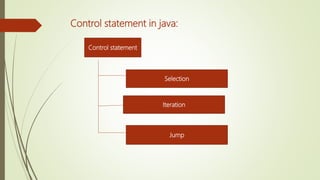
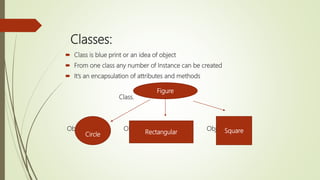
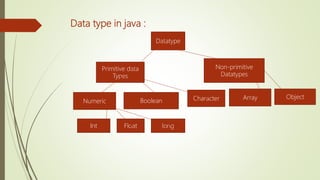
This document provides an overview of advanced Java programming concepts covered in the unit, including object-oriented programming, data types, variables, arrays, operators, inheritance, and control statements. It defines key concepts like classes, objects, encapsulation, polymorphism, and inheritance. For data types, it covers primitive types like int, float, boolean and char, as well as arrays. Operators covered include unary, arithmetic, relational, logical, and assignment operators. The document also discusses variables, arrays, and control statements like selection, iteration, and jump statements.













![Separators:
Few character are used, most commonly used semicolon.
() method definition
{} define block of code,class method
[] declare array types
. Separate package name
, separate consecutive identifier in a variable declaration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcst11overviewofjava-201219085412/85/PCSTt11-overview-of-java-16-320.jpg)



![Variable and Array :
Variable:
A variable is a named field containing information that your program uses
A variable as a name of the memory location where the variable value is stored
Declaring variable:
Type identifier [=value ][,identifier [=value ]…..]
Array:
An array is group of like _typed variables that are referred to by a common name
An array can be of any type
Specific element in an array is accessed by its indax
Can have more than one dimention](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcst11overviewofjava-201219085412/85/PCSTt11-overview-of-java-21-320.jpg)
![Declaration OF ARRAY
The general form of Array
Type[]var_name
int a1[]= new int[3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcst11overviewofjava-201219085412/85/PCSTt11-overview-of-java-22-320.jpg)