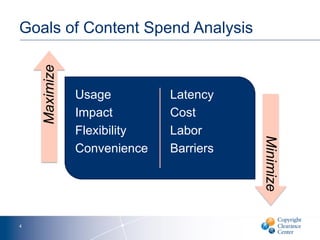
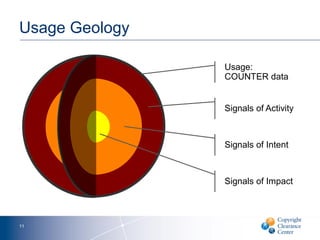
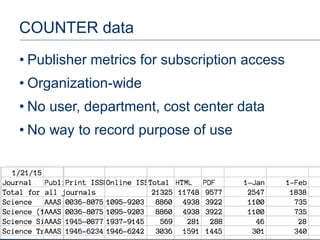
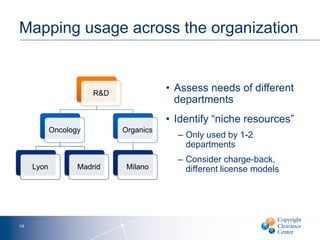
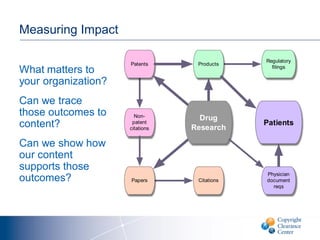
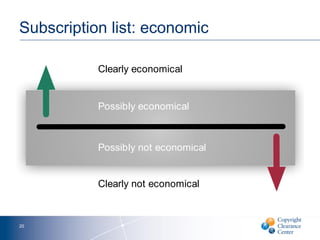
The document discusses goals and challenges associated with content spending analytics, focusing on various types of content such as scholarly journals and databases. It emphasizes the importance of measuring usage, intent, and impact to optimize content spending and resource allocation across departments. Additionally, it proposes data-driven strategies for managing subscriptions and enhancing negotiation processes for content access.