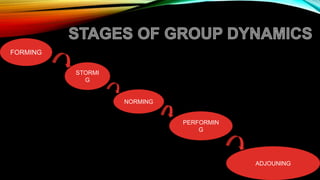
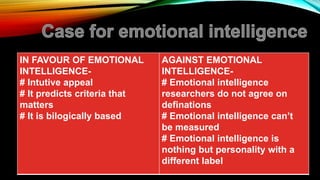
The document discusses interpersonal skills, group dynamics, and emotional intelligence. It defines these terms and discusses their importance. Interpersonal skills include communication, social and cooperation abilities. Group dynamics examines how groups are formed and function. Emotional intelligence involves recognizing one's own and others' emotions to guide thinking and actions. Developing interpersonal skills, understanding group dynamics, and increasing emotional intelligence can help managers and organizations succeed.