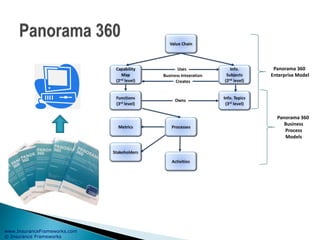
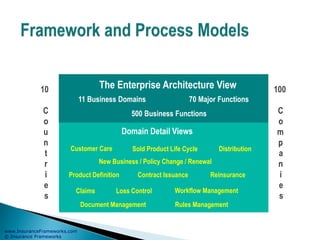
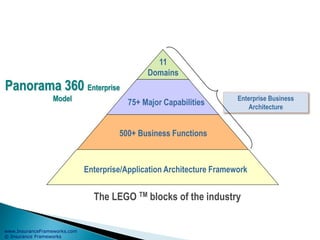
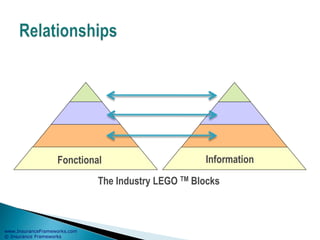
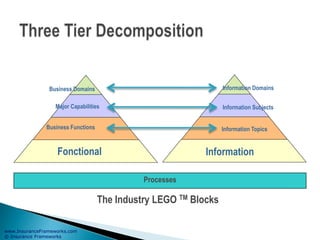
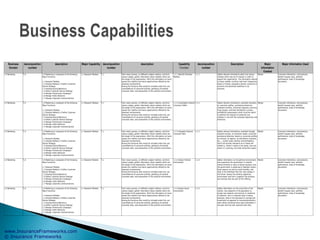
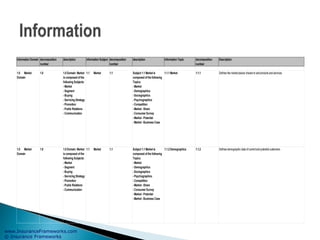
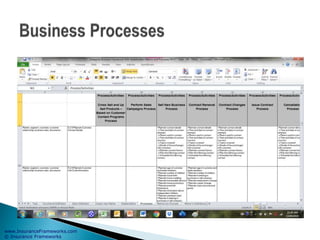
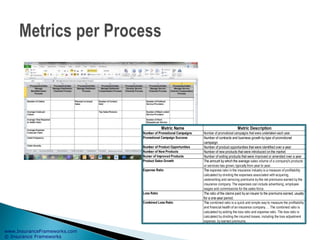
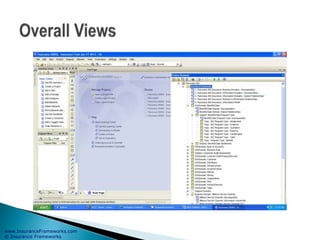
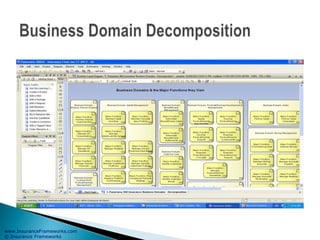
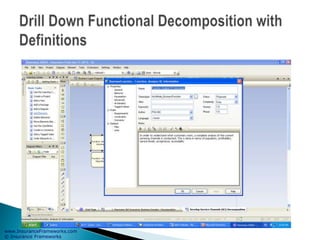
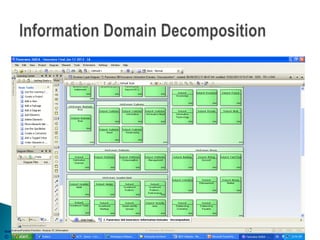
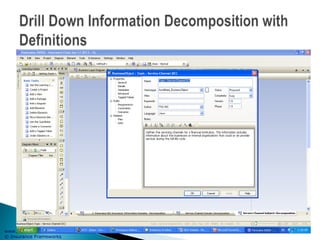
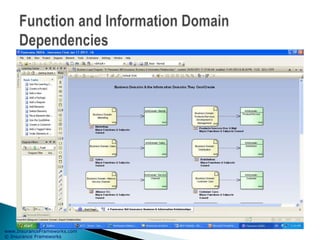
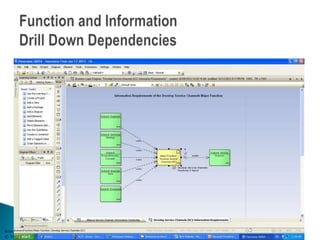
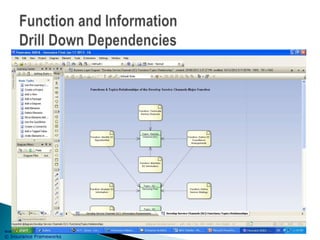
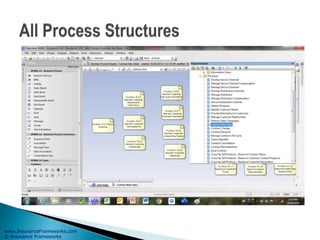
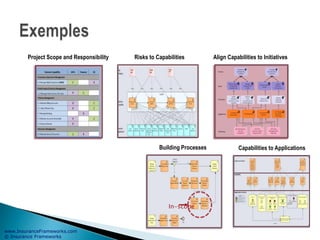
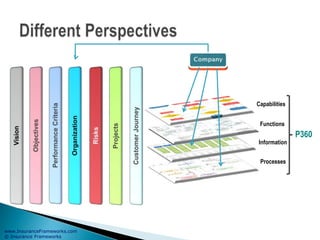
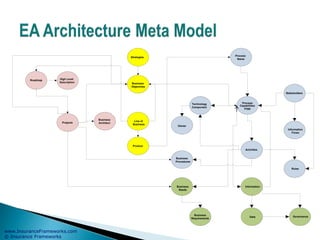
The document outlines an enterprise business architecture framework for managing organizations, business processes, and technology in the insurance and wealth management sectors. It presents various business domains, capabilities, and functions, detailing processes such as marketing, customer care, product management, and compliance. Additionally, it includes metrics for evaluating promotional campaign effectiveness and overall business performance.