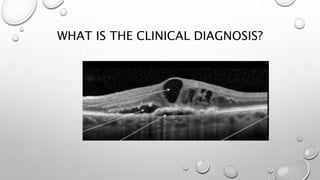
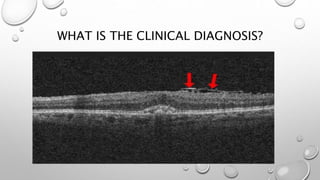
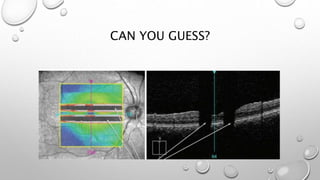
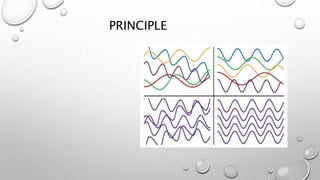
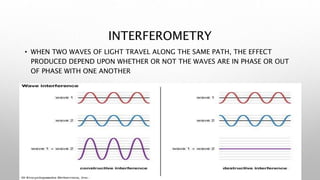
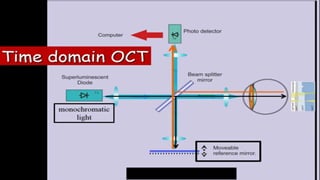
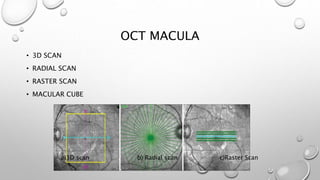
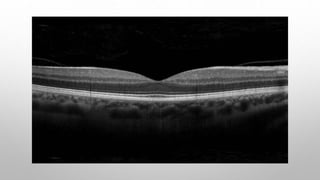
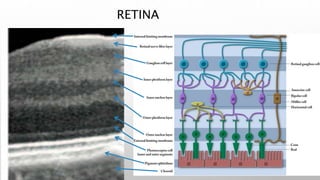
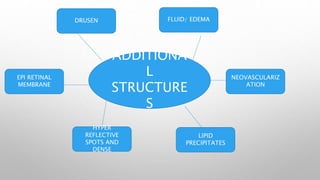
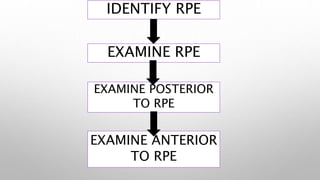
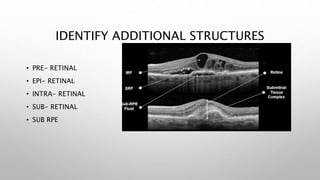
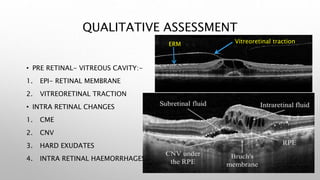
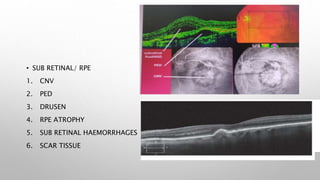
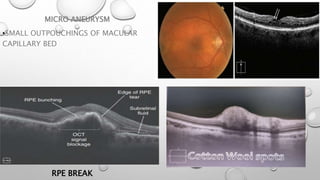
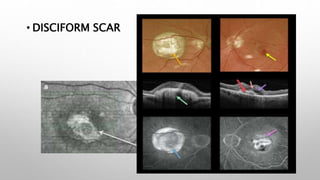
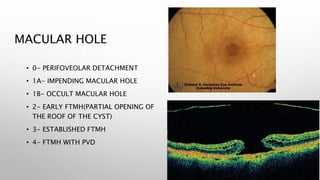
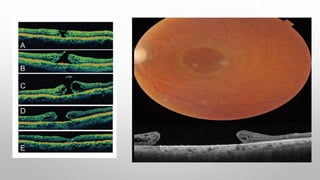
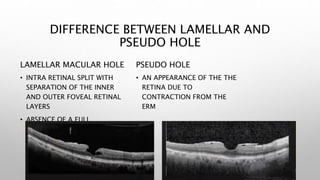
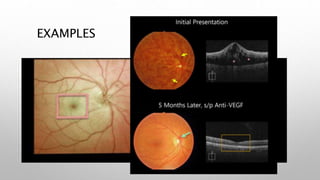
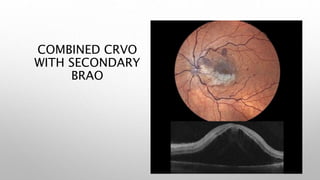
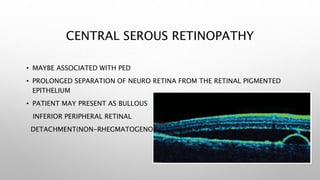
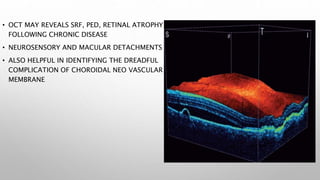
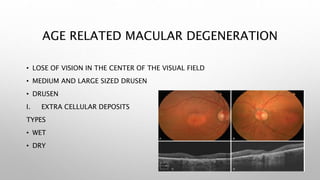
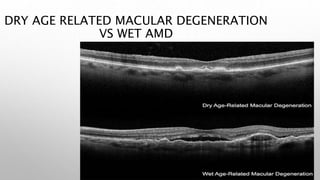
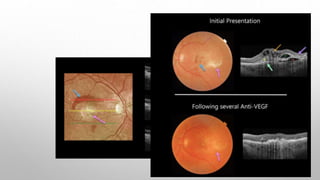
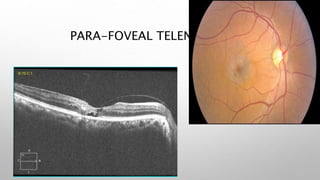
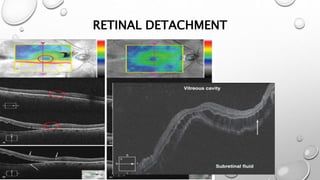
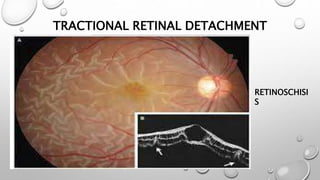
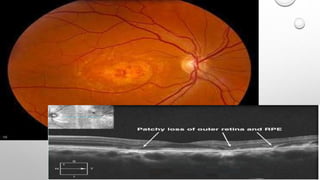
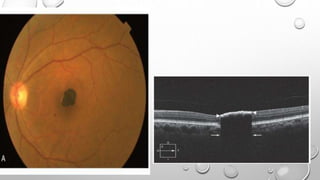
