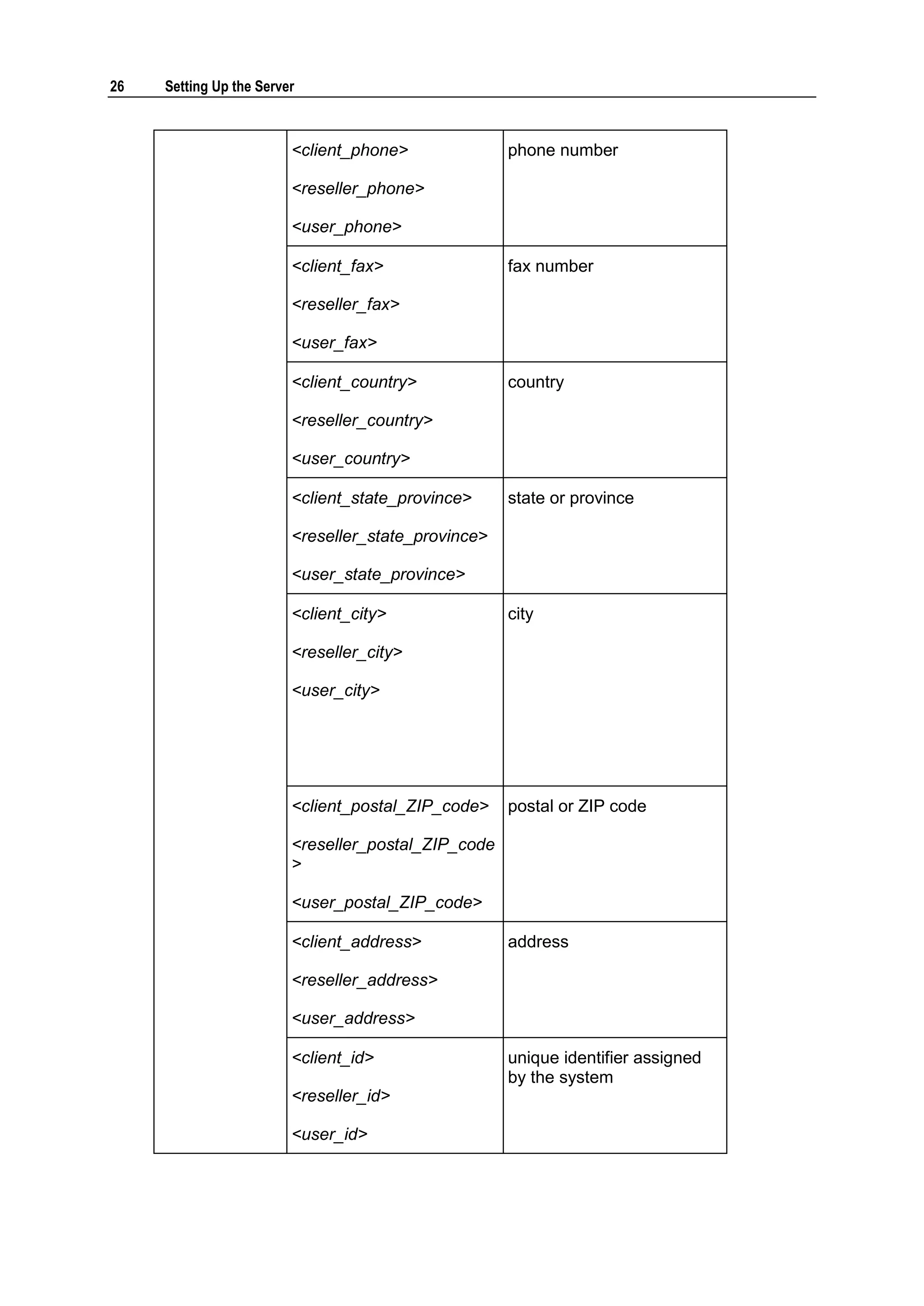
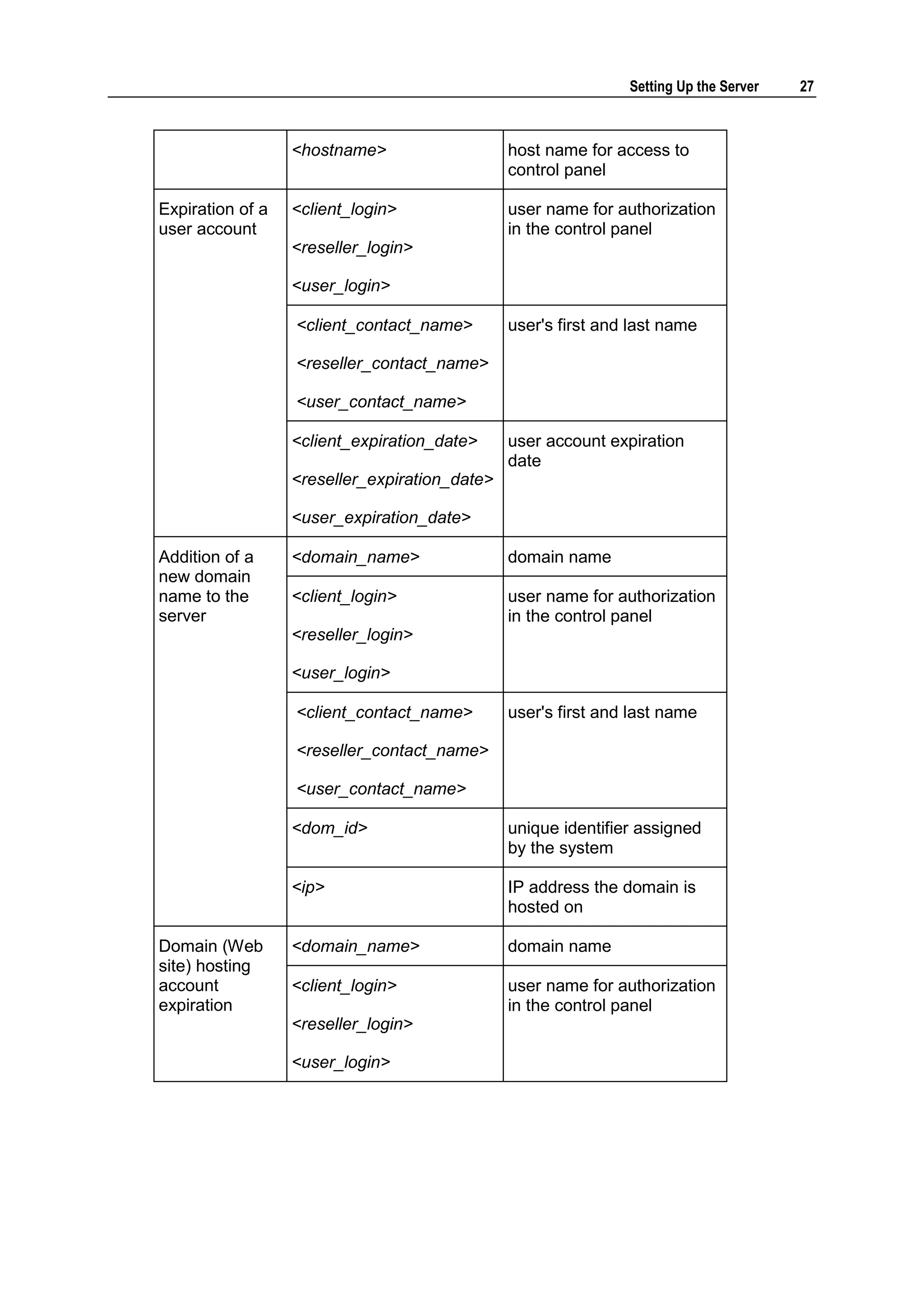
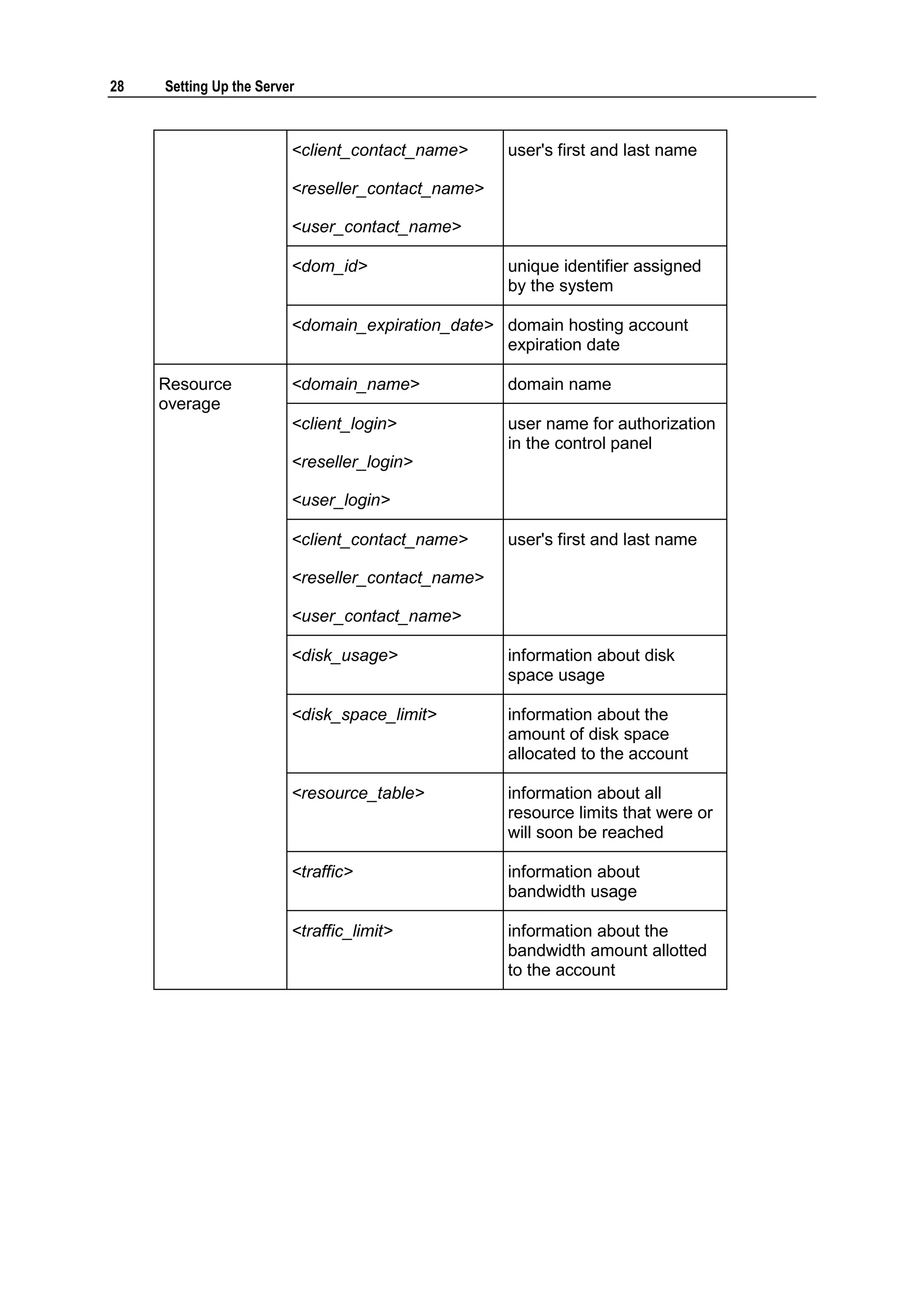
