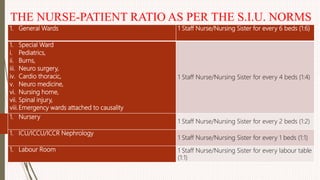
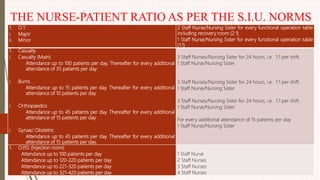
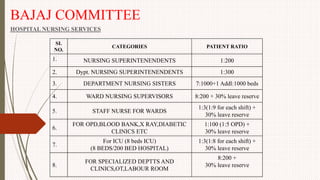
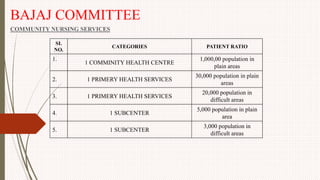
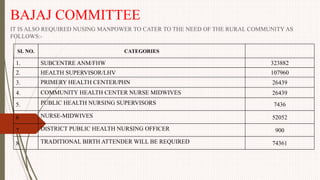
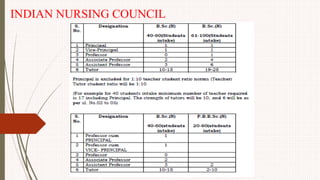
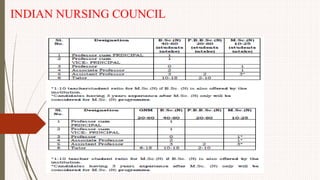
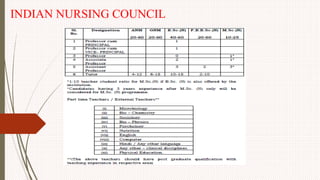
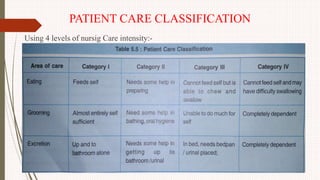
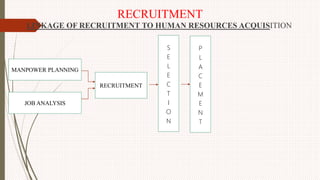
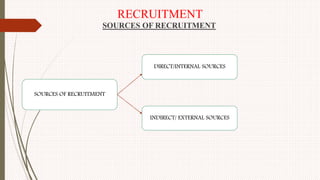
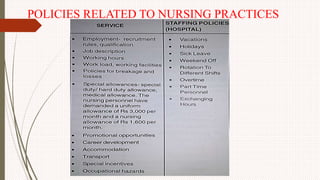
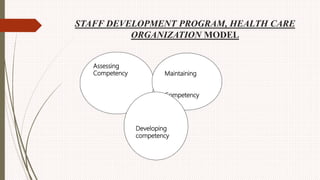
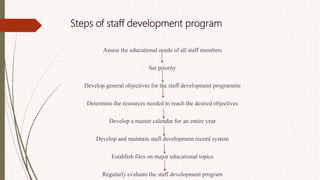
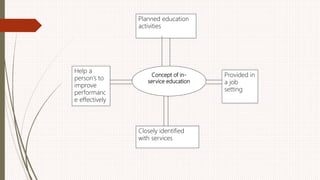
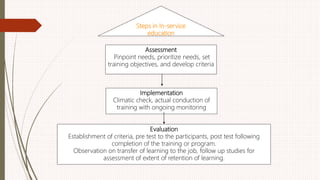
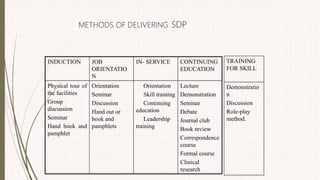
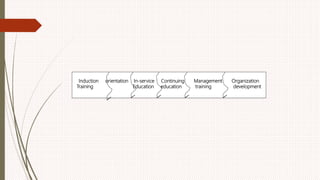
The document outlines the philosophy, norms, and processes of staffing in nursing, emphasizing the systematic approach to recruiting, training, and retaining nursing personnel to meet patient care demands. It includes recommendations from various committees on staffing ratios, employment standards, working conditions, and nursing education. Furthermore, it addresses the need for improved infrastructure and policies to enhance the effectiveness and quality of nursing services in healthcare settings.