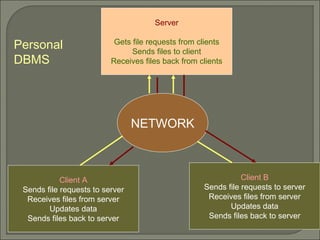
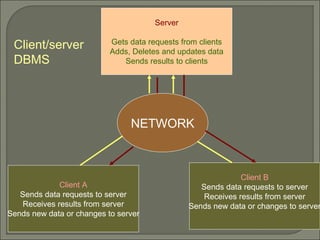
This document provides an overview of personal and client/server database management systems (DBMS). It discusses the differences between the two approaches, including that personal DBMSs place more demand on clients and networks while client/server DBMSs are more fault tolerant and perform table locking automatically. The document also provides examples of SQL commands and a PL/SQL stored procedure example.





![Sqlplus username/password
ALTER USER user-name IDENTIFIED BY newpassword
START filename | @ filename
CLEAR SCREEN
HELP <command>
SAVE filename[.ext] REPLACE|APPEND
EXIT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclesql-140429120747-phpapp01/85/Oracle-PL-SQL-8-320.jpg)


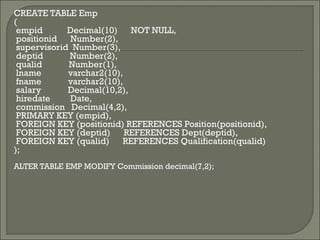
![Data Definition Language:
CREATE TABLE {table}
( {column datatype [DEFAULT expr]
[column_constraint] ... | table_constraint}
[, { column datatype [DEFAULT expr]
[column_constraint] ...
)
ALTER TABLE {table}
[ADD|MODIFY {column datatype [DEFAULT expr] [column_constraint]}
[DROP drop_clause]
DROP TABLE {table} [cascade constraints]
DESC {table}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclesql-140429120747-phpapp01/85/Oracle-PL-SQL-12-320.jpg)
![Data Manipulation Language:
INSERT INTO {table | view} [ (column [, column] ...) ]
VALUES (expr,expr ...)
UPDATE {table | view }
SET { (column [, column] = { expr | }
[WHERE condition]
DELETE [FROM] {table | view} [WHERE condition]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclesql-140429120747-phpapp01/85/Oracle-PL-SQL-14-320.jpg)

![Data Retrieval:
SELECT [DISTINCT | ALL] {table|view}
FROM {table | view}
[WHERE condition ]
[GROUP BY expr [, expr]]
[ORDER BY {expr} [ASC | DESC]]
select * from dept;
select deptname from dept where deptid='10';
select lname,fname from emp order by lname desc;
select max(salary) from emp group by positionid;
select deptname from dept,emp where
dept.deptid=emp.deptid and emp.empid='111';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclesql-140429120747-phpapp01/85/Oracle-PL-SQL-16-320.jpg)
![Transaction Control:
COMMIT
ROLLBACK [ to {savepoint}]
SAVEPOINT {name}
commit;
savepoint point1;
rollback to point1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclesql-140429120747-phpapp01/85/Oracle-PL-SQL-17-320.jpg)
![Data Control Language:
GRANT [privileges]
ON object TO user|public
[WITH GRANT OPTION]
REVOKE [privileges]
ON object TO user|public
[CASCADE CONSTRAINTS]
grant select,update on emp to XYZ ;
revoke update on emp to XYZ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclesql-140429120747-phpapp01/85/Oracle-PL-SQL-18-320.jpg)
