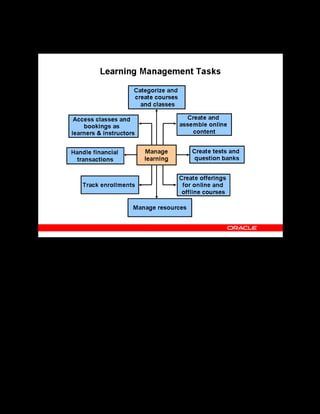
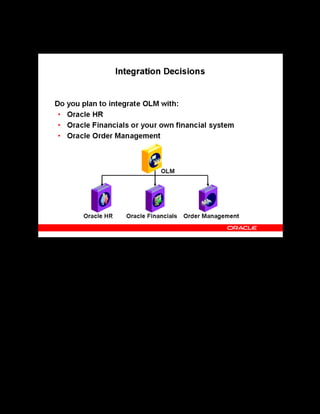
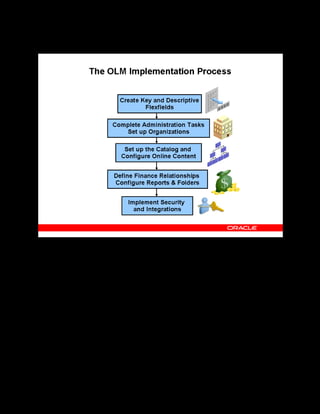
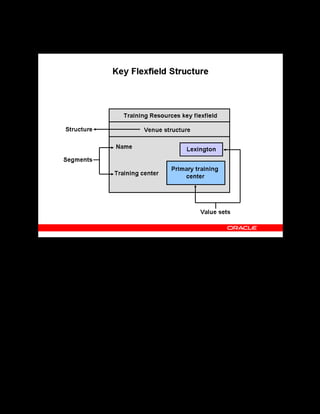
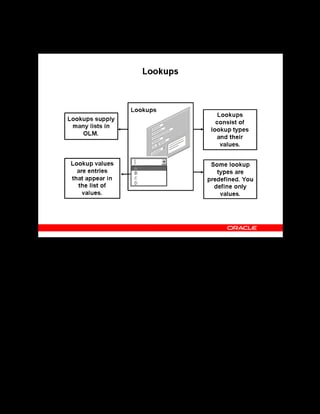
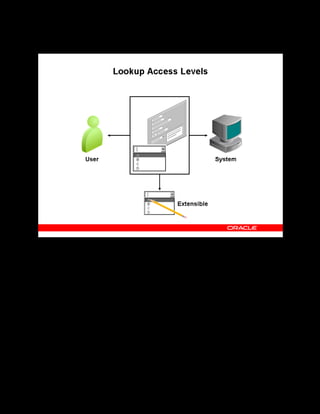
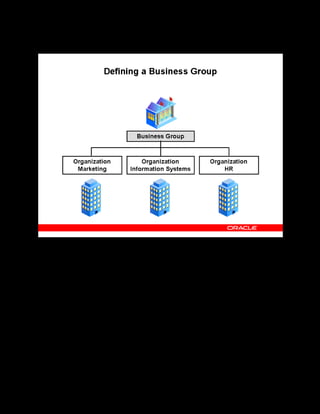
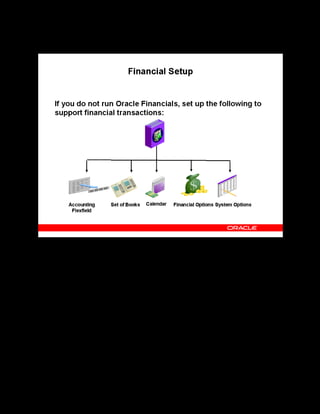
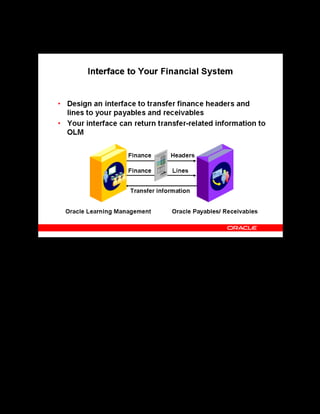
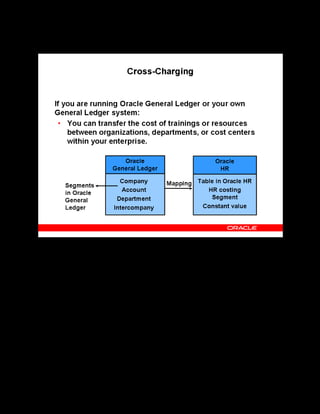
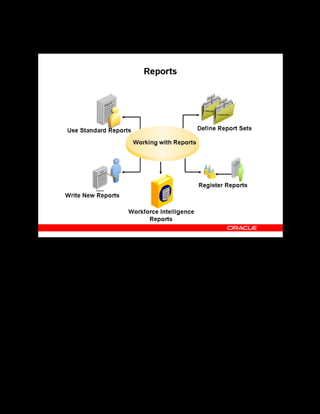
