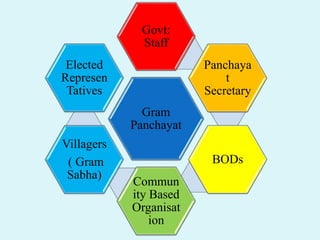
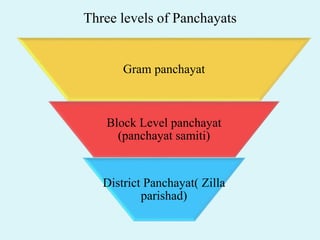
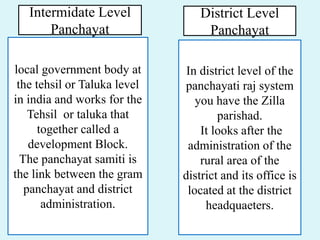
This document discusses Panchayati Raj, the three-tier system of local self-government in India. It was established to decentralize governance and empower communities at the grassroots level. The three levels are: gram panchayat at the village level, panchayat samiti at the block level, and zilla parishad at the district level. The gram panchayat is the basic administrative unit and is responsible for local planning and development. The panchayat samiti acts as a link between the gram panchayat and the district administration. The zilla parishad oversees rural administration at the district level.