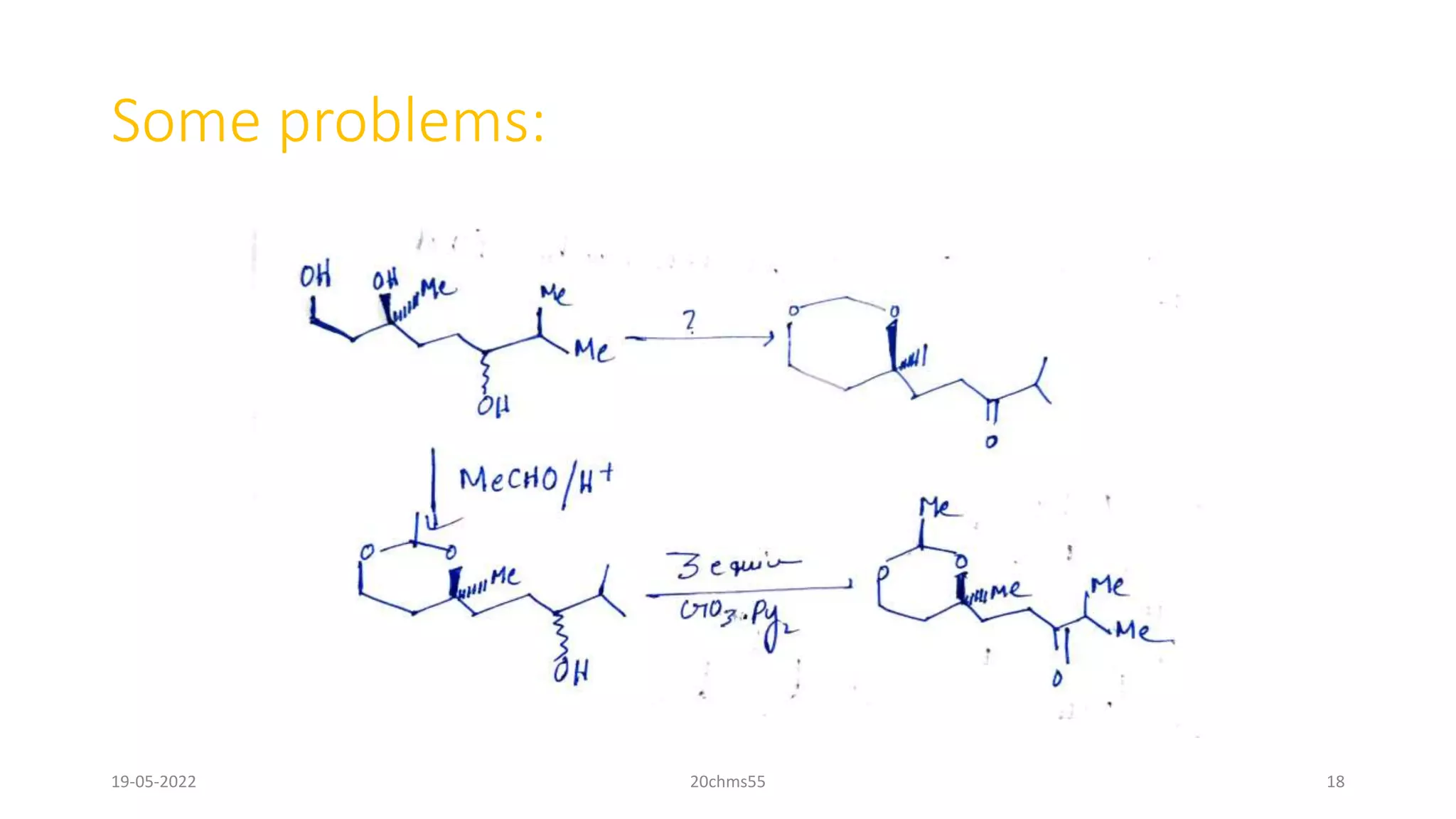
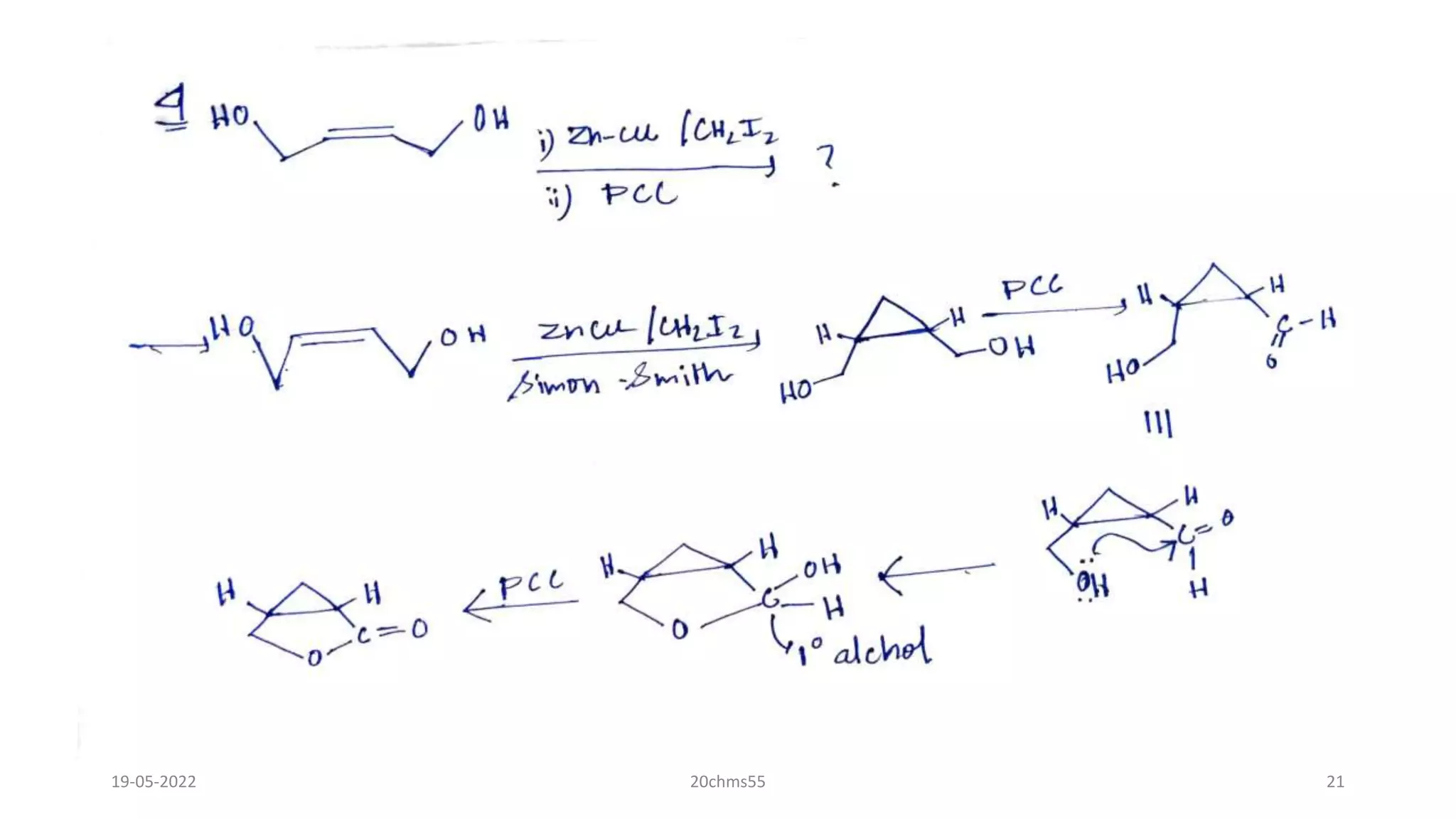
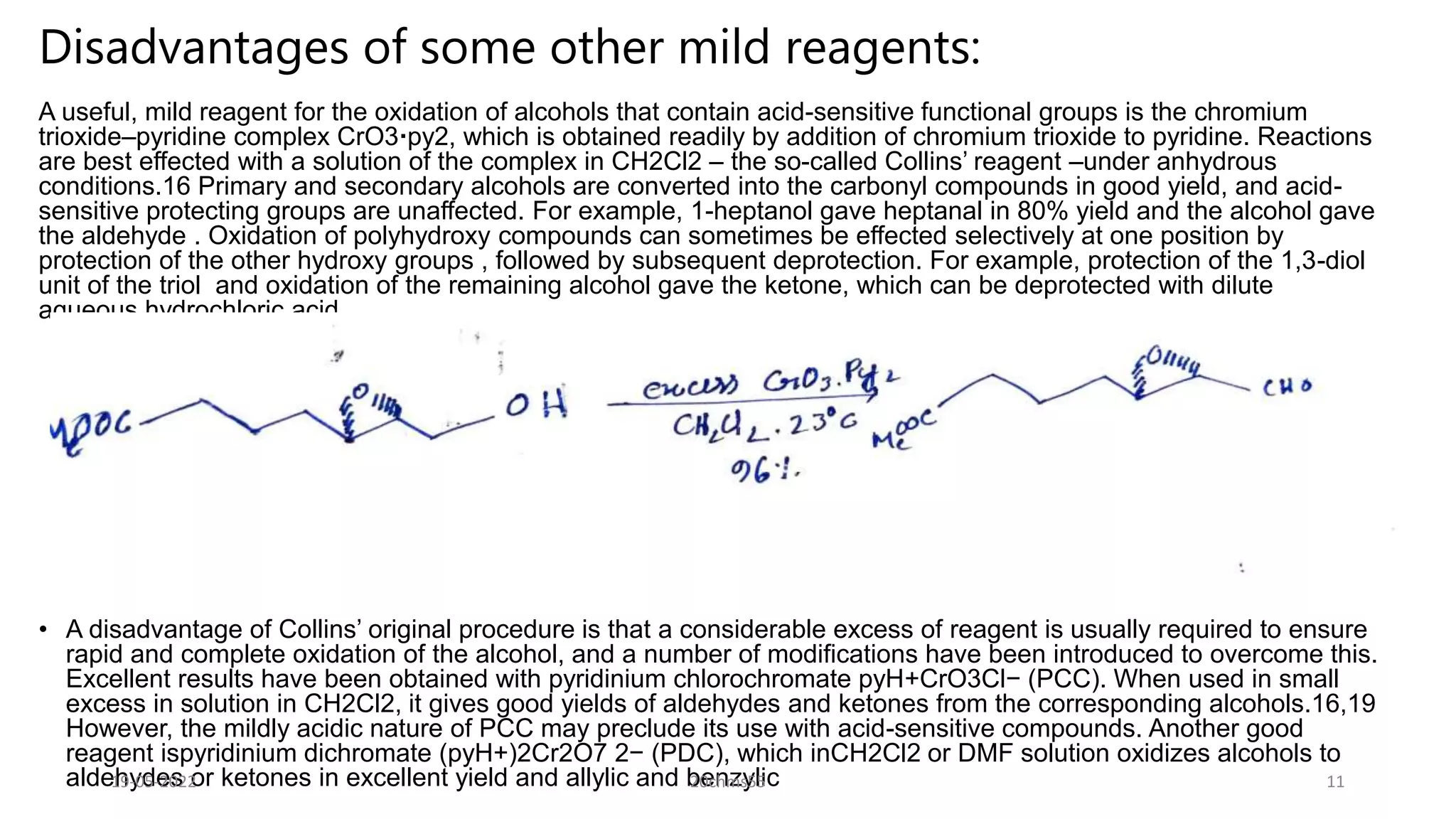
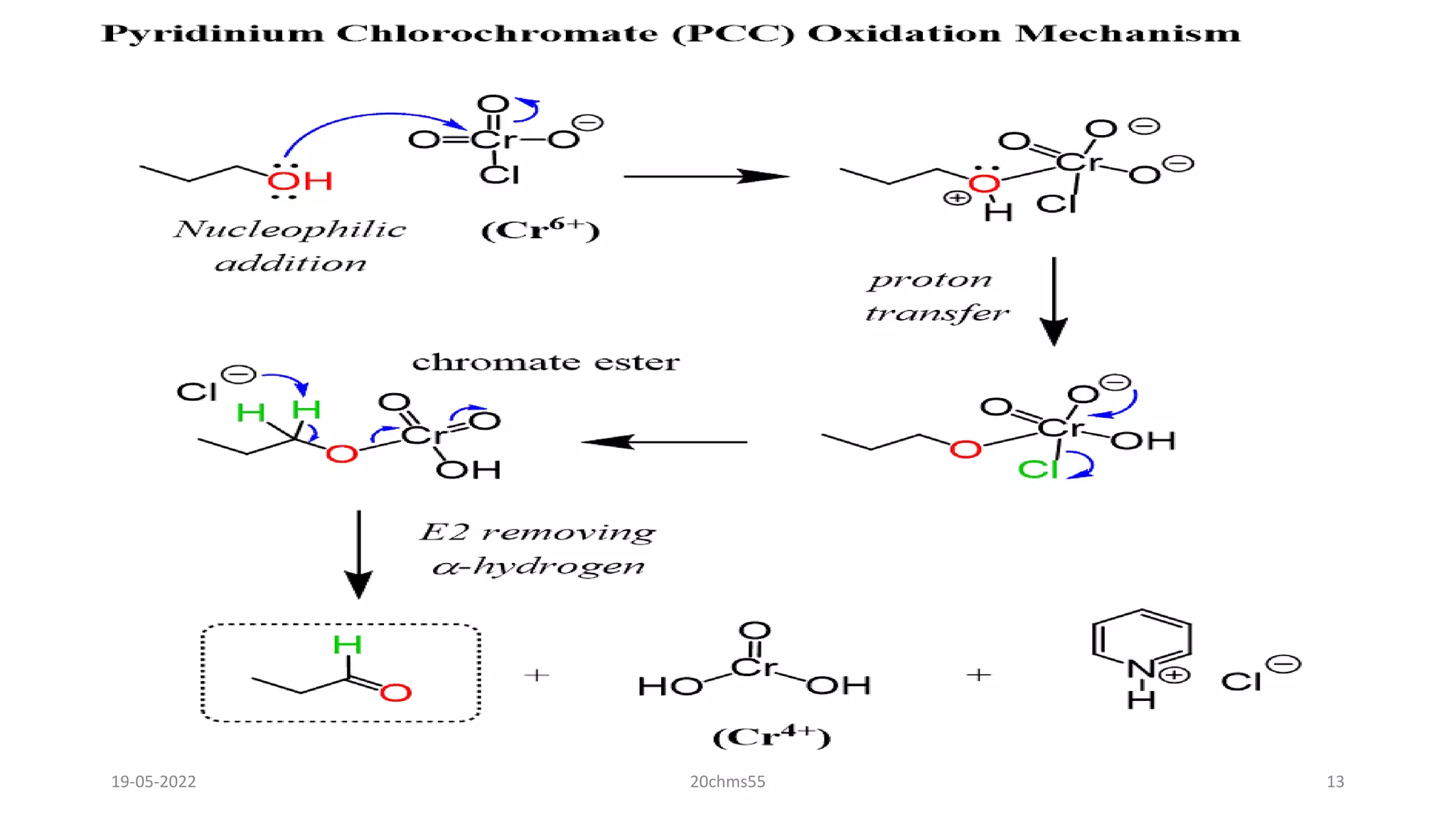
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a mild and selective oxidizing reagent used to convert primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones respectively. It was first described in 1975 by Elias Corey and J. William Suggs as an efficient reagent for alcohol oxidation. PCC is prepared by adding pyridine to a solution of chromium trioxide in hydrochloric acid. It is a stable, yellow-orange solid that is soluble in organic solvents. PCC oxidizes alcohols more selectively than related reagents like Jones reagent with little chance of over-oxidation to carboxylic acids. While still used, its usage has declined in recent decades as

![What Is Pcc?
• Inventor:
Elias James "E.J." Corey J. William Suggs
•
• PCC is also known as: Corey-Suggs reagent
19-05-2022 20chms55 2
• Pyridinium chlorochromate
(PCC) is a yellow-orangesalt with
the formula
[C5H5NH]+[CrO3Cl]−.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pccoxidation-220519101733-b4d464ba/75/PCC-OXIDATION-pptx-2-2048.jpg)





![Alternative method of formation of pcc :
In one alternative method, formation of chromyl chloride(CrO2Cl2) fume during the making of
the aforementionedsolution was minimized by simply changing the order ofaddition: a cold
solution of pyridine in concentratedhydrochloric acid was added to solid chromium
trioxideunder stirring.