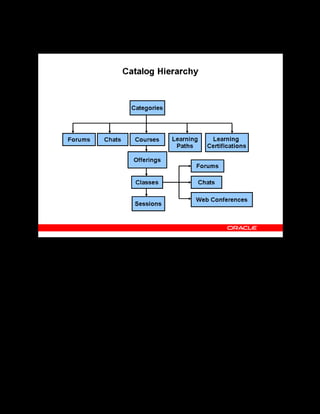
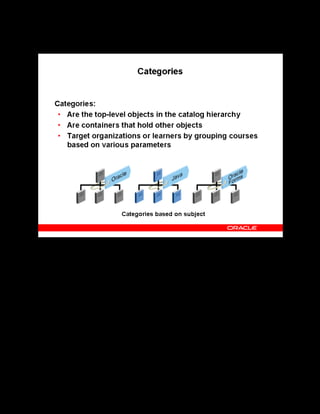
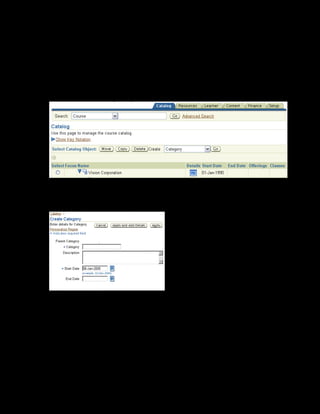
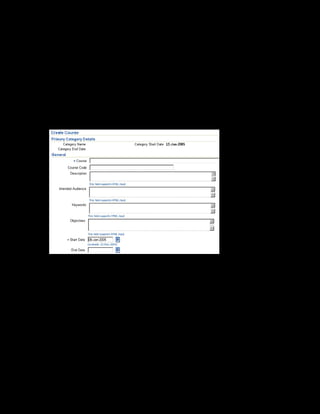
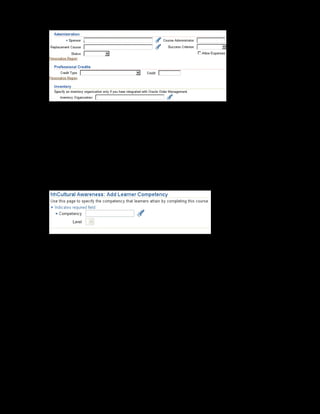
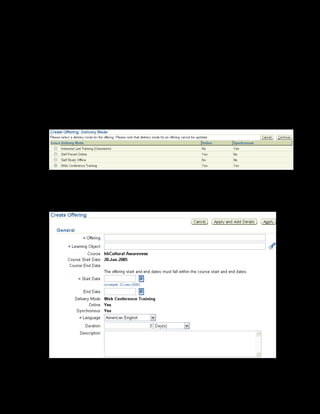
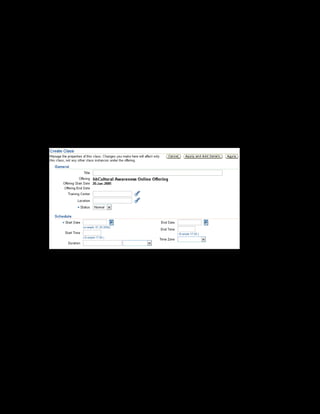
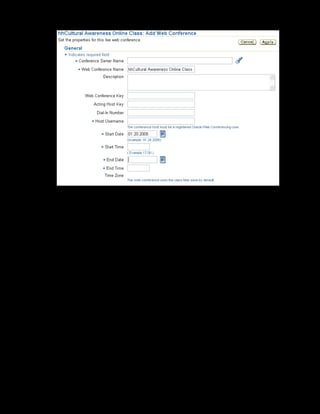
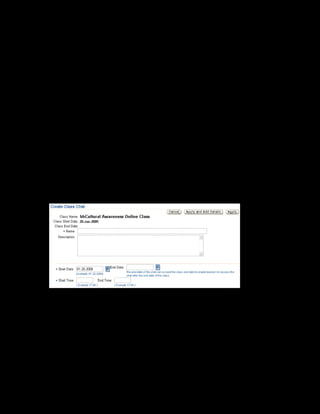
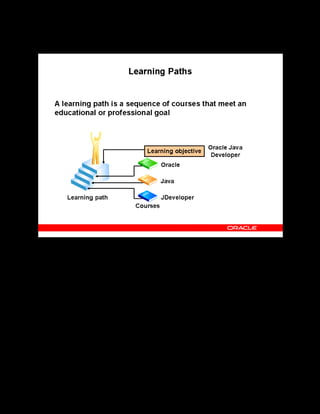
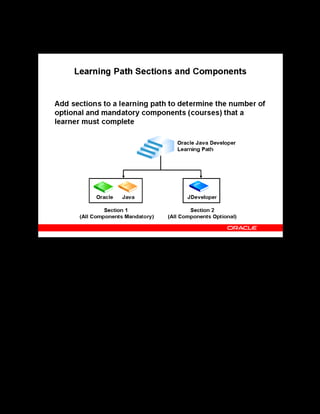
