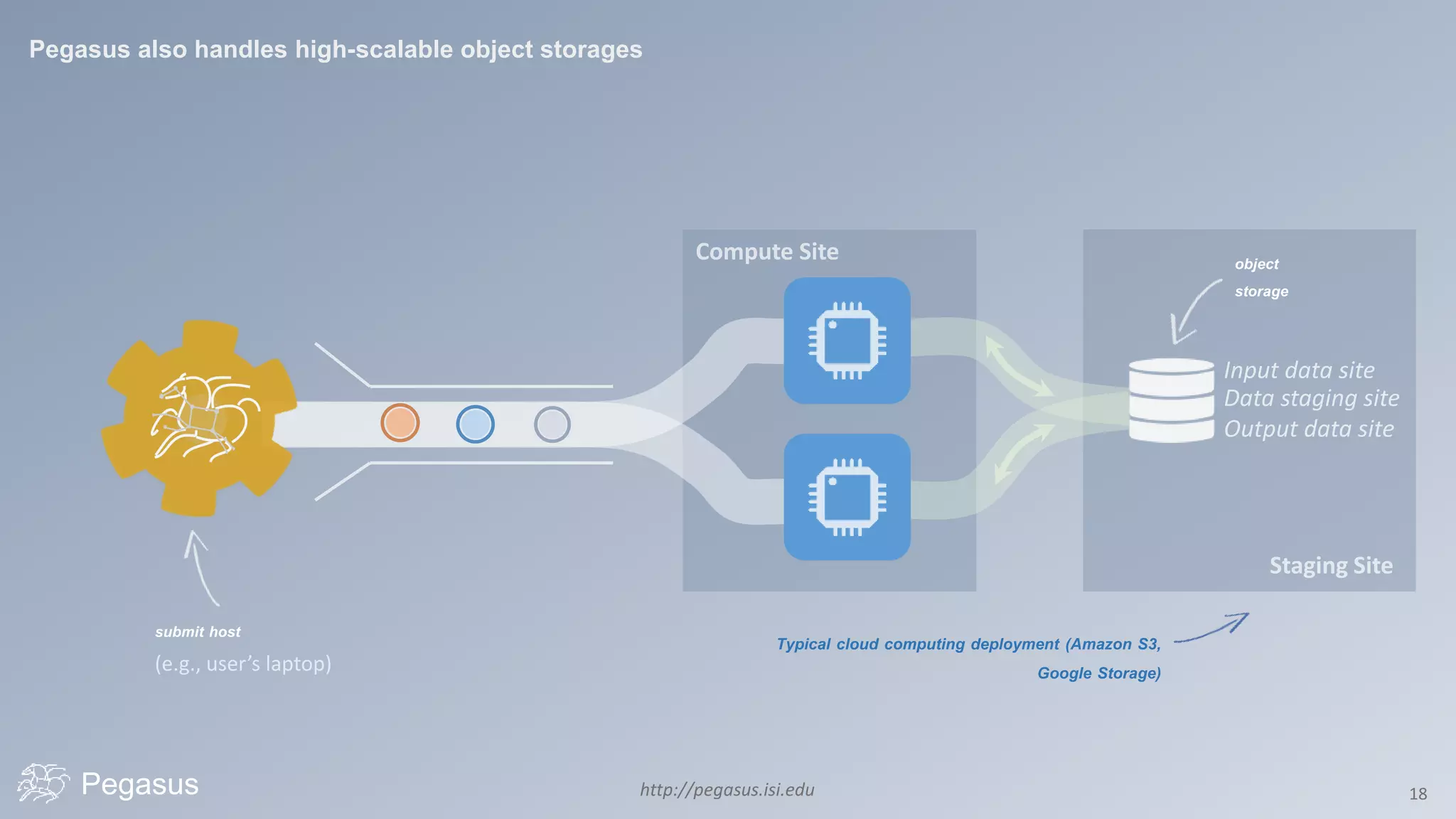
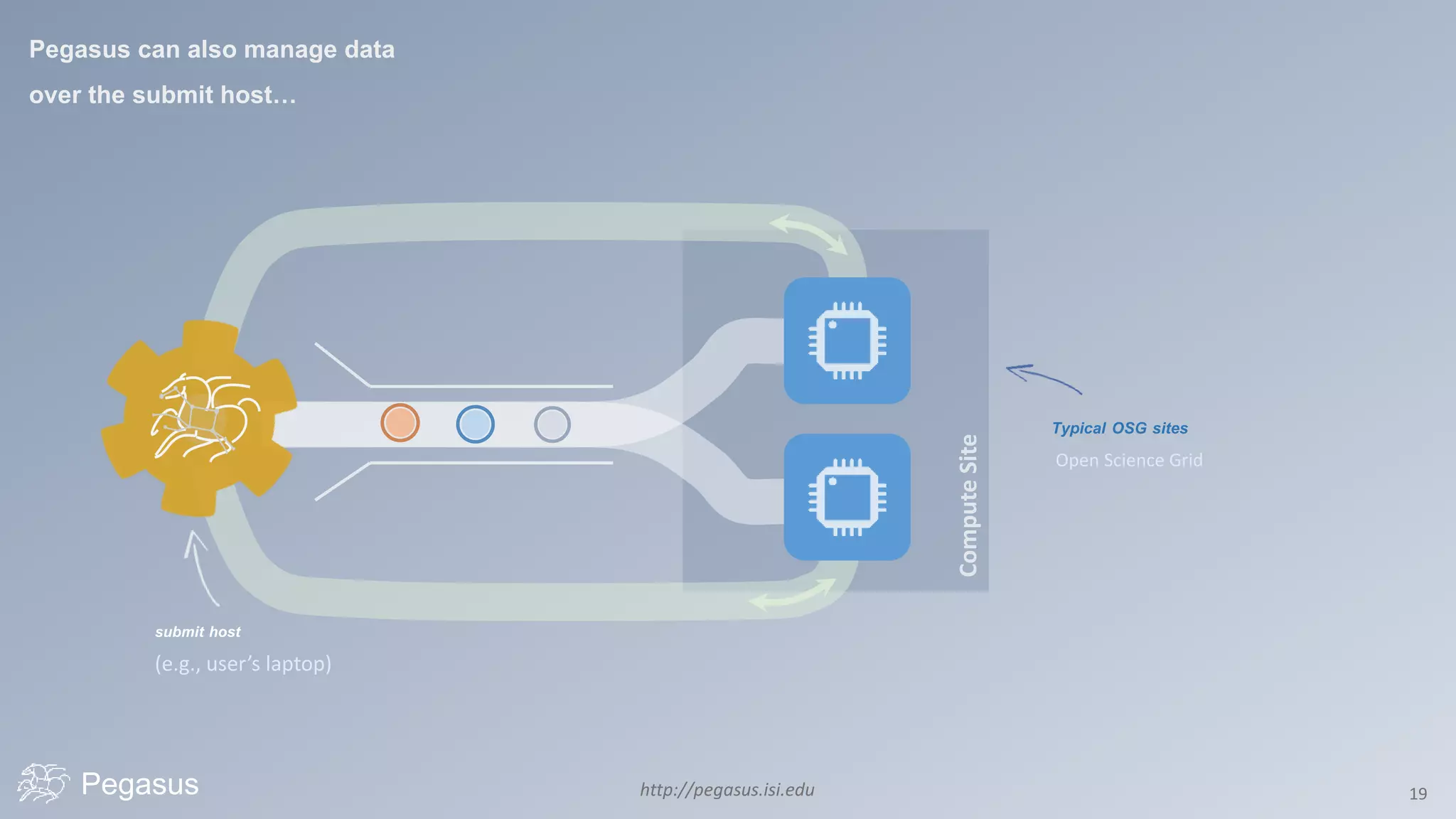
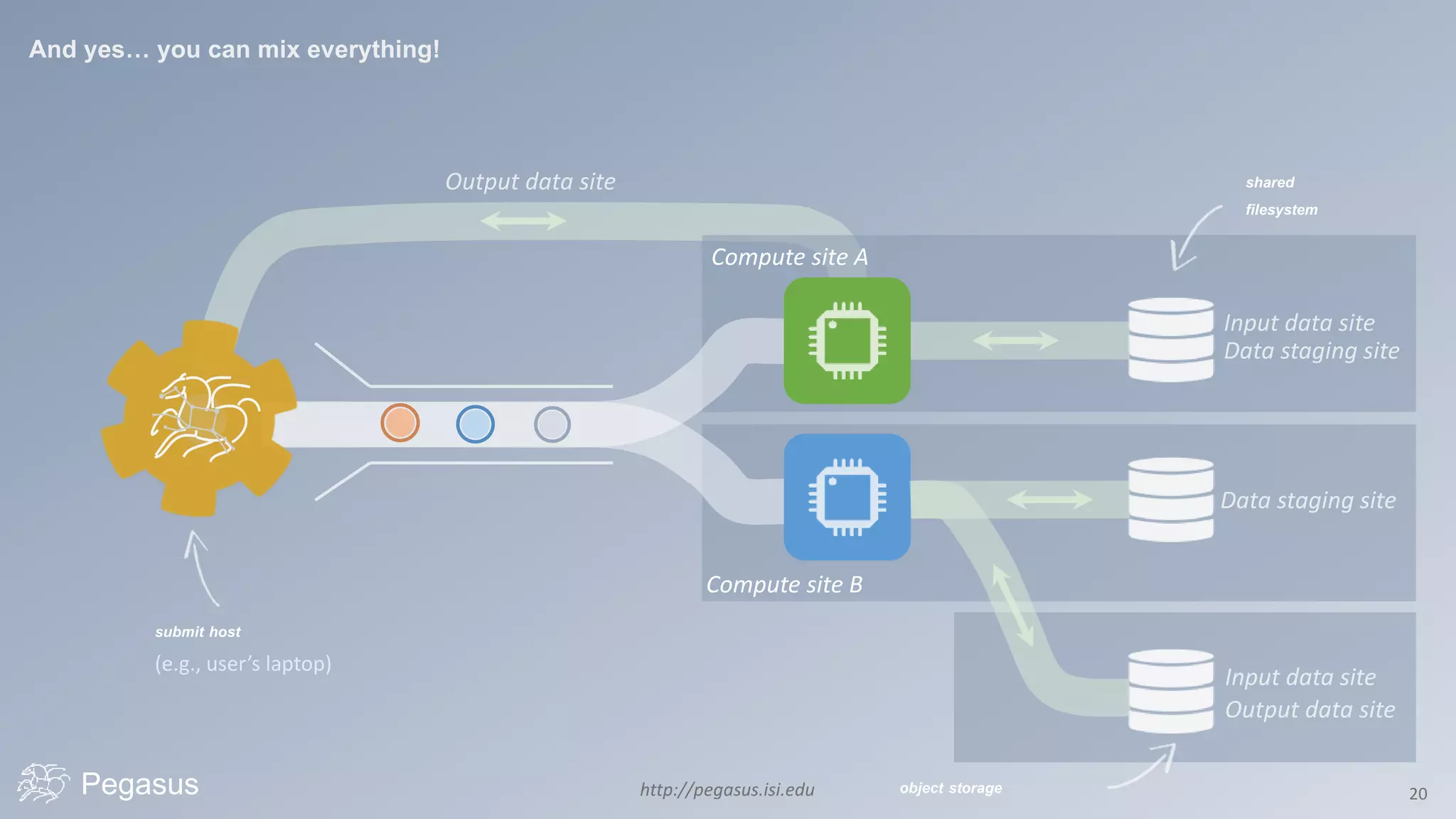
