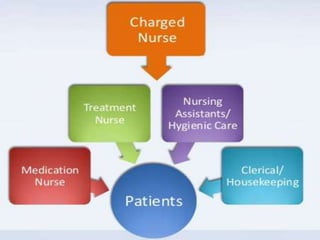
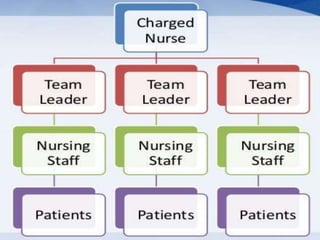
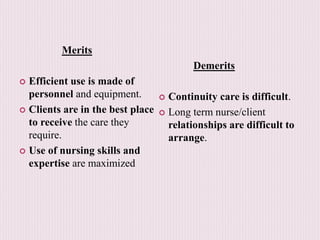
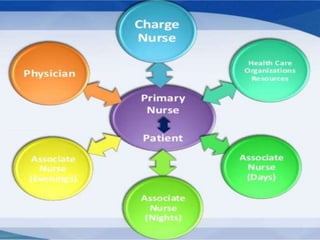
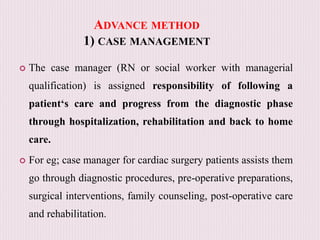
The document outlines the organization and administration of nursing services and patient care, emphasizing the importance of high-quality care for hospitals to fulfill their responsibilities. It discusses the objectives of nursing service, including patient care, education, administration, research, and performance appraisal, while also detailing various methods of organizing patient care. It concludes by highlighting the critical role of nurses in healthcare and the need for systematic organization to enhance service quality.


![I ] ORGANIZING NURSING
SERVICES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organzingnsgservices-240427133734-7d4489fc/85/organizing-nursing-patient-assignment-pptx-3-320.jpg)














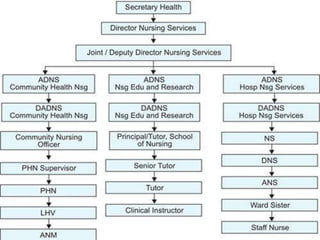
![1] ORGANIZATIONAL SET-UP OF NURSING
SERVICE AT CENTRAL LEVEL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organzingnsgservices-240427133734-7d4489fc/85/organizing-nursing-patient-assignment-pptx-18-320.jpg)
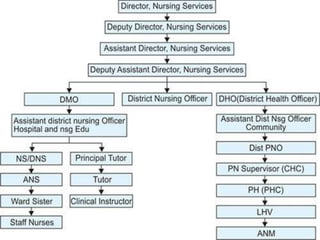
![2] ORGANIZATIONAL SET-UP OF NURSING
SERVICE AT STATE LEVEL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organzingnsgservices-240427133734-7d4489fc/85/organizing-nursing-patient-assignment-pptx-20-320.jpg)





![II] ORGANIZING PATIENT
CARE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organzingnsgservices-240427133734-7d4489fc/85/organizing-nursing-patient-assignment-pptx-28-320.jpg)