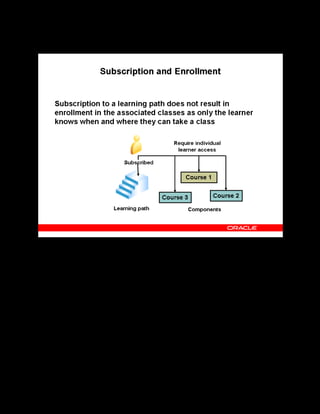
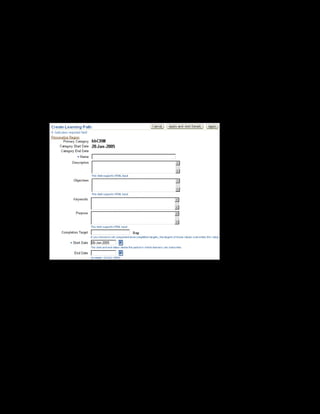
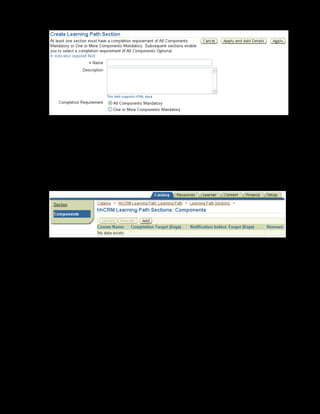
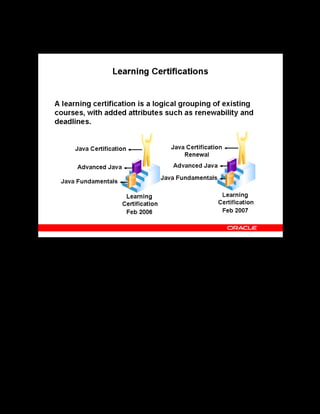
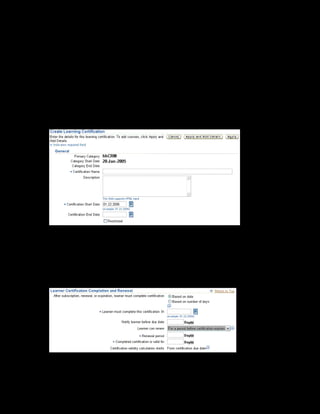
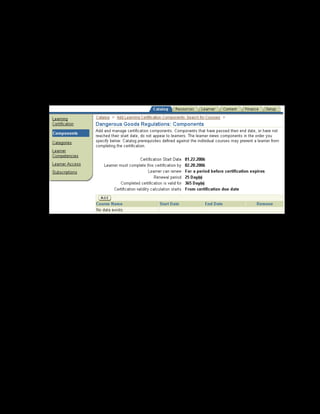
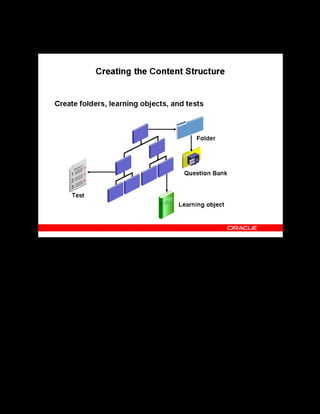
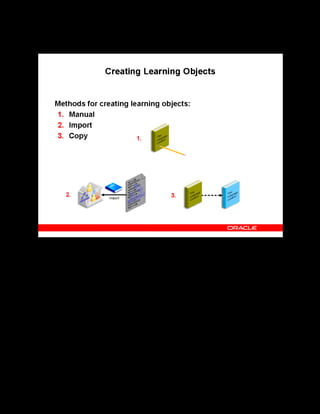
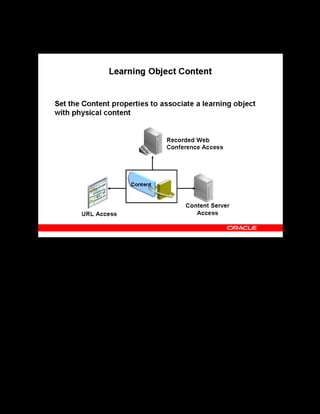
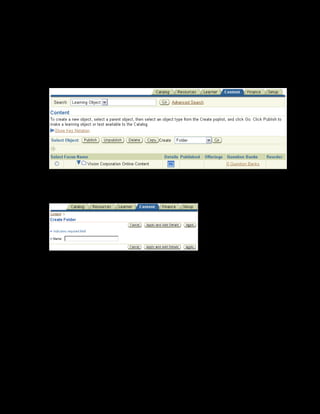
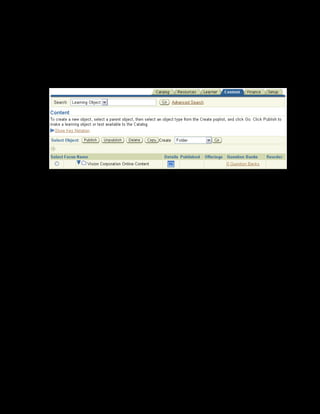
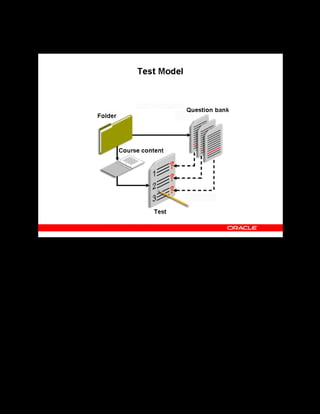
