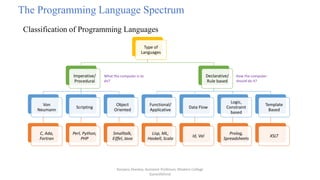
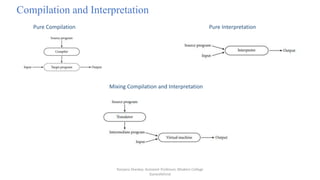
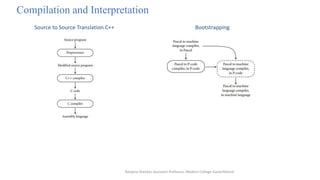
This document discusses programming language paradigms and provides an overview of different types of programming languages. It describes why there are many programming languages, including factors like evolution, special purposes, personal preference, and economics. The document also classifies programming languages as imperative/procedural, scripting, object-oriented, declarative/rule-based, functional/applicative, data flow, and logic/constraint-based. Finally, it discusses compilation vs interpretation and provides examples of programming environments like Microsoft Visual Studio .NET and NetBeans.