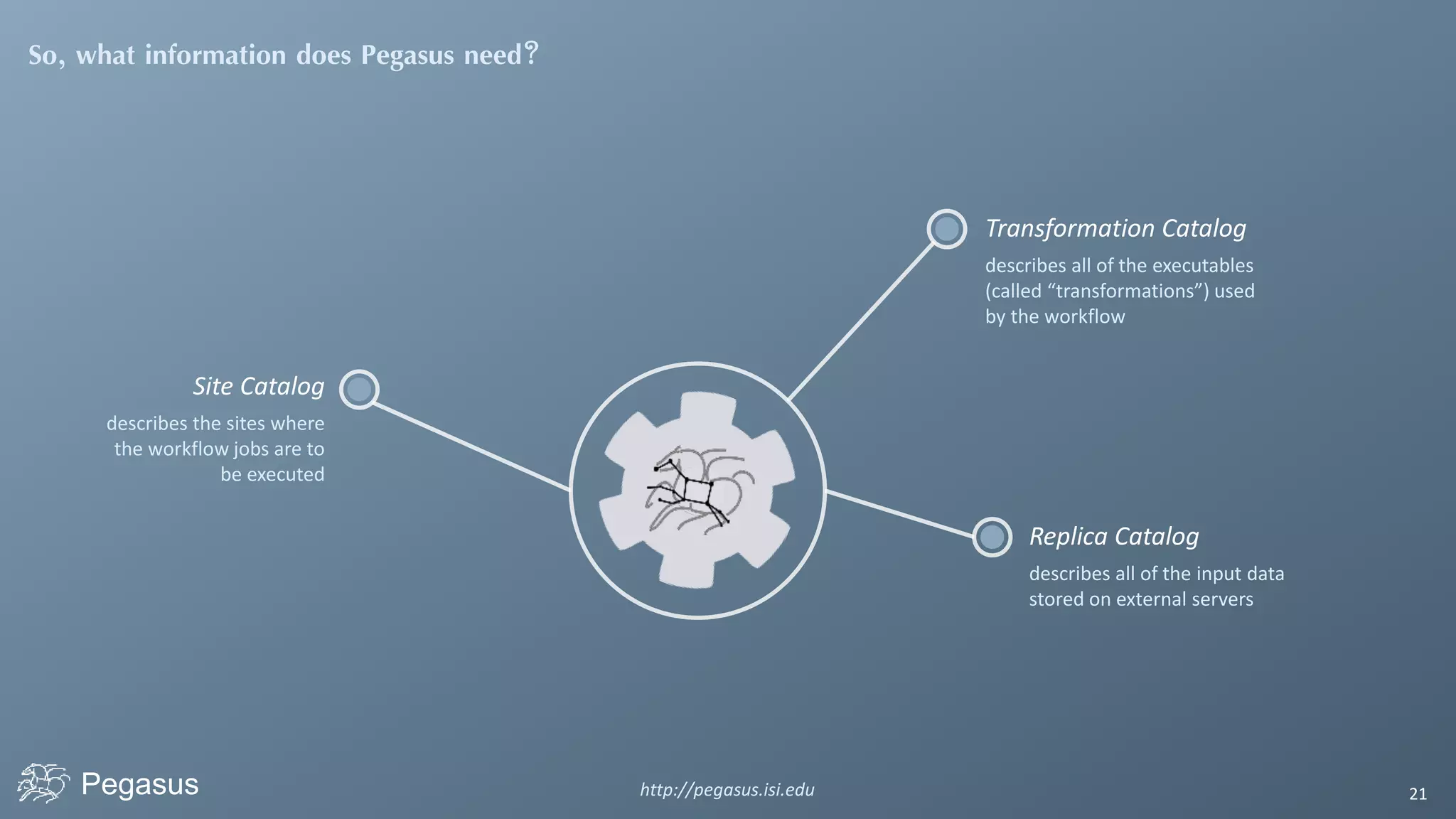
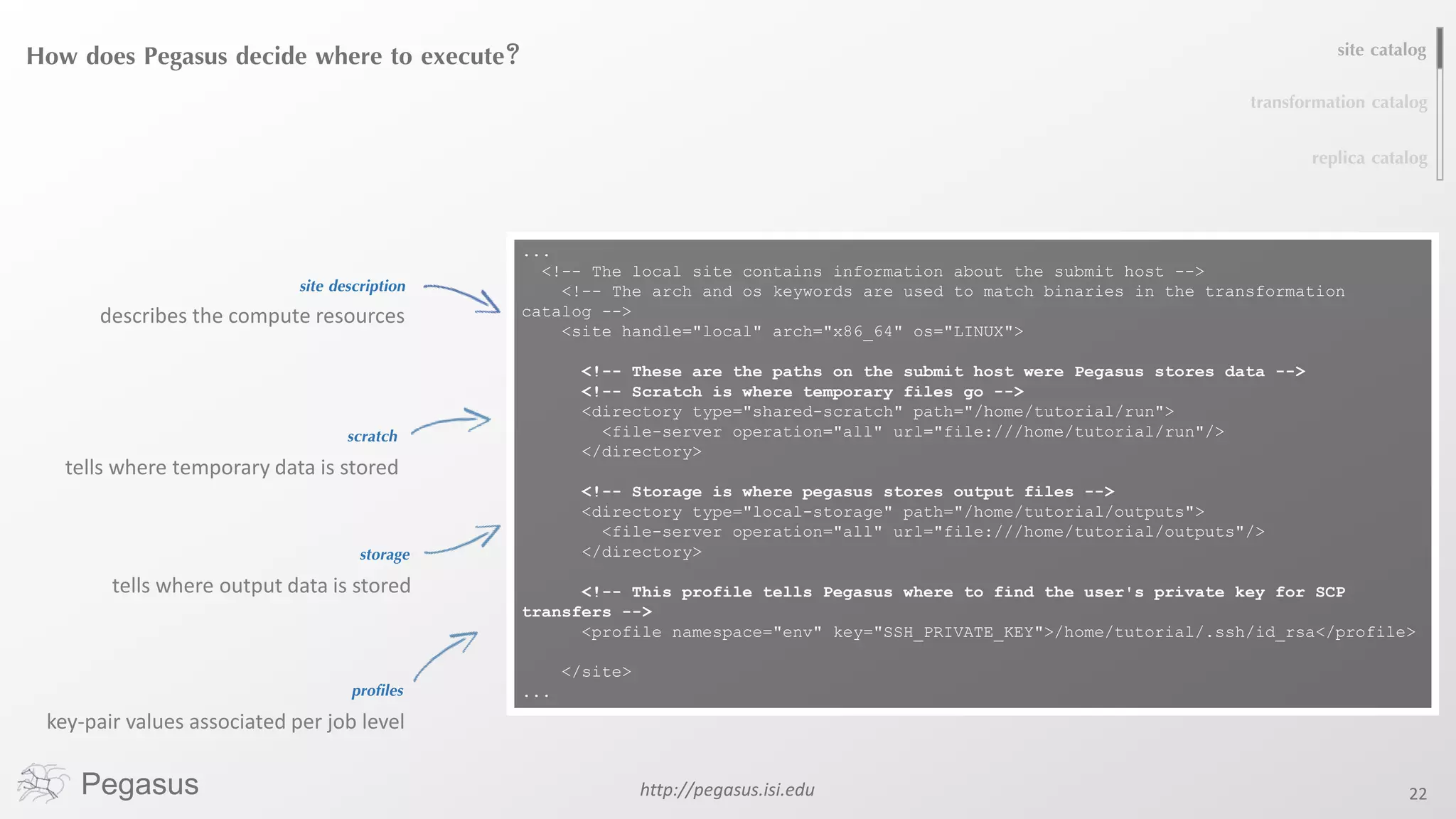
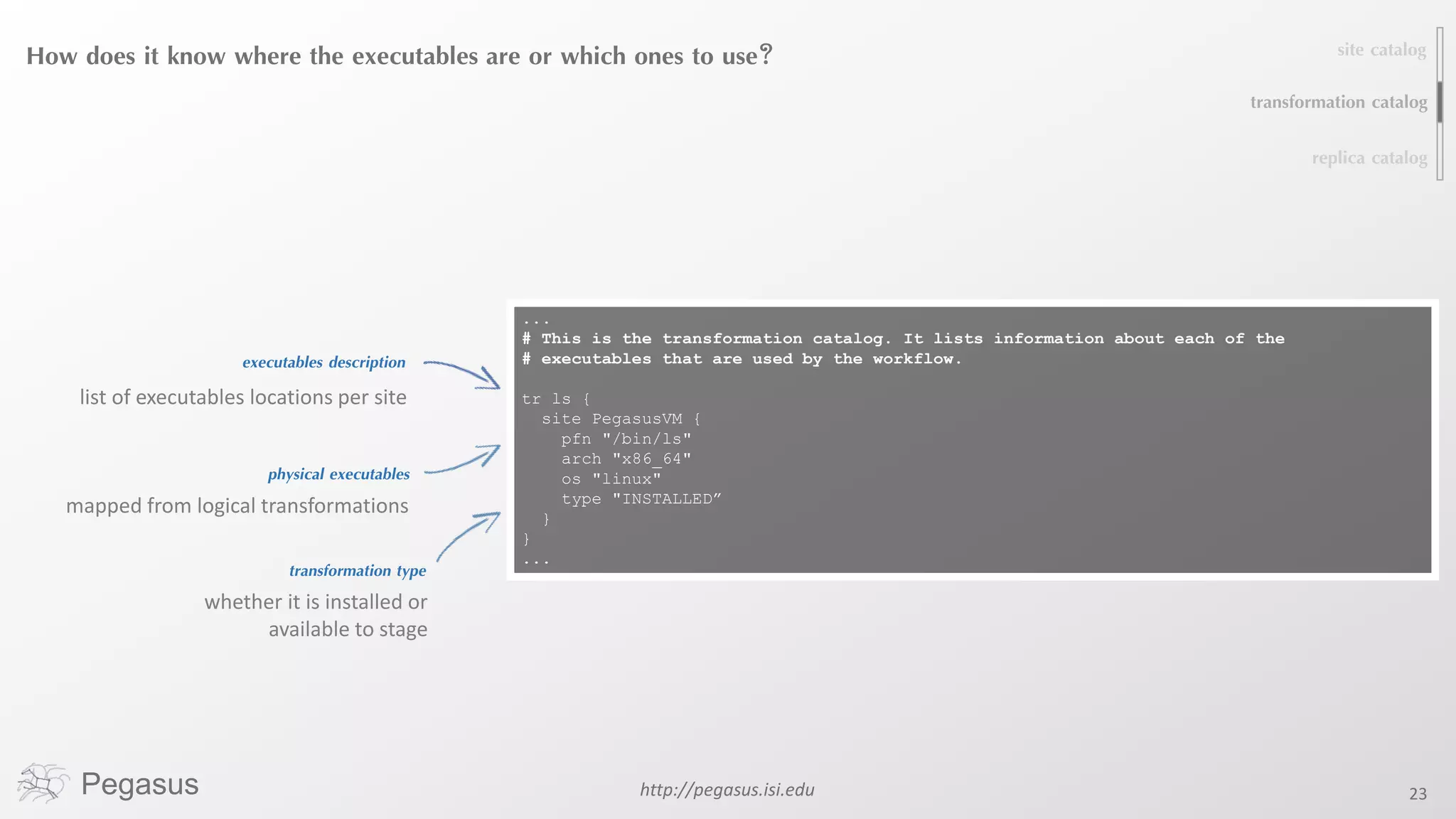
