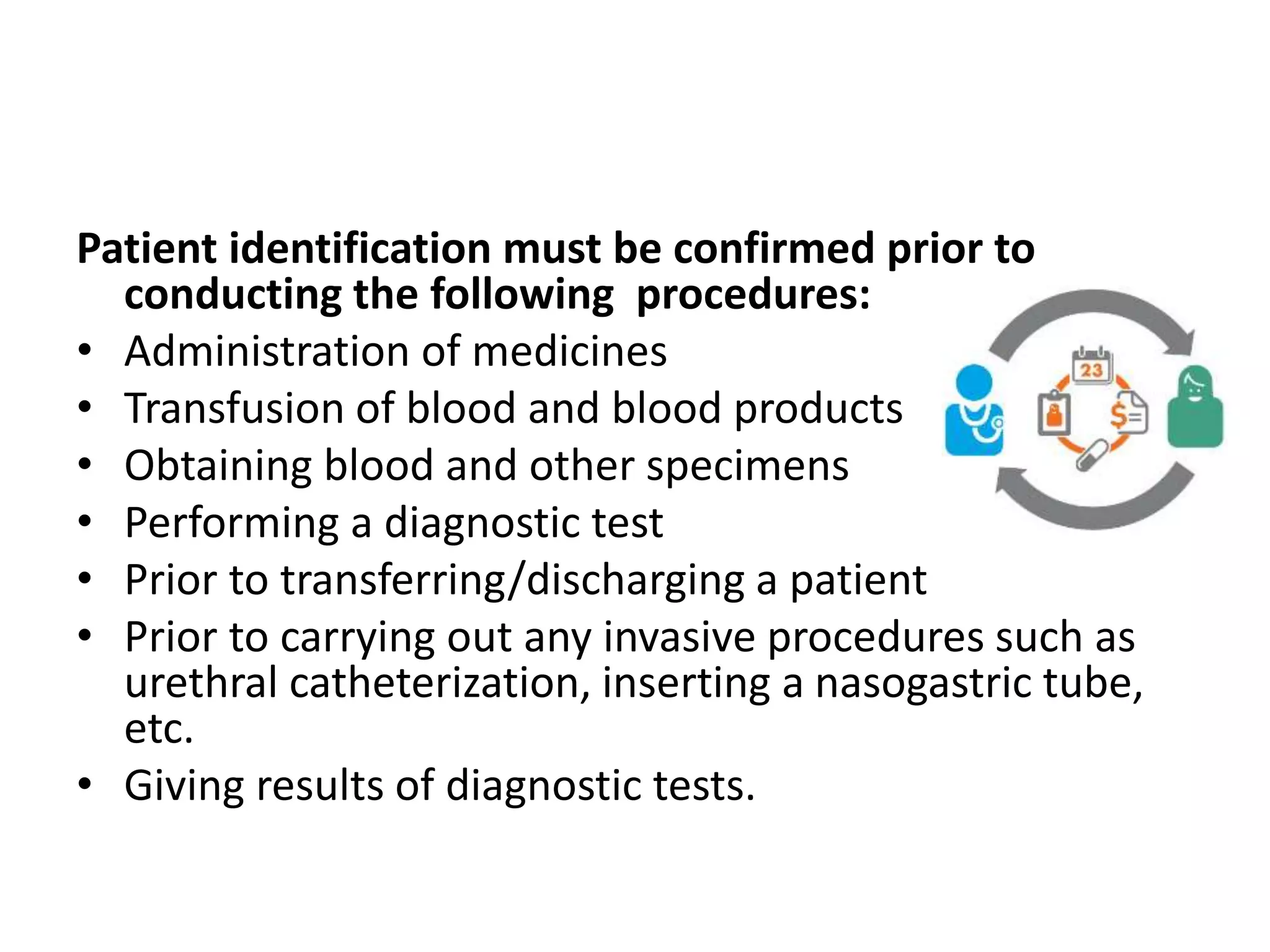
This document outlines international patient safety goals for correctly identifying patients. It lists six goals, including correctly identifying the patient, improving communication, and reducing healthcare-associated infections. To ensure correct patient identity, multiple patient identifiers like name, ID number, and date of birth must be used and confirmed prior to procedures. Nurses are responsible for verifying the patient is wearing correct ID bands that match the medical record. Failure to correctly identify the patient can lead to medication errors, transfusion mistakes, wrong testing or procedures being performed.