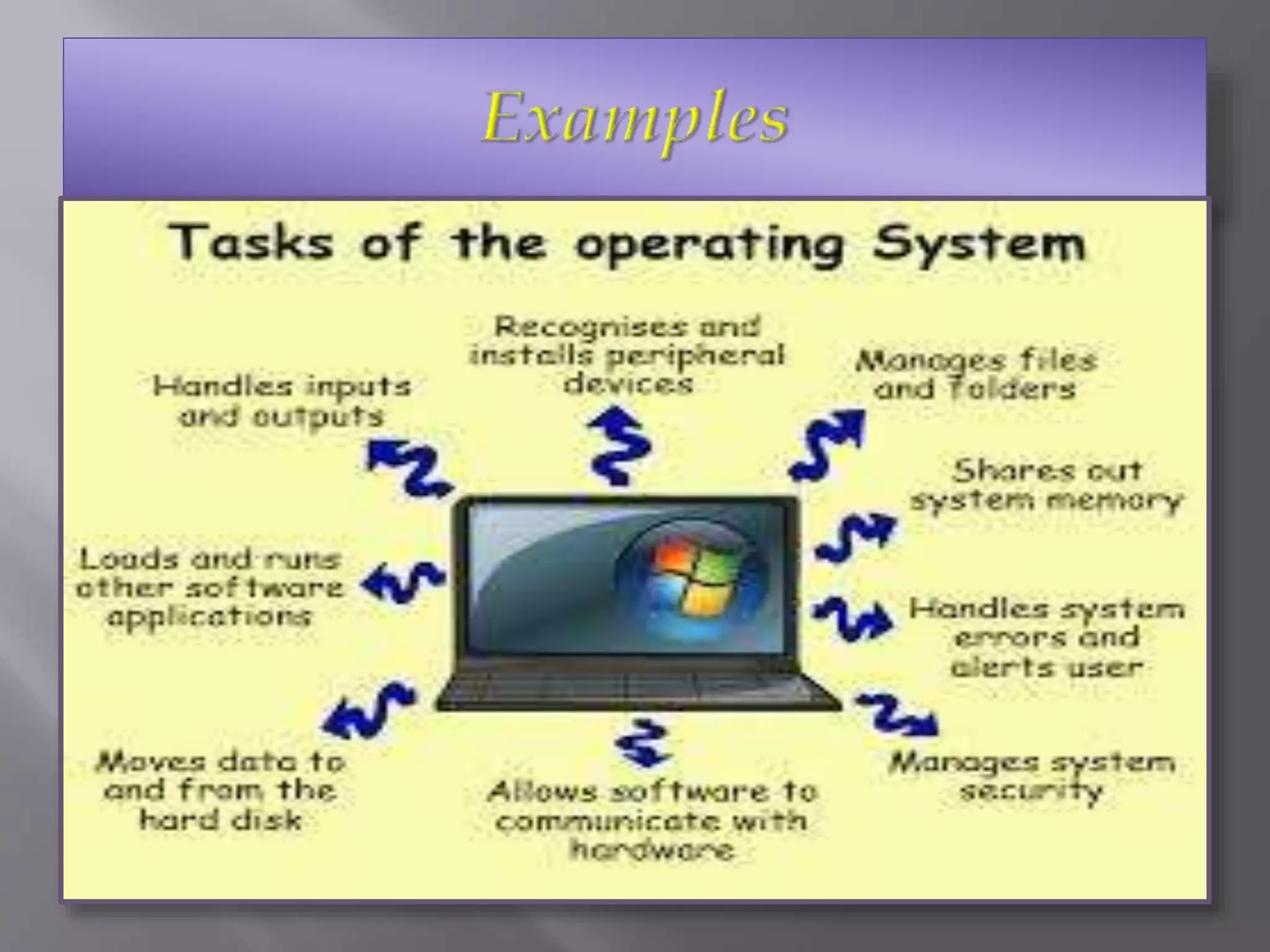
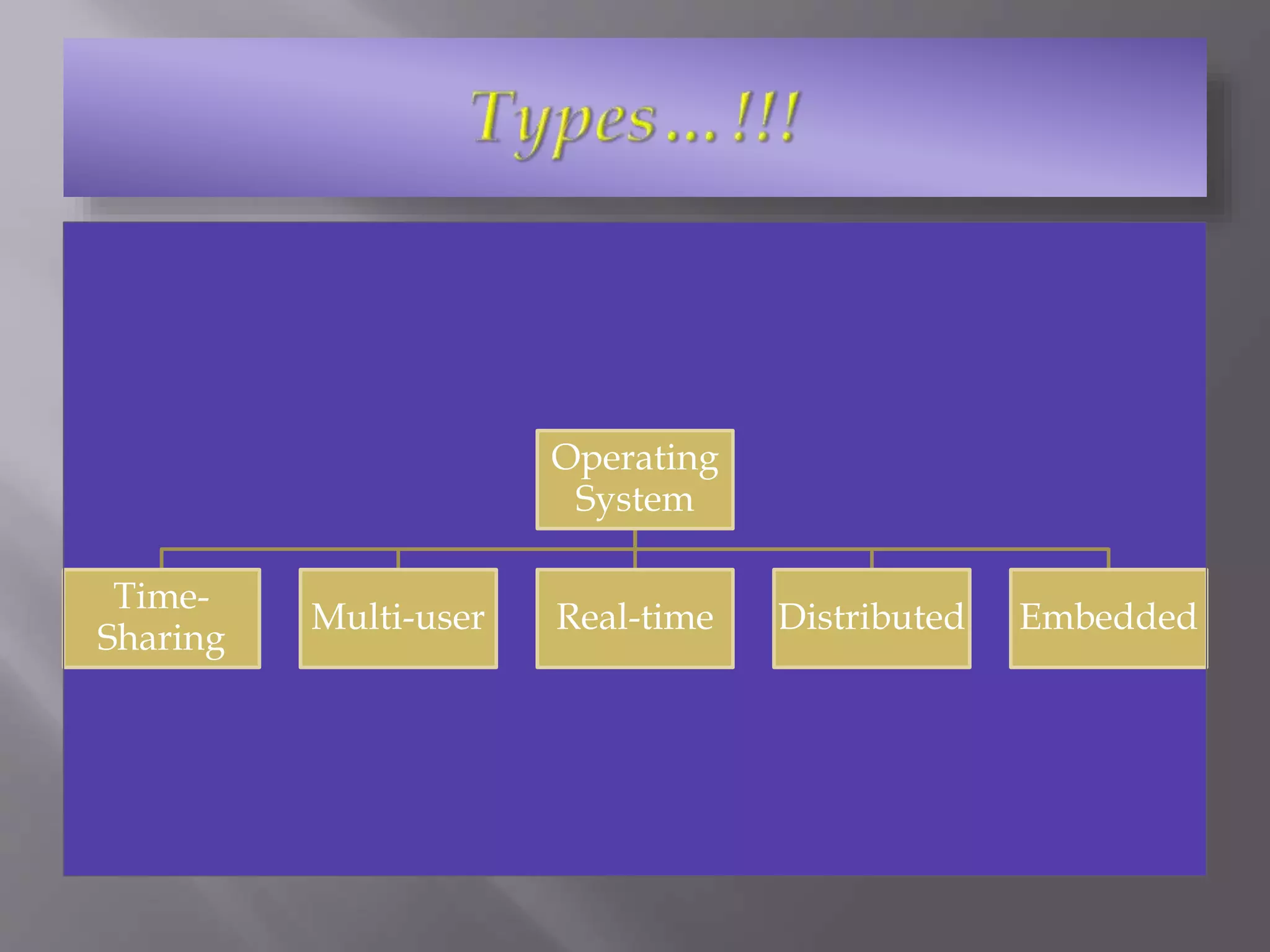
An operating system (OS) manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services to programs. Gary Kildall developed the first PC operating system, which was text-based, and he pioneered operating systems by making his OS hardware-independent. The OS is essential software that allows computers to interact with users and run other applications. Common types of operating systems include time-sharing, multi-user, real-time, distributed, and embedded OSs. Key OS components are the kernel, networking, security, and user interface. Popular past and present OSs include DOS/360, Mac OS, UNIX, Linux, Windows, Android, iOS.