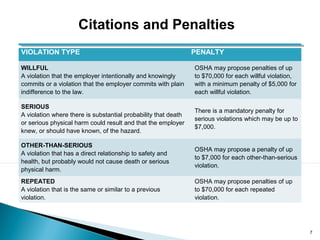
This document discusses preparing for an OSHA inspection at a recycling facility. It outlines common exposures in the recycling industry like hazards from equipment operation and chemical handling. It provides statistics on OSHA inspections and violations. The document advises having proper documentation of training programs and safety policies, and knowing how to interact with OSHA during an inspection, including accompanying the inspector and not interfering with employee interviews.