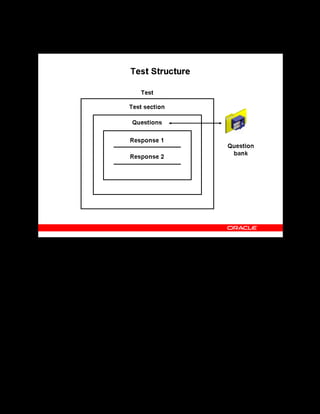
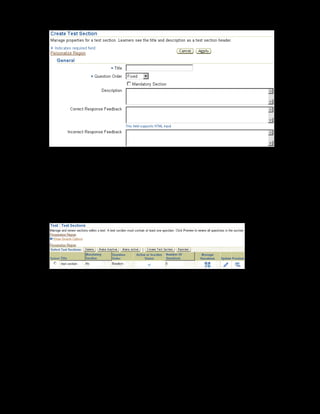
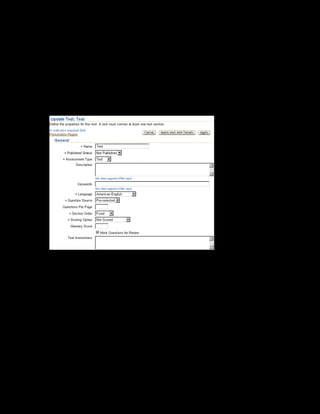
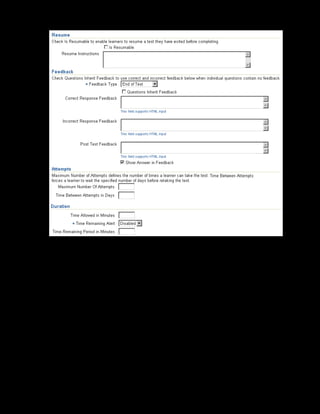
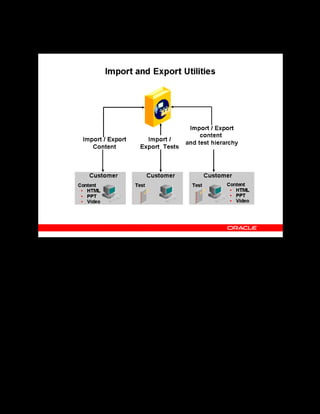
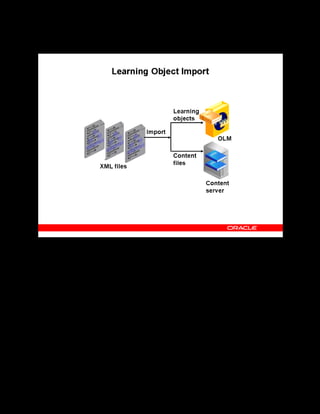
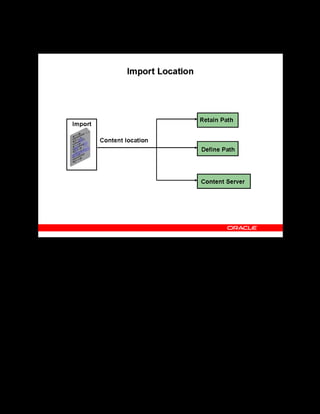
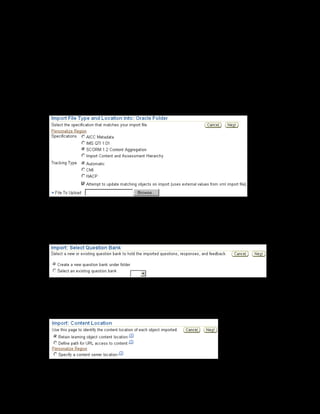
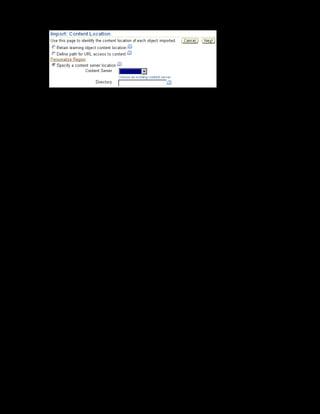
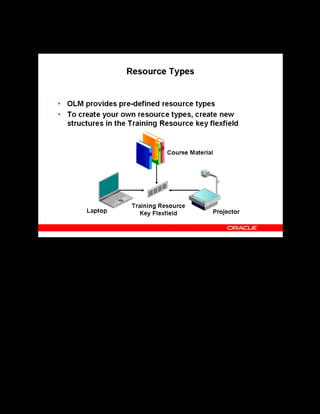
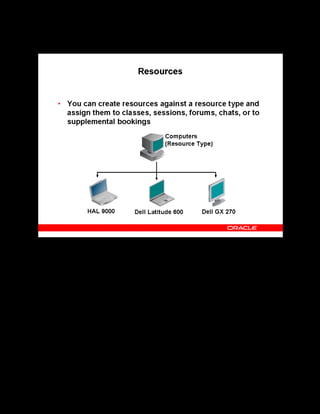