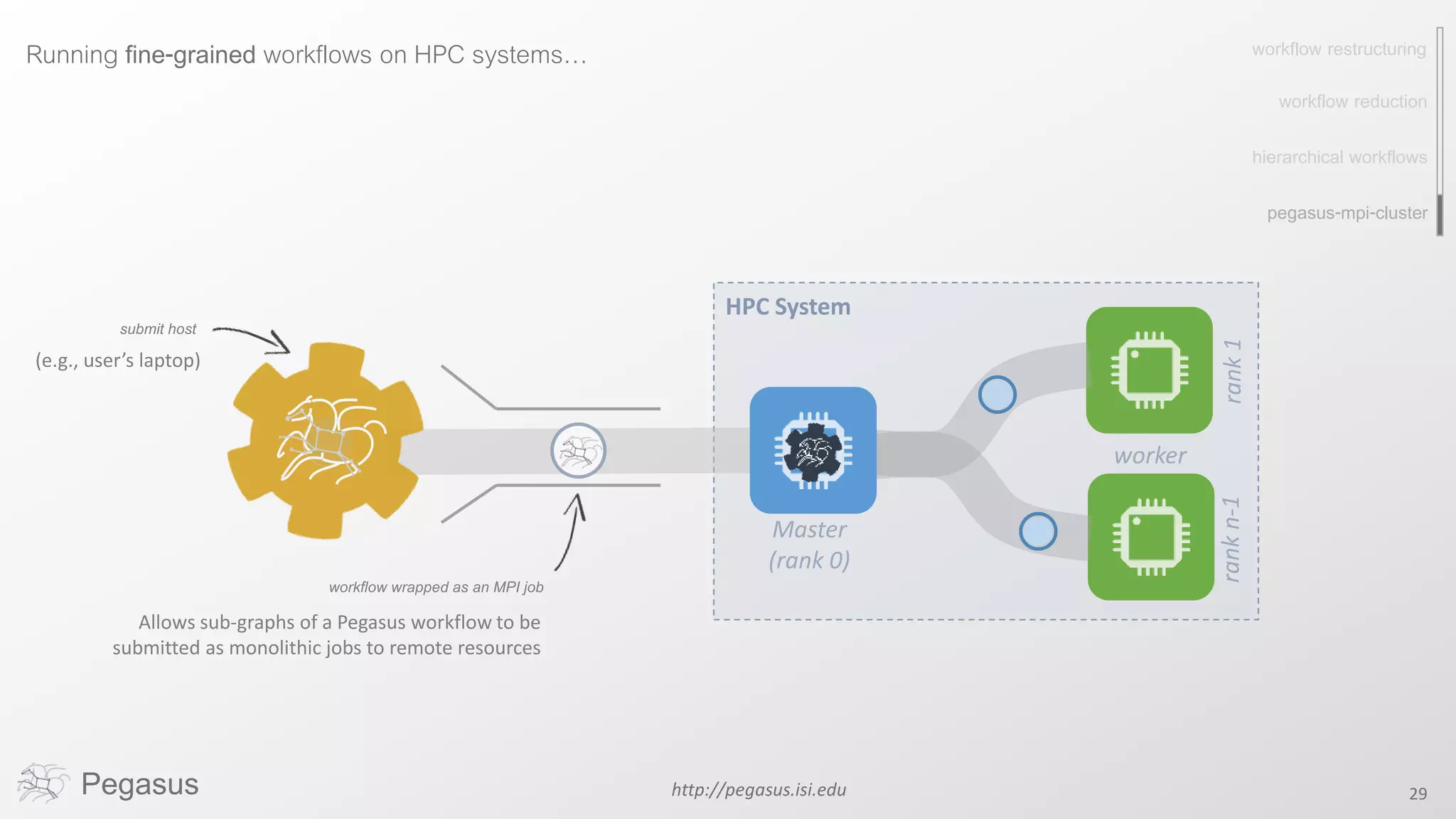
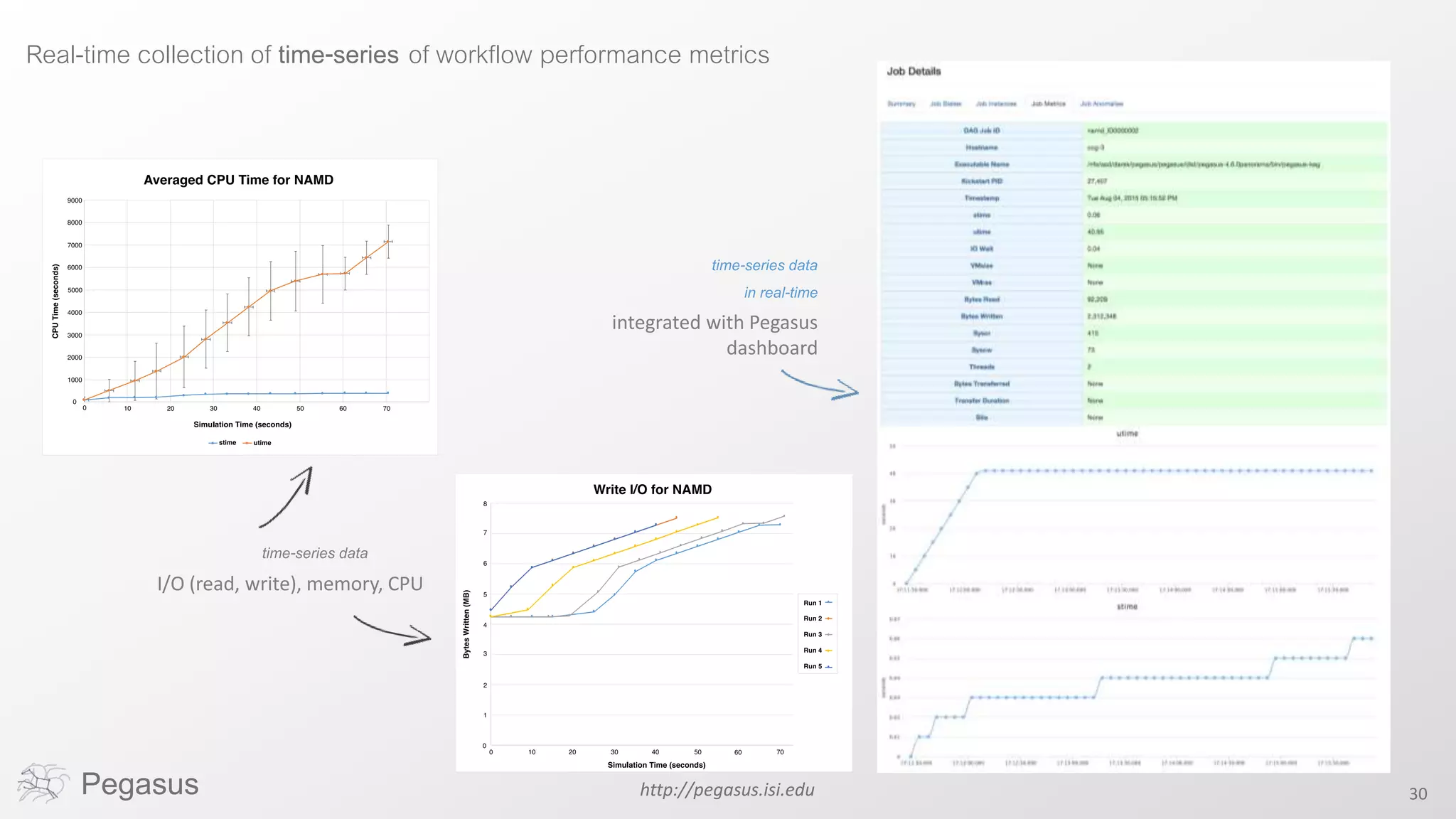
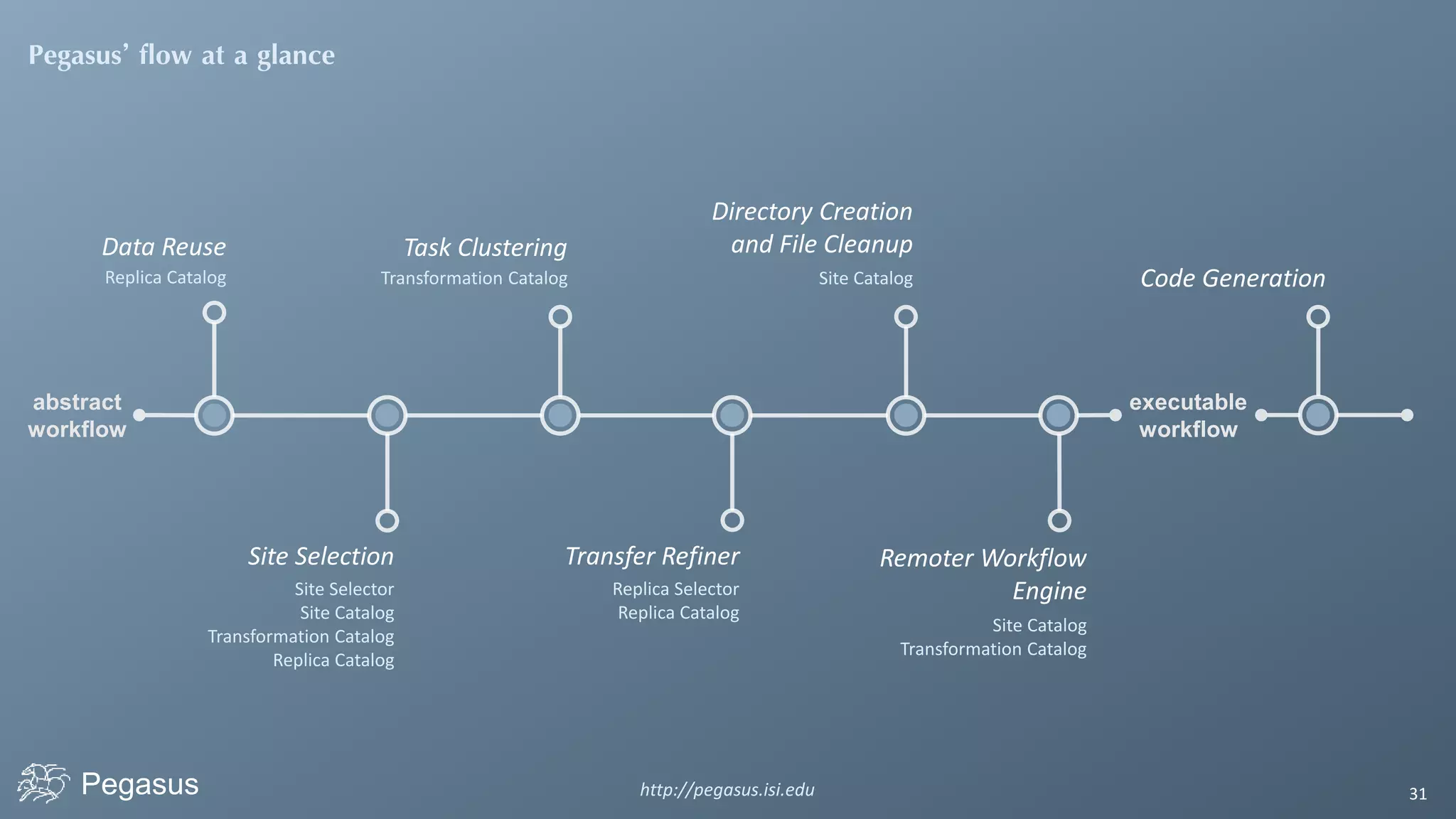
Pegasus is a workflow management system that automates complex computational experiments. It handles tasks such as automating multi-step processing pipelines, enabling parallel distributed computations, automatically transferring data, and handling failures to provide reliability. Pegasus records provenance data to keep track of how results were produced and allows experimental workflows to be reproduced. It generates executable workflows from abstract descriptions to run experiments on distributed computing resources including clusters, grids, and clouds.