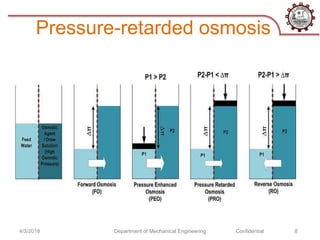
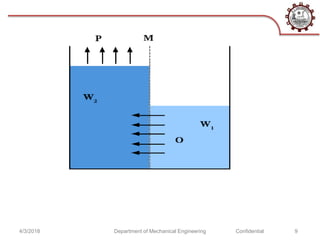
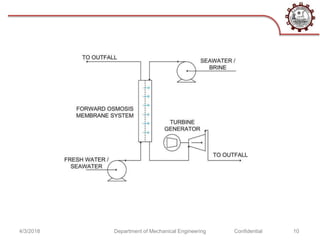
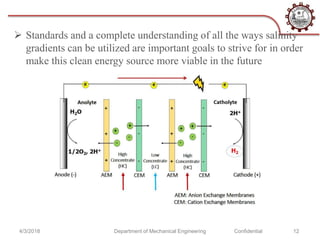
The document discusses osmotic power generation through salinity gradient power. It describes two main methods - pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) and reverse electrodialysis. PRO involves pumping seawater and freshwater into a pressure chamber separated by a membrane, where the pressure differences drive a turbine. Reverse electrodialysis uses a series of alternating cation and anion exchange membranes to generate electricity from the free energy of river and seawater. While still being researched, these methods harness the natural process of osmosis to generate renewable energy from salinity gradients between fresh and salt water sources.