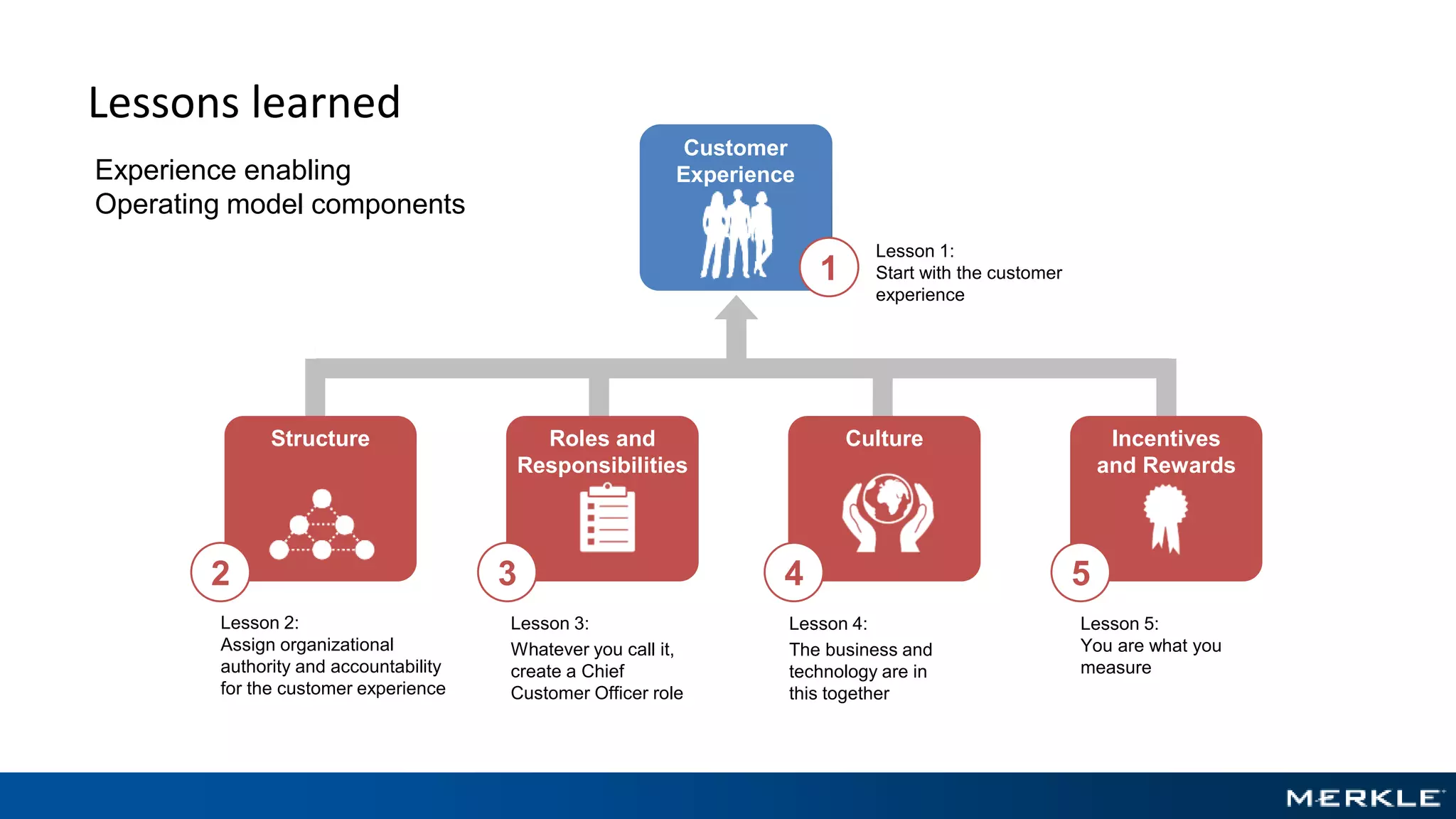
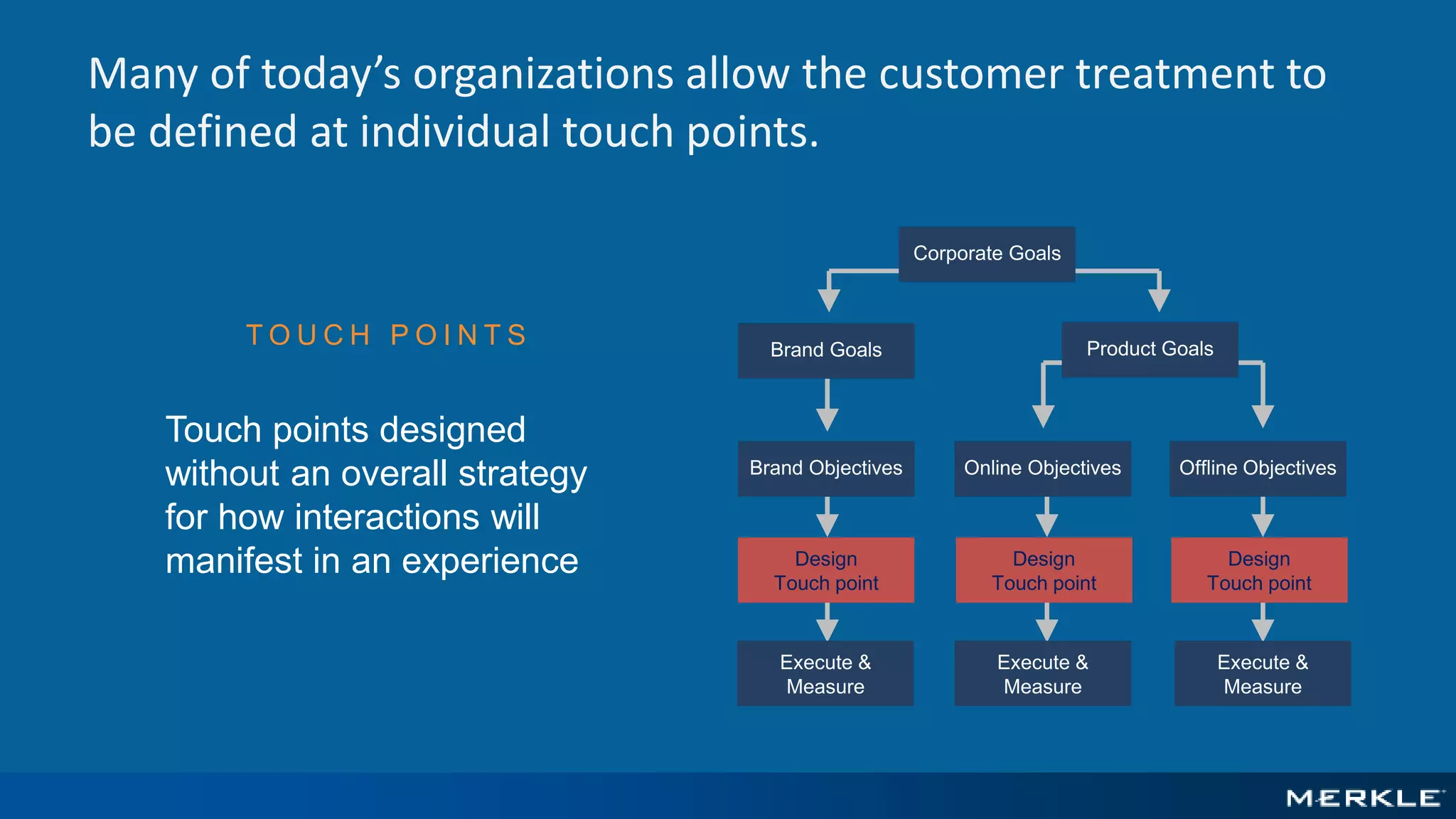
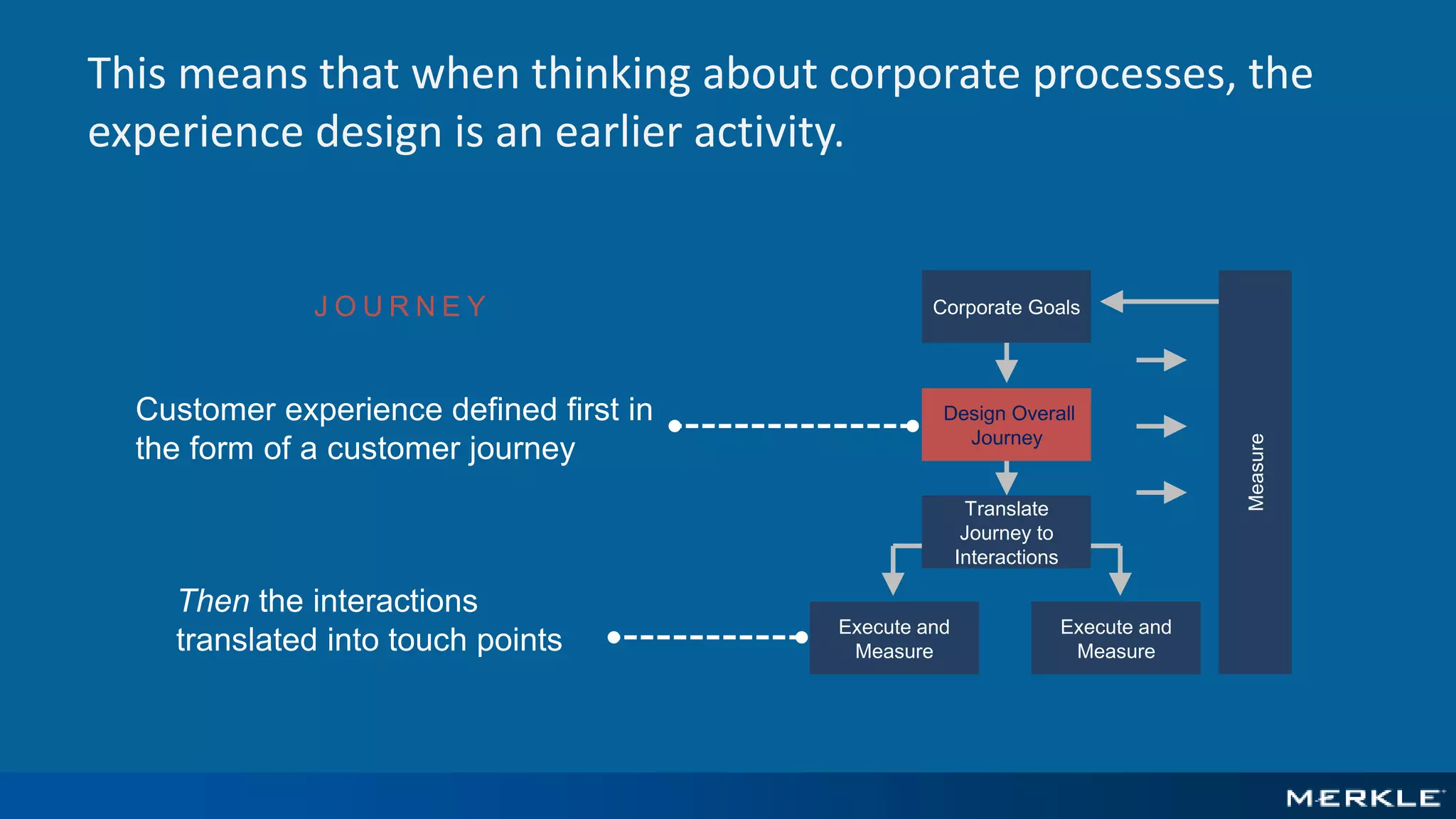