19-05-2022 20chms55 8
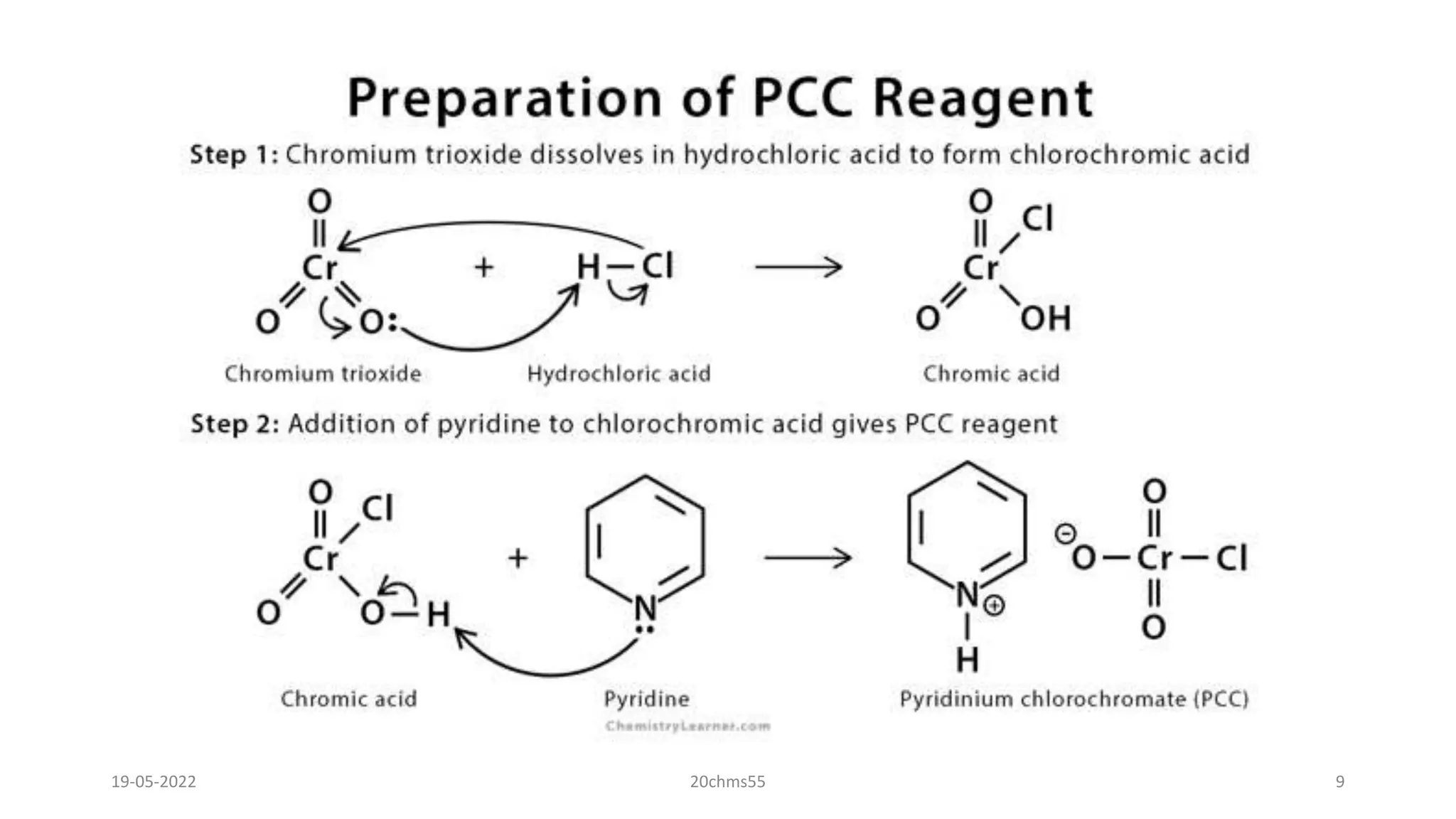
Preparation of PCC-
"To 184 ml of 6 M HCl (1.1 mol) was added 100 g (1 mol) ofCrO3 rapidly with stirring. After 5 min.
the homogeneous solution was cooled to 0o and 79.1 g (1mol) of pyridine was carefully added over
10 min. Recooling to 0o gave a yellow-orange solid which was collected on a sintered glass funnel
and dried for 1 h.r in vacuuo (yield 180.8 g, 84%). The solid is not appreciably hygroscopic and
can be stored for extended periods at room temperature without change."