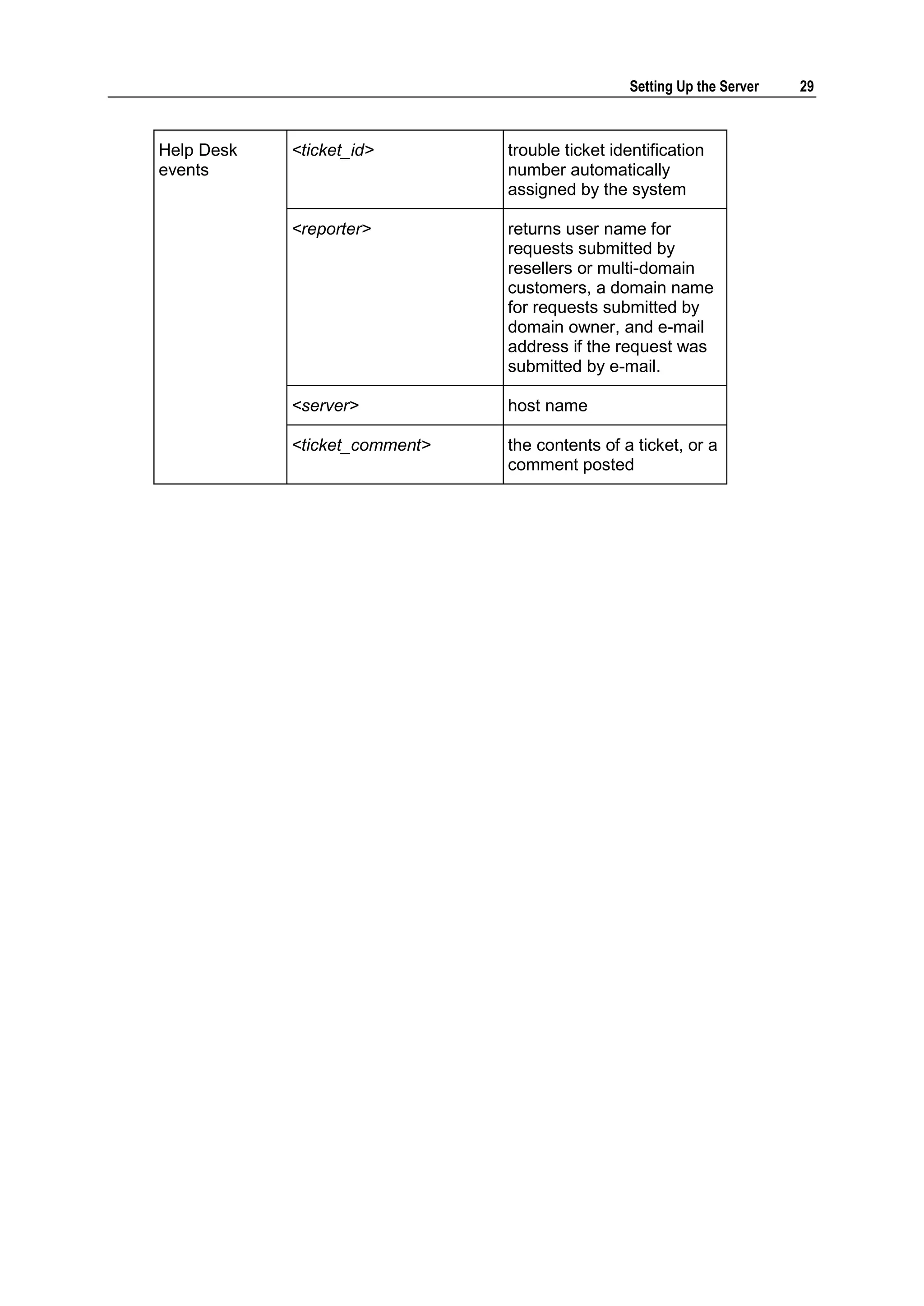
This document provides copyright information and terms of use for Parallels Plesk Panel. It notes that Parallels holds copyright on the software and lists patents related to the product. Distribution of the software or derivatives requires written permission from Parallels.