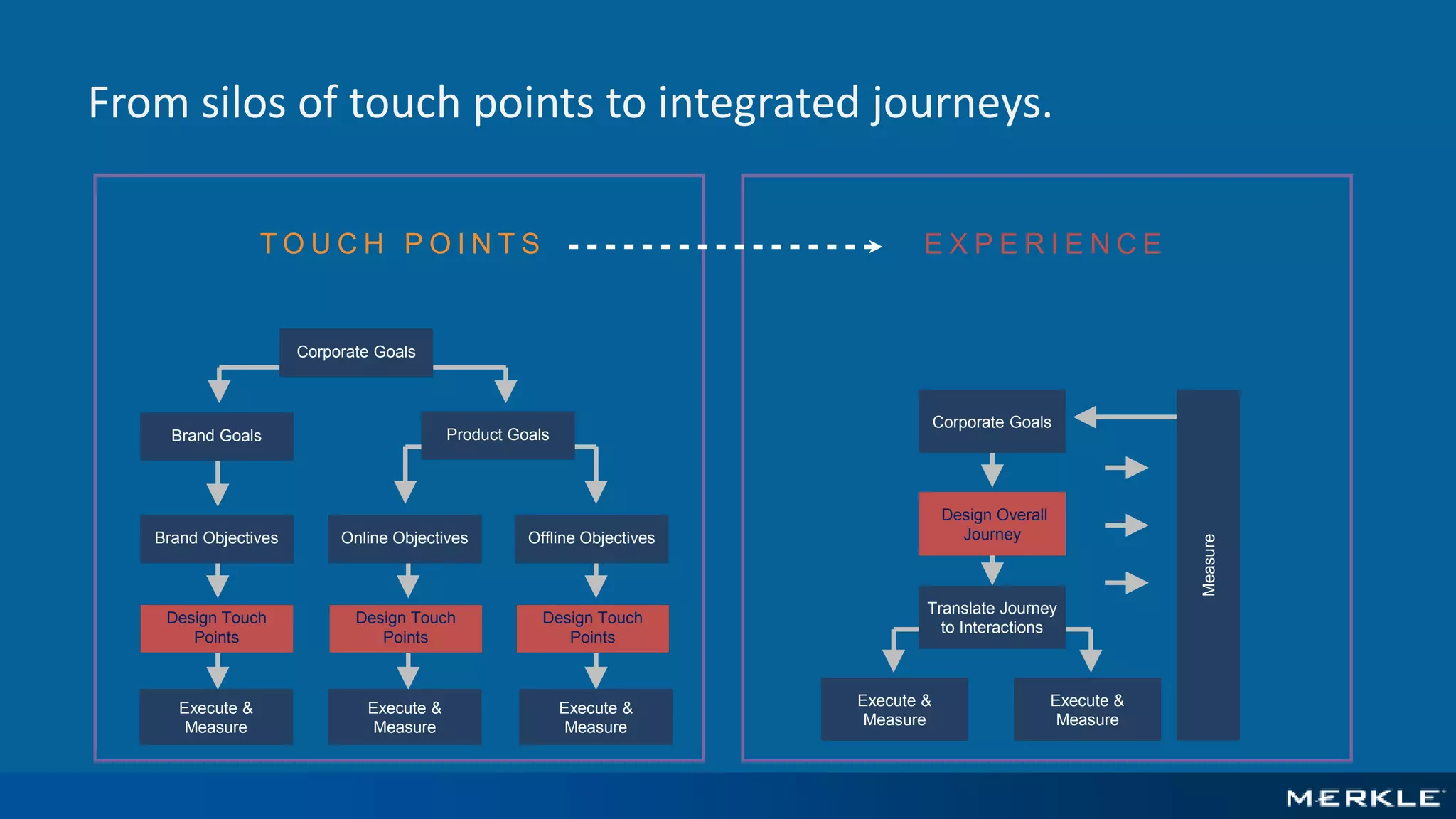
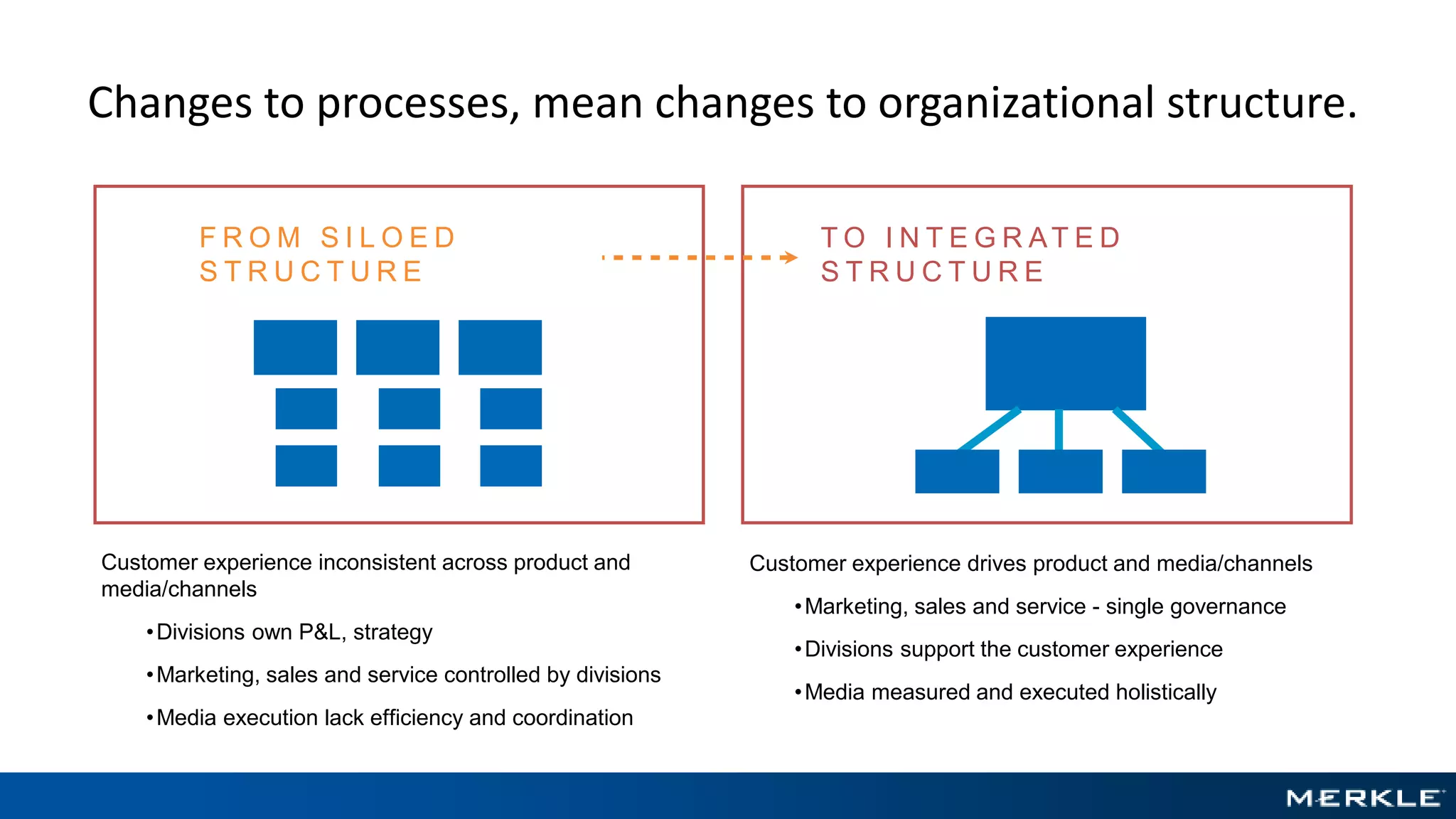
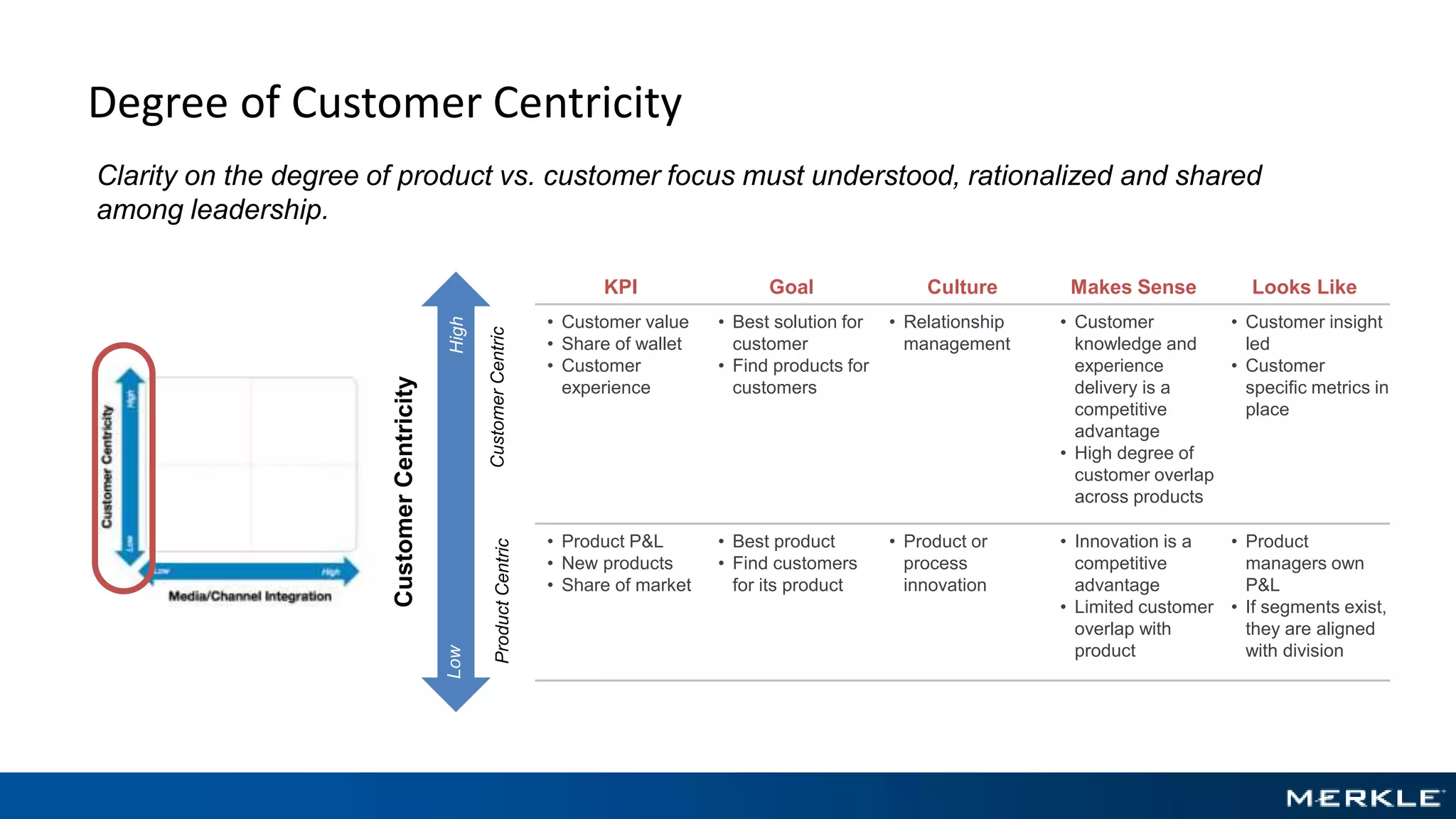
