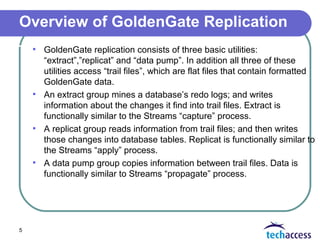
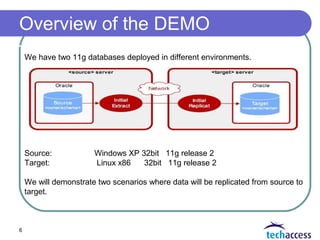
GoldenGate is a replication utility that provides flexible data propagation between databases. It consists of extract, replicat, and data pump processes that access trail files containing change data. An extract process mines source database redo logs and writes changes to trail files. A replicat process reads from trail files and applies changes to target database tables. The demo will show two scenarios for replicating data from a Windows source database to a Linux target database using different GoldenGate configuration methods.