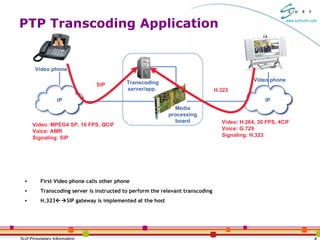
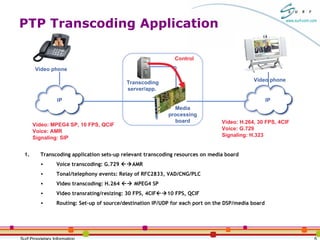
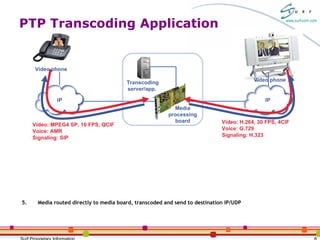
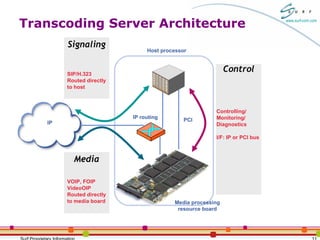
The document discusses packet-to-packet media processing and transcoding applications using the SurfUP media processing platform. It highlights the needs for these applications, optimal system architectures, and how SurfUP supports them through solutions at the chip-level and board-level. It provides value propositions of using SurfUP for transcoding, including supporting multiple media types on the same DSP, direct DSP to network interfaces, an open platform, flexibility across applications, and streaming diagnostics.