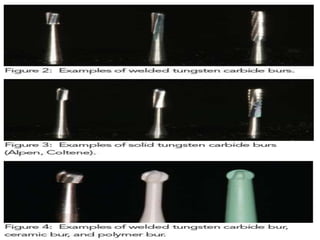
The document discusses the dental home concept and minimally invasive dental techniques. It defines the dental home as an ongoing relationship between dentist and patient to provide comprehensive and family-centered oral healthcare from age 1. This includes preventive services, risk assessments, anticipatory guidance, and treatment. Minimally invasive techniques aim to preserve tooth structure by reducing bacteria, using preventive measures, and remineralizing early lesions. They involve minimal cavity preparation and surgery using adhesive materials, as well as repairing restorations to prevent further decay.