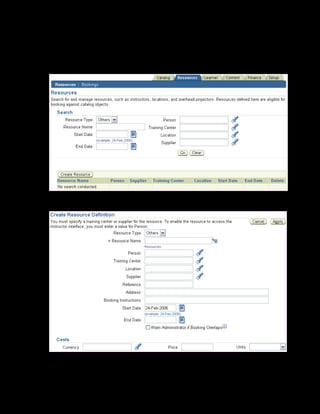
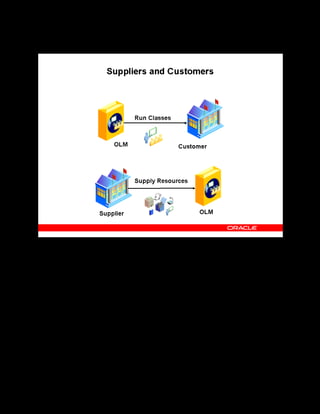
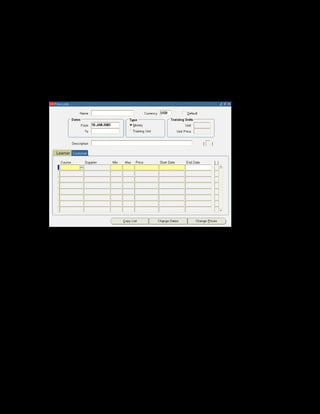
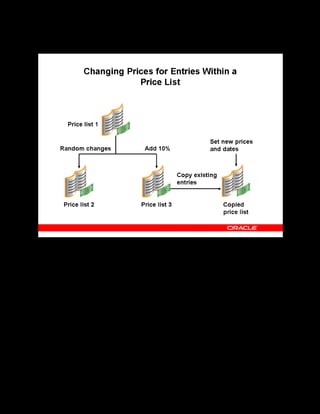
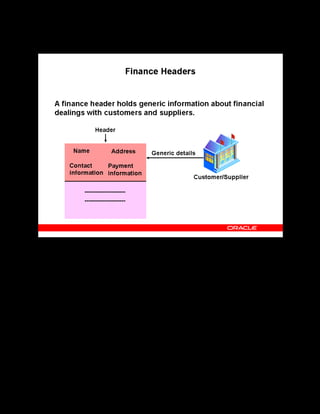
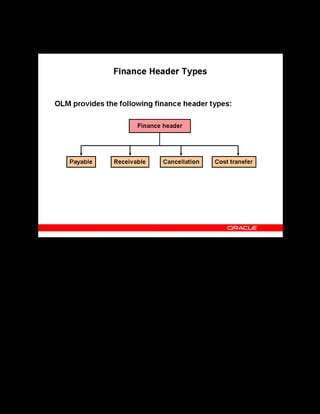
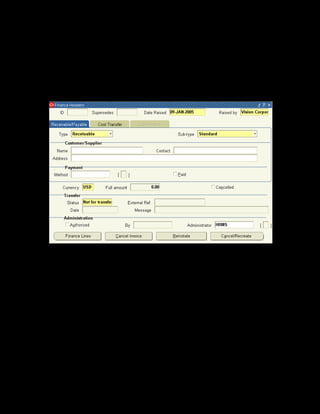
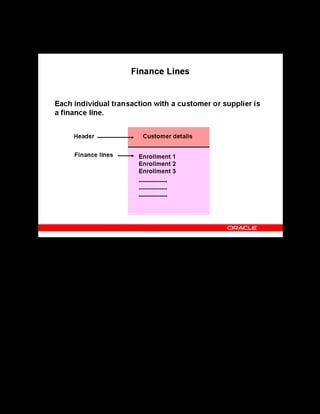
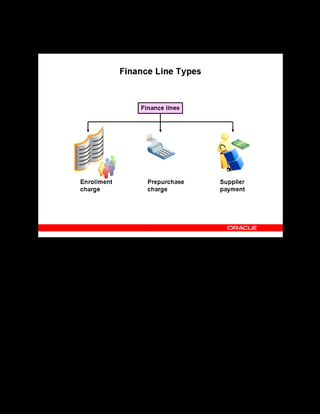
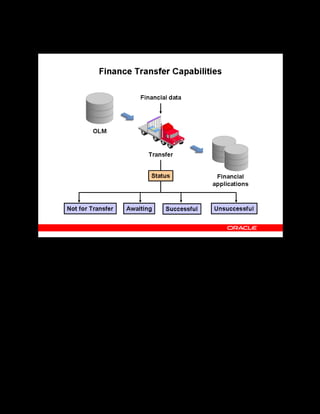
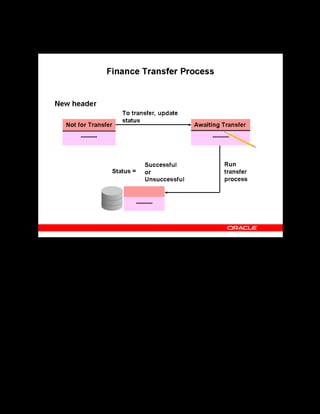