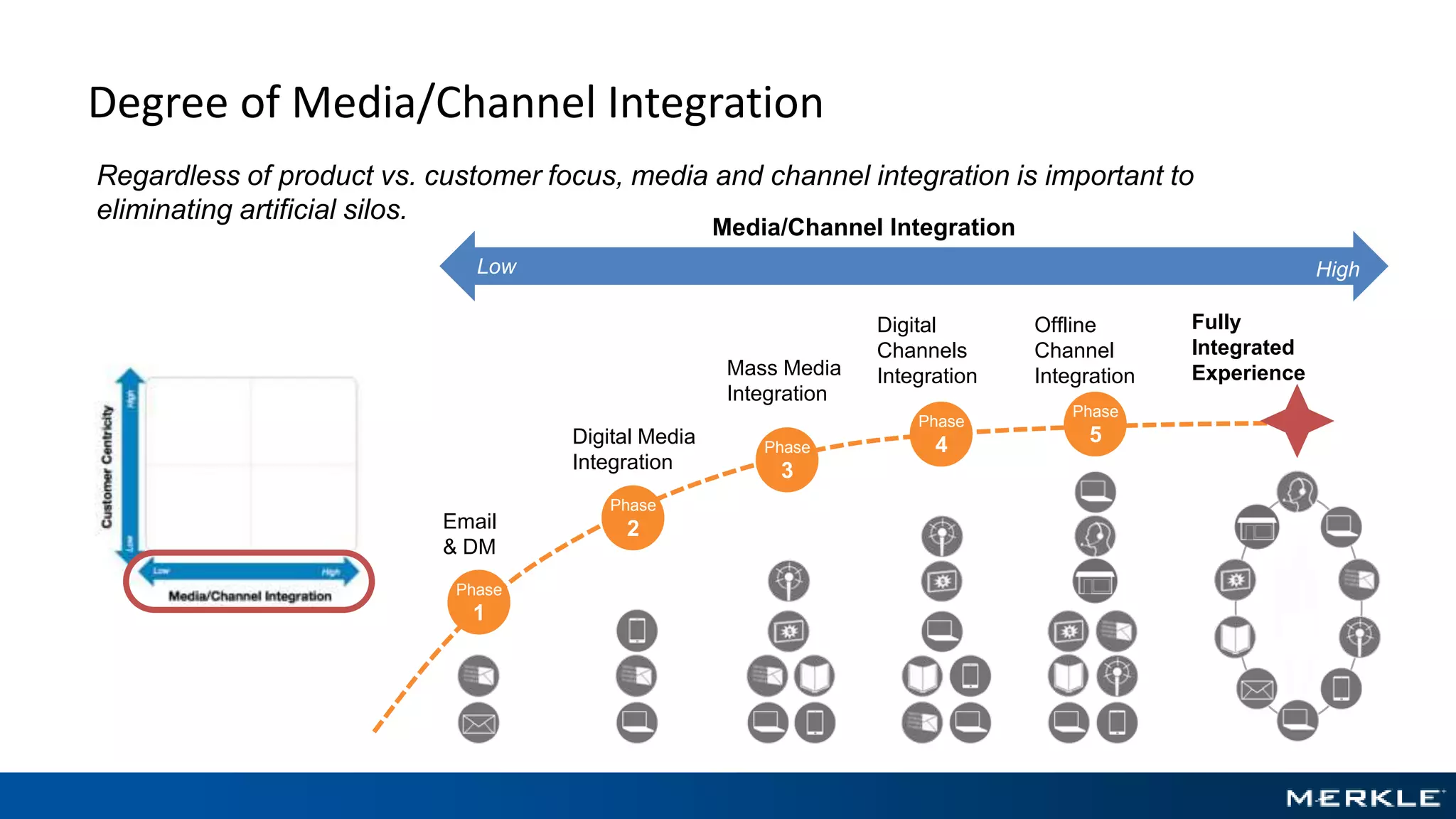
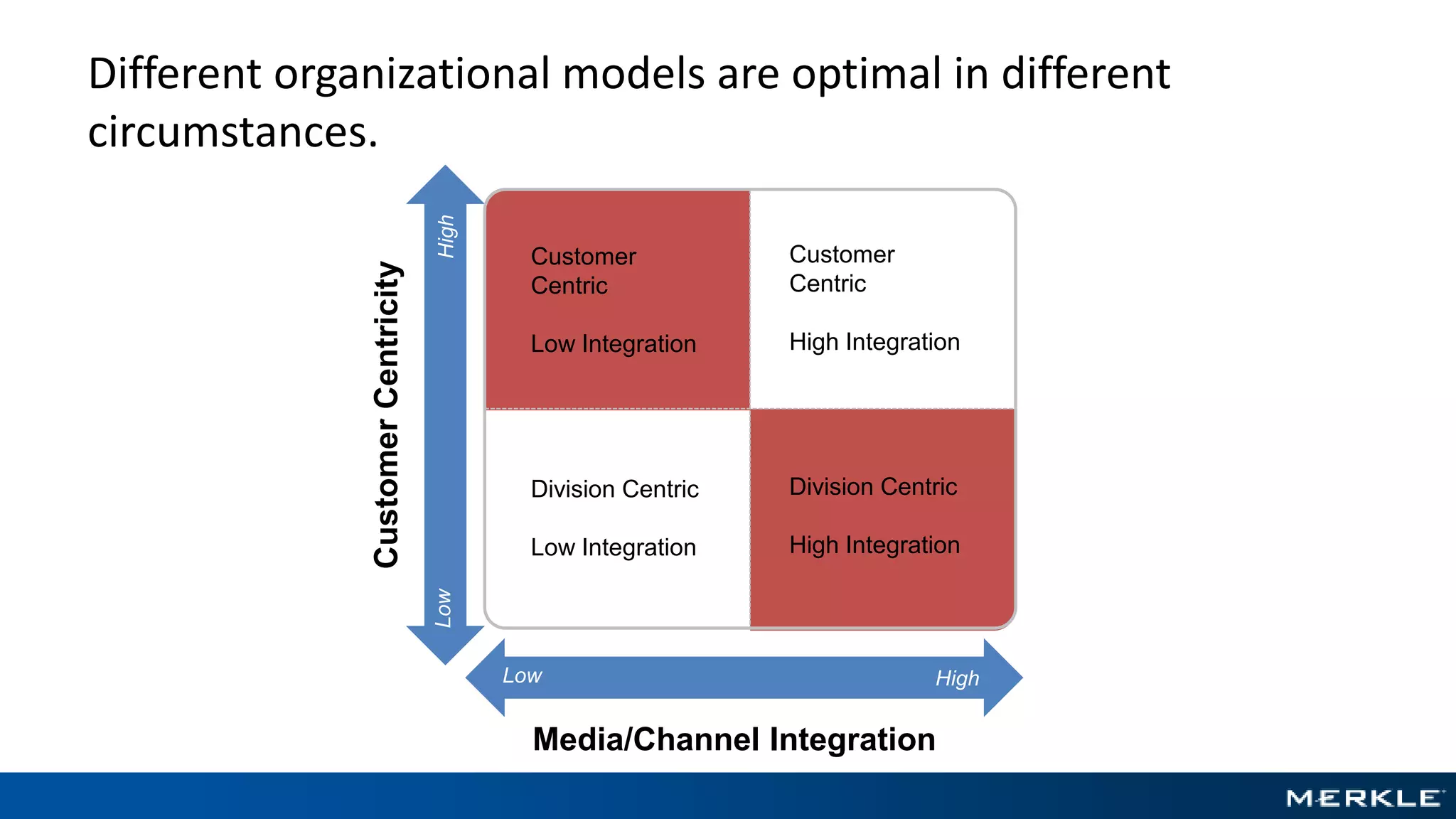
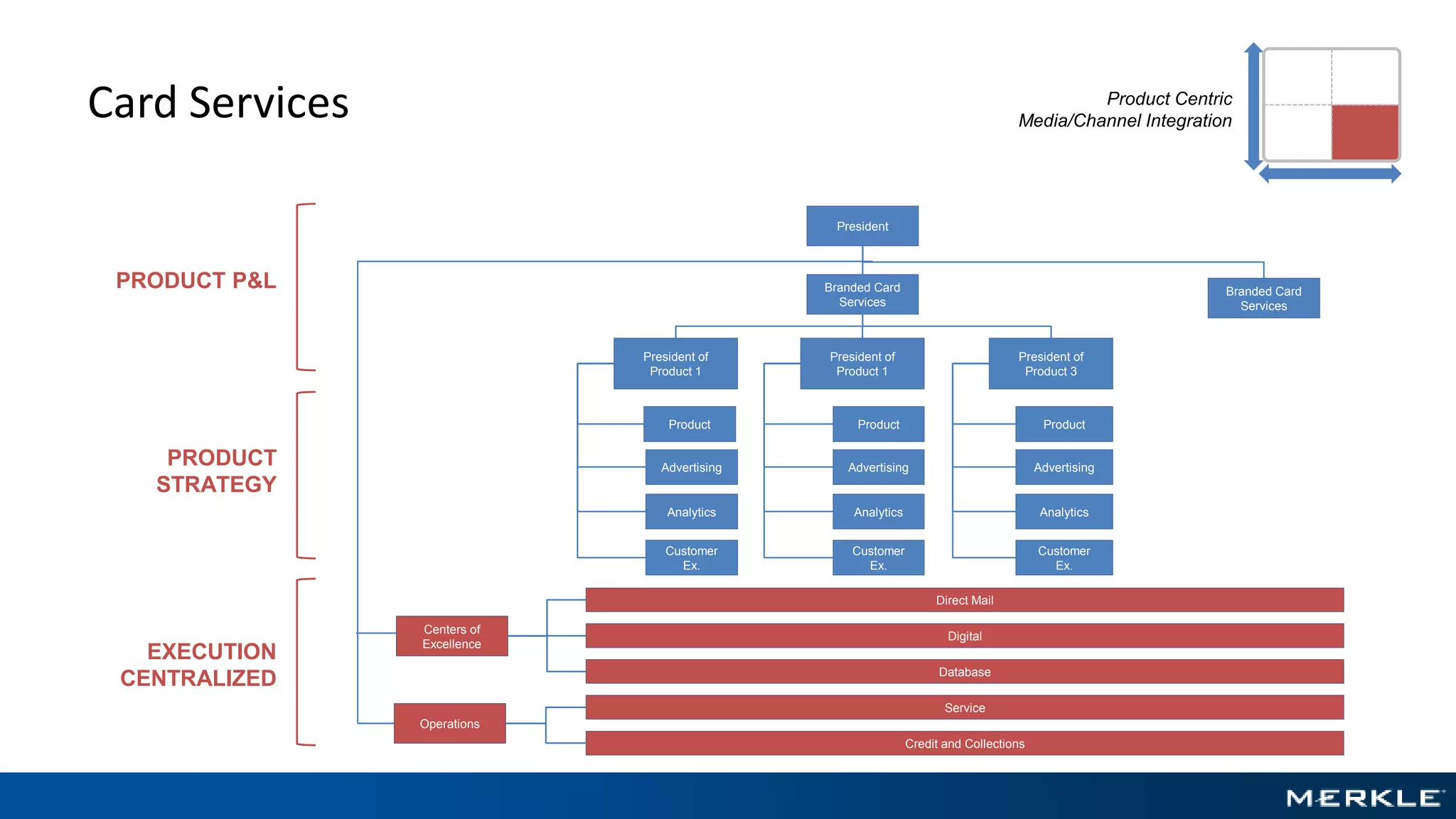