C5H5N + HCl + CrO3 → [C5H5NH][CrO3Cl]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pccoxidation-220519101733-b4d464ba/75/PCC-OXIDATION-pptx-8-2048.jpg)


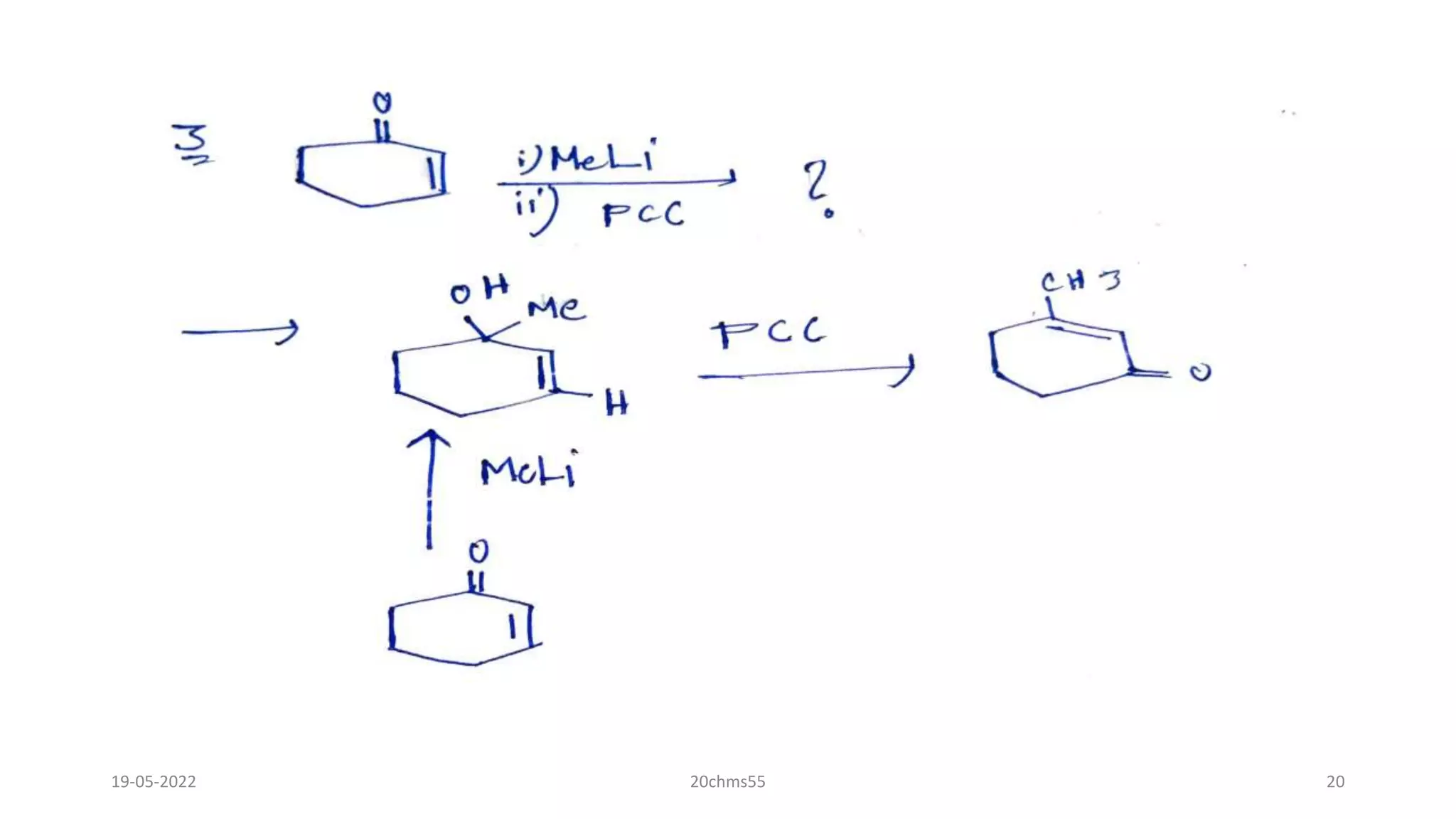
![How does pcc reacts with tertiary alchols?
• With tertiary alcohols, the chromate ester formed from PCC can isomerize via a [3,3]-
sigmatropicreaction and following oxidation yield an enone, in a reaction known as the Babler
oxidation
• This type of oxidative transposition reaction has been synthetically utilized, e.g. for the synthesis
ofmorphine.Using other common oxidants in the place of PCC usually leads to dehydration, because
such alcoholscannot be oxidized directly
19-05-2022 20chms55 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pccoxidation-220519101733-b4d464ba/75/PCC-OXIDATION-pptx-14-2048.jpg)