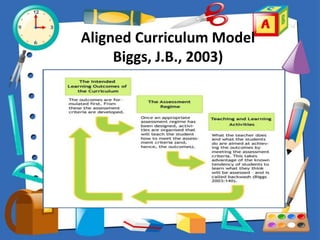
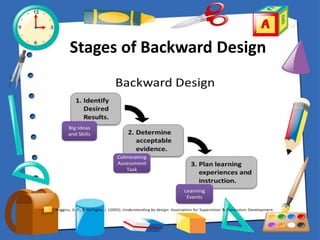
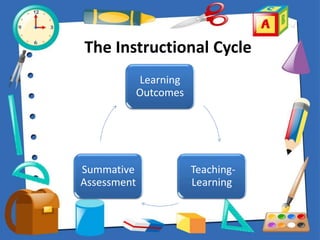
This document discusses outcomes-based education and assessment. It defines outcomes as the skills and competencies students are expected to demonstrate after a learning experience. Outcomes can be immediate or deferred. Constructive alignment is introduced as designing instruction to directly support the achievement of intended learning outcomes. The principles of outcomes-based education emphasize clarity of outcomes, designing learning down from outcomes, high expectations for all learners, and expanded opportunities. Understanding by Design and the instructional cycle are also presented as frameworks that are aligned with outcomes-based approaches.