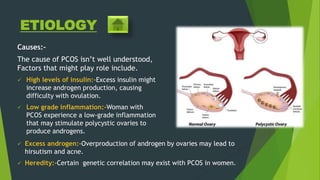
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder affecting 5-10% of women of reproductive age, characterized by abnormal ovarian function and elevated androgen levels. It has various types linked to causes such as insulin resistance and genetic factors, and can lead to complications like infertility and cardiovascular disease. Diagnosis involves physical exams and tests, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms through lifestyle changes and medications.