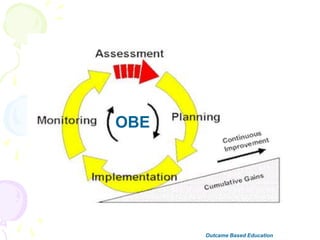
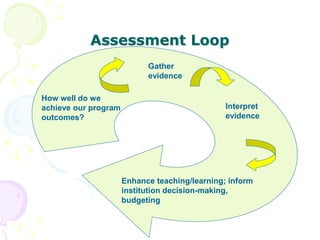
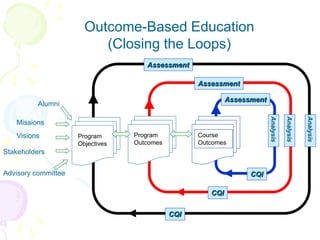
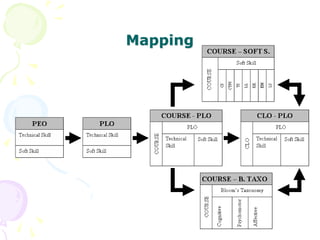
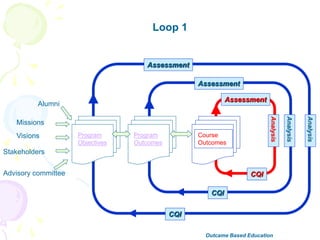
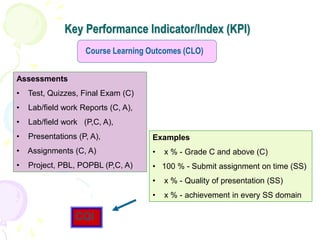
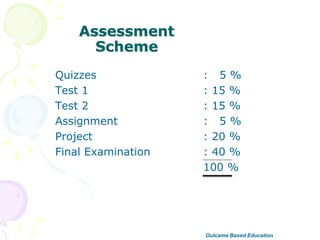
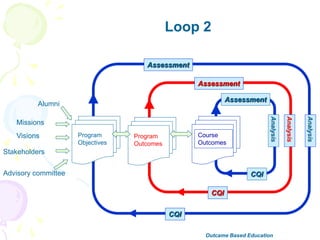
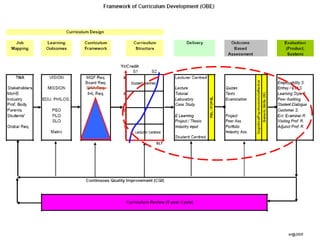
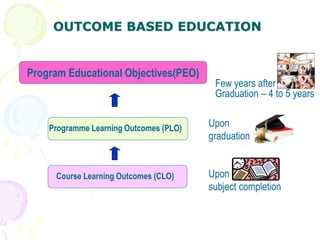
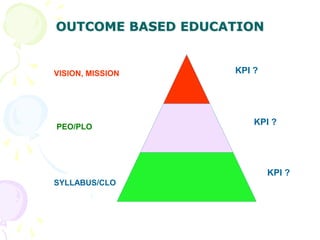
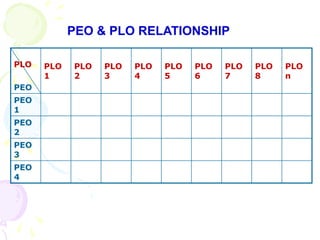
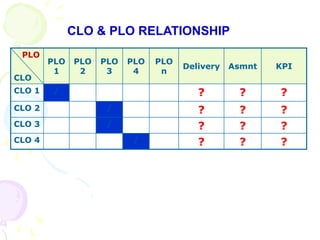
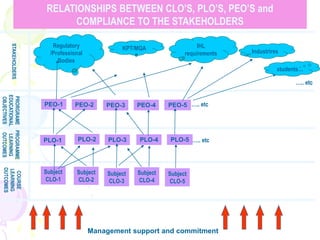
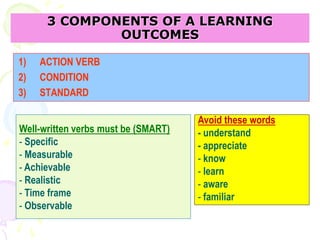
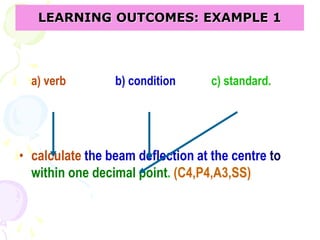
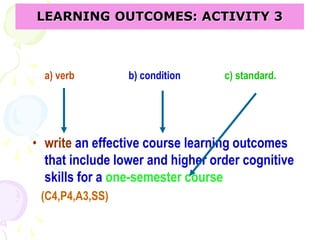
This document discusses outcome-based education (OBE) and related concepts. It defines OBE as focusing on student learning by using learning outcome statements, providing learning activities to help students achieve outcomes, and assessing how well students meet outcomes. It discusses constructive alignment, where teaching methods and assessments are aligned with intended learning outcomes. The document also covers continuous quality improvement (CQI) and closing the assessment loop to enhance teaching/learning based on evidence. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to measure achievement of course, program, and institutional learning outcomes and objectives.











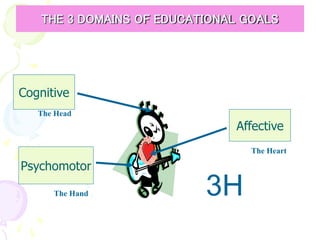
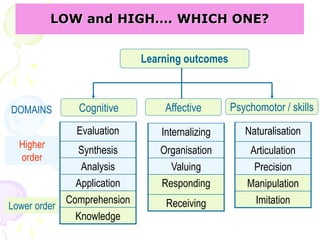
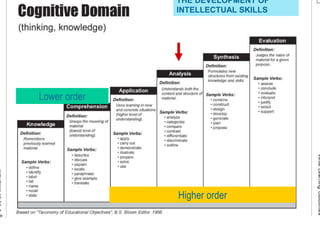
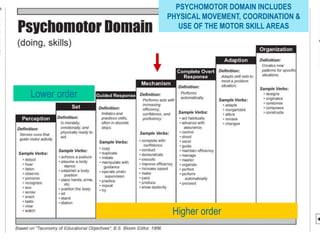








![[ 63 ]
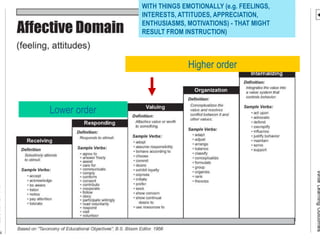
Claus Brabrand (ITU) DMLF Årsmøde 2007 – keynote Sep 20, 2007
Teacher’s
intention
Student’s
activity
Exam’s
assessment
e.g.
- explain
- relate
- prove
- apply
e.g.
- memorize
- describe
UNALIGNED COURSE
e.g.
- memorize
- describe
"Dealing with the test"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obe-240224142809-fb4bc7c8/85/Output-Based-Education-curriculum-in-masters-36-320.jpg)
![[ 64 ]
Claus Brabrand (ITU) DMLF Årsmøde 2007 – keynote Sep 20, 2007
Teacher’s
intention
Student’s
activity
Exam’s
assessment
e.g.
- explain
- relate
- prove
- apply
ALIGNED COURSE
e.g.
- explain
- relate
- prove
- apply
e.g.
- explain
- relate
- prove
- apply
e.g.
- explain
- relate
- prove
- apply
e.g.
- explain
- relate
- prove
- apply](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obe-240224142809-fb4bc7c8/85/Output-Based-Education-curriculum-in-masters-37-320.jpg)