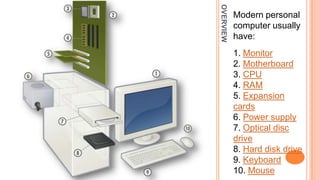
The document defines the core hardware components of a modern personal computer and provides an overview of each. A typical personal computer contains: (1) a monitor, (2) a motherboard that holds crucial components, (3) a CPU that carries out computer programs, (4) RAM for data storage, (5) expansion cards that add functionality, (6) a power supply, (7) an optical disc drive, (8) a hard disk drive, (9) a keyboard for input, and (10) a mouse. Peripheral devices like printers can connect to expand capabilities but are not core components.