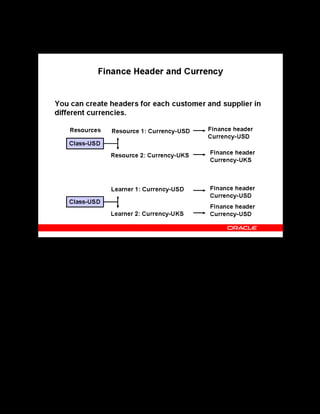
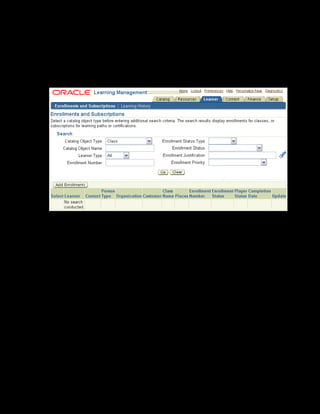
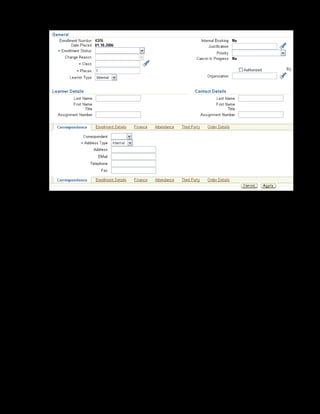
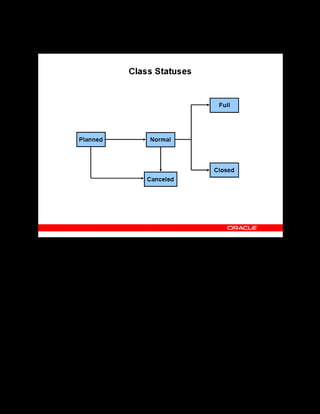
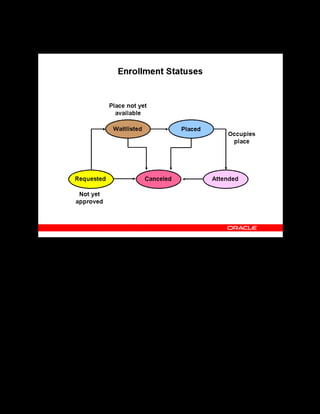
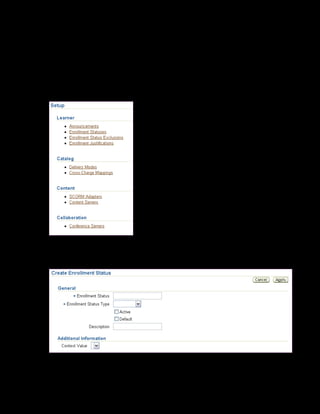
This document provides an overview of the Oracle Learning Management system and discusses some key decisions that must be made when implementing it. It describes how OLM supports online and offline learning delivery and integrates with other Oracle applications like Human Resources and Financials. The document outlines OLM's main features, including catalog management, content administration, resources, enrollments, self-service interfaces, and its ability to handle internal and for-profit learning. It stresses the importance of planning before setting up OLM and adopting a staged approach, focusing first on essential areas based on an organization's learning requirements.