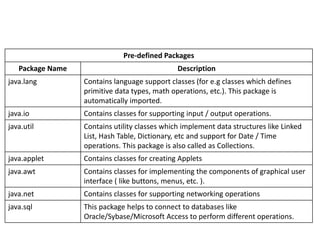
A package in Java is a grouping of related classes and interfaces that provides namespacing to avoid naming conflicts. There are two types of packages: predefined packages provided by Java and user-defined packages. Packages provide advantages like reusability and better organization. Some key predefined packages include java.lang, java.io, java.util, java.applet, and java.awt. To define a user package, include the package statement as the first line in a Java source file, which specifies the package name. Classes in that file will belong to that package.



![package calculation;
public class Calculator
{
public int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Calculator obj = new Calculator();
System.out.println(obj.add(10, 20));
}
}
Compilation for package program
//this will creates package in your directory
•javac -d . Filename.java
//compile and stores class file in your package
•javac –d .. Filename.java
// this is running command
•java packagename.Filename
Demonstrate user defined package by the help of java programs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/package-230405062407-faeef7e6/85/Package-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![import calculation.Calculator;
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Calculator obj = new Calculator();
System.out.println(obj.add(100, 200));
}
}
package import](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/package-230405062407-faeef7e6/85/Package-pptx-6-320.jpg)
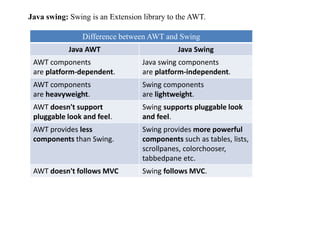
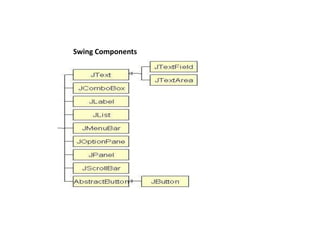
![import javax.swing.*;
public class FirstSwingExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//creating instance of JFrame
JFrame f=new JFrame();
//creating instance of JButton
JButton b=new JButton("click");
//x axis, y axis, width, height
b.setBounds(130,100,100, 40);
//adding button in JFrame
f.add(b);
//400 width and 500 height
f.setSize(400,500);
//using no layout managers
f.setLayout(null);
//making the frame visible
f.setVisible(true);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/package-230405062407-faeef7e6/85/Package-pptx-9-320.jpg)