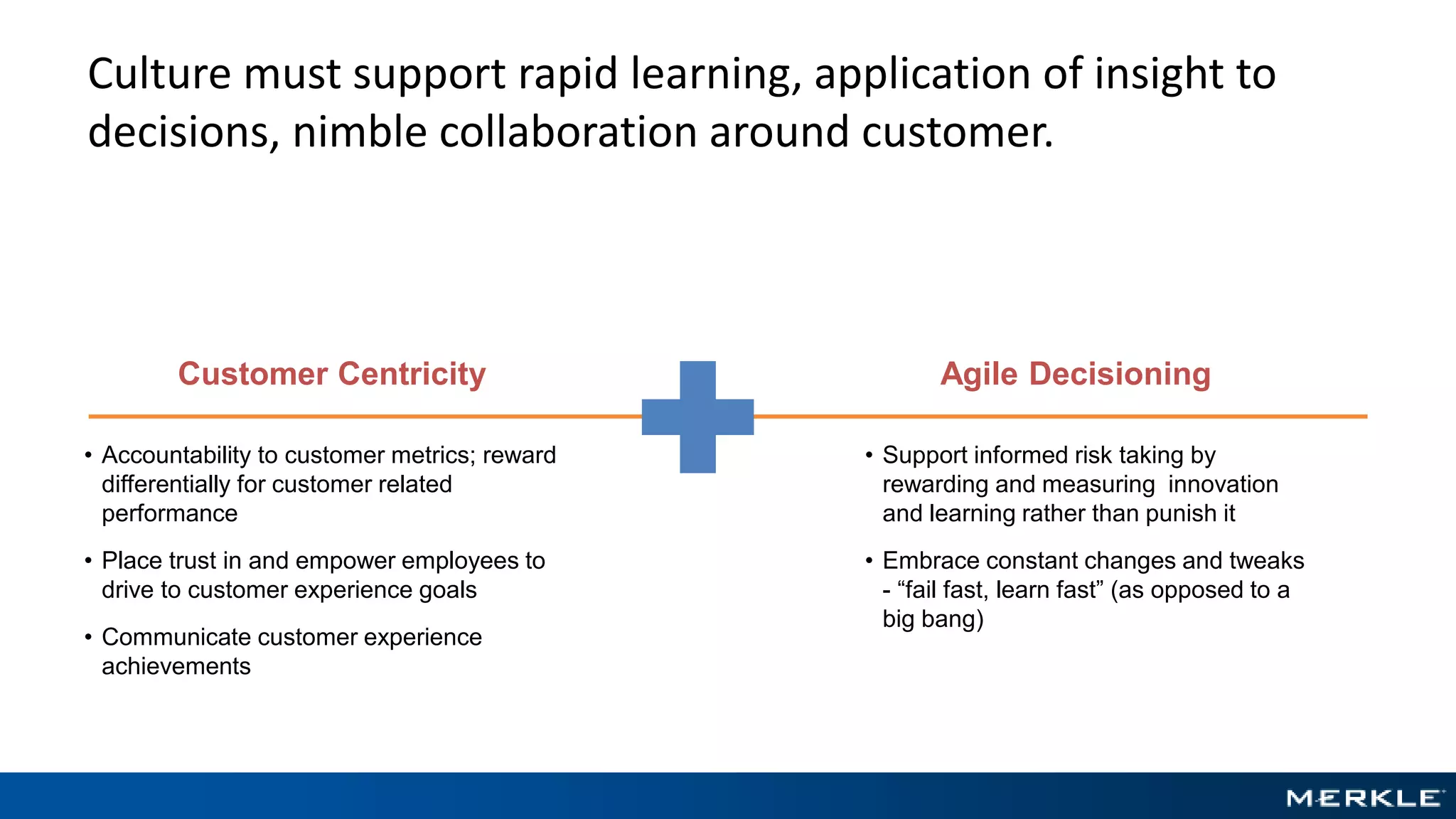
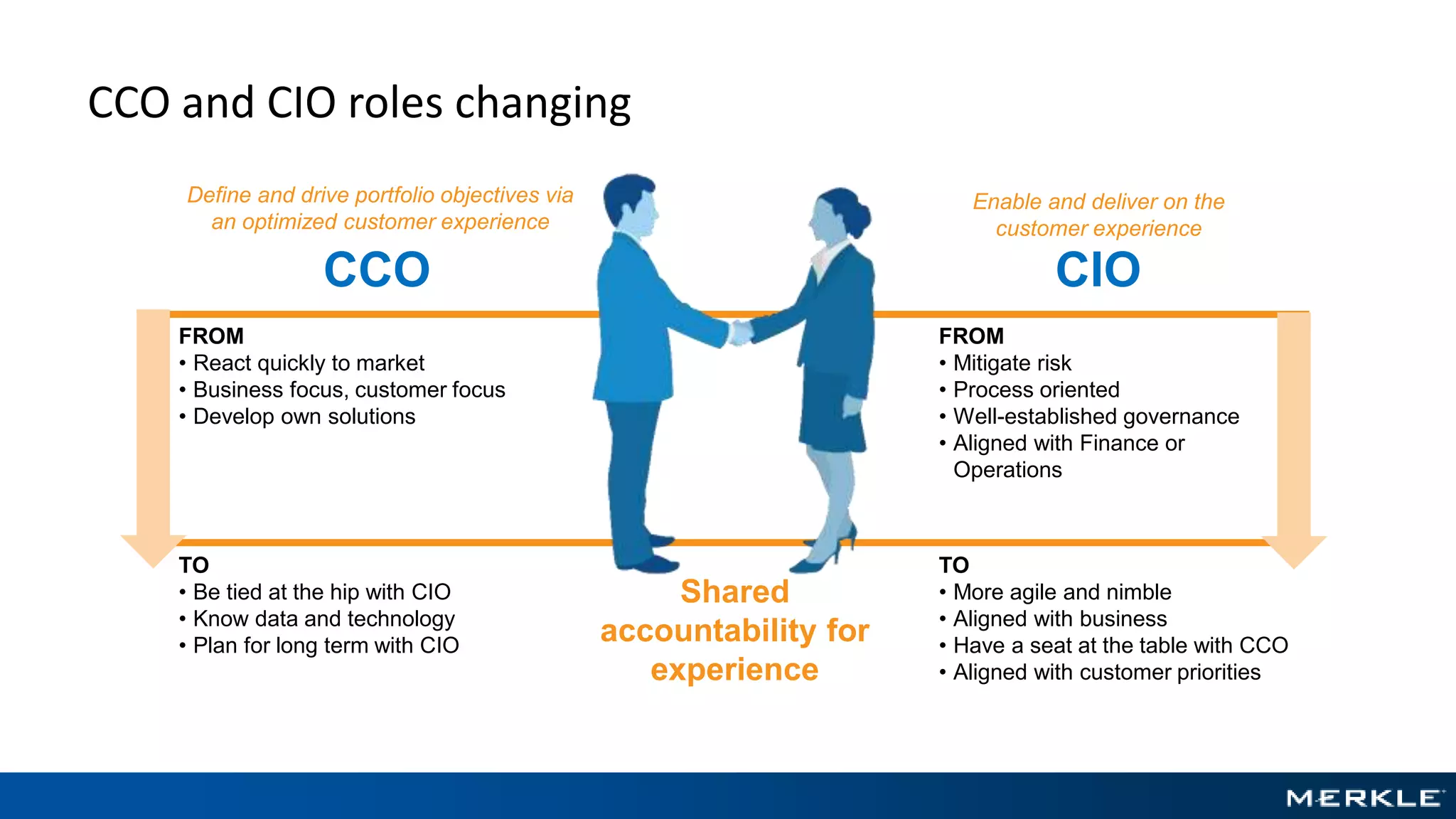
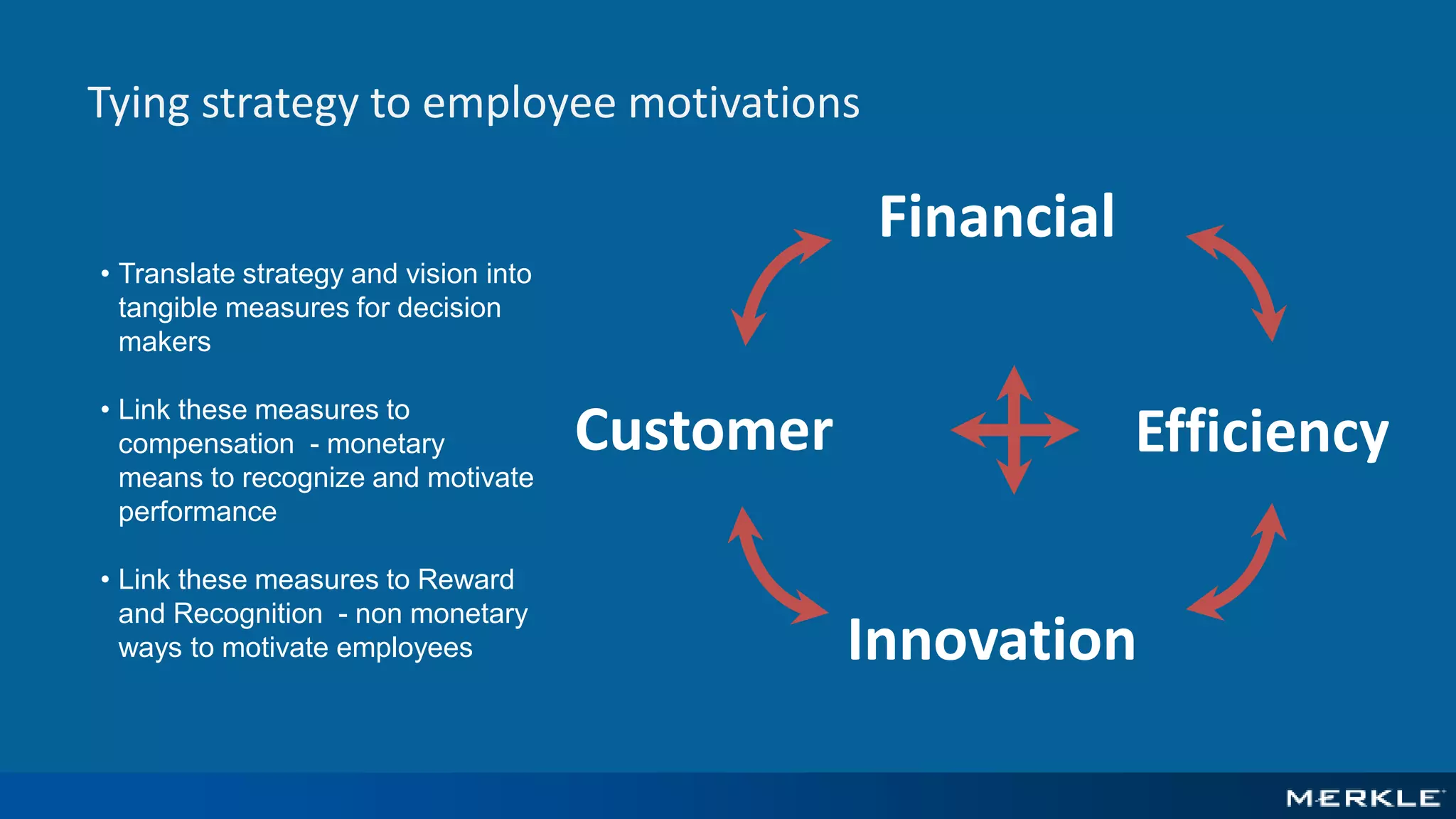
