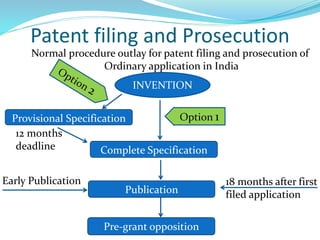
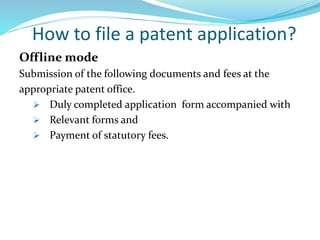
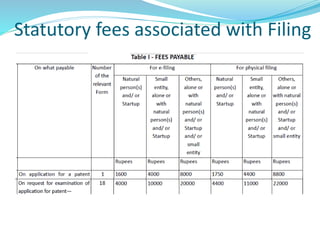
Dr. I. G. Rathish gave a presentation on filing patent applications in India. He discussed who can apply, where and when applications can be filed, the application process, forms and fees required. The key steps include filing an application with the appropriate patent office, submitting a provisional or complete specification describing the invention, and paying statutory fees. If filing relates to biological material, it must be deposited with an international depository authority. The Intellectual Property Rights Cell at CUSAT provides assistance to researchers and startups on patent filing and related procedures in India.