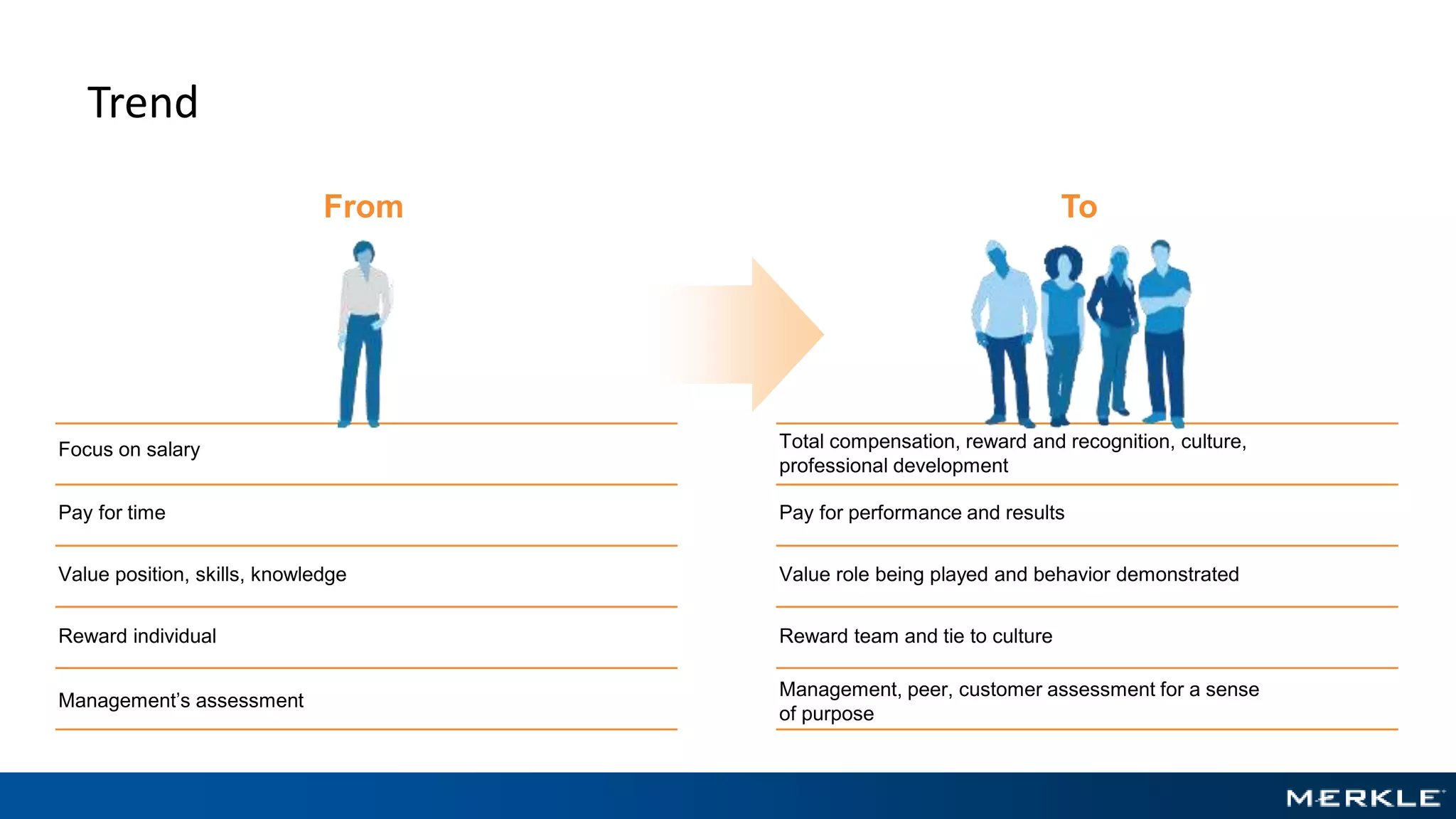
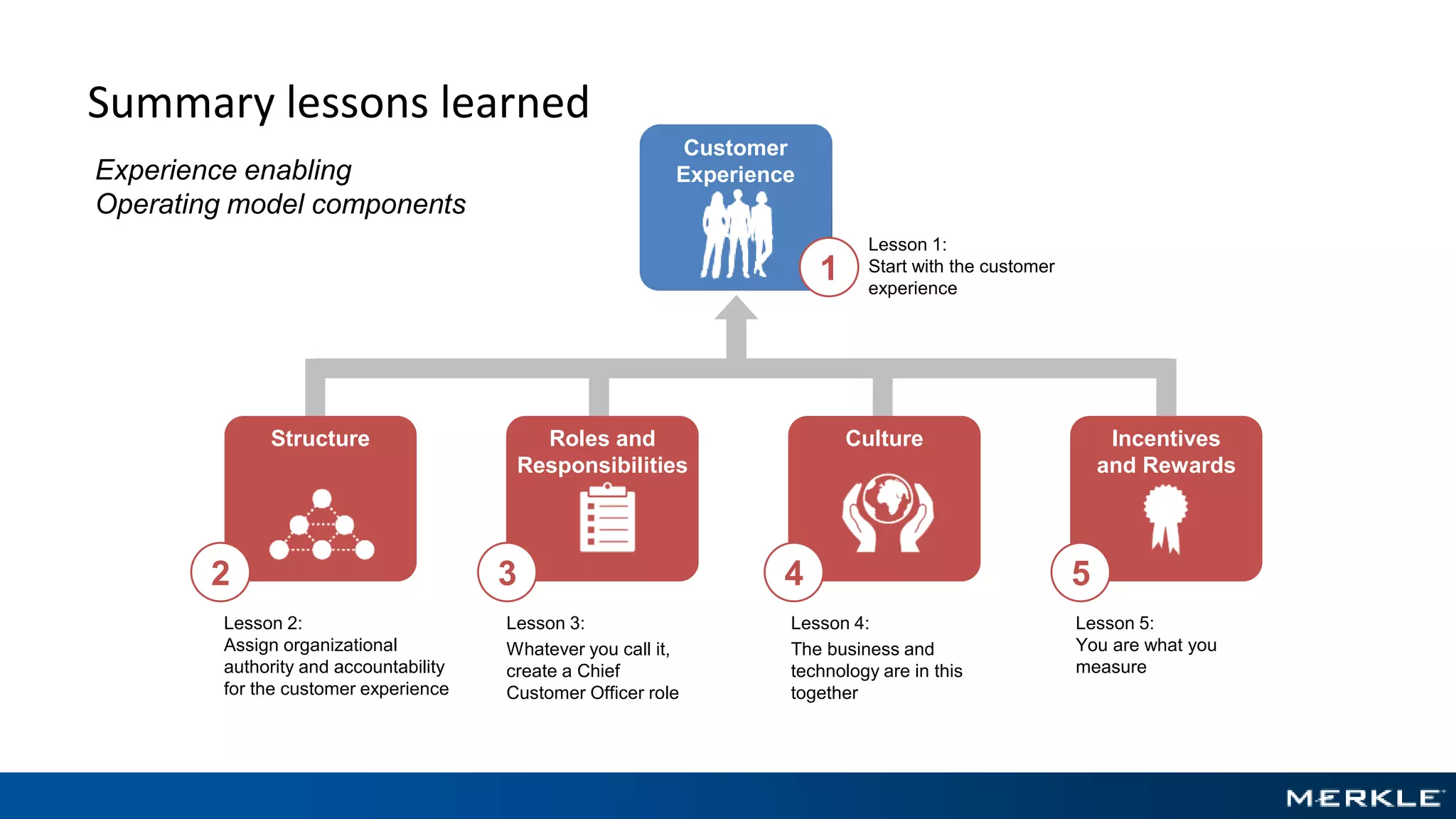
The document emphasizes the importance of establishing a customer-centric organizational strategy to enhance customer experience and drive investment decisions. It discusses the need for a chief customer officer role, accountability for customer experience, and alignment between business and technology. Key lessons include focusing on customer journeys, integrating media channels, and creating metrics that support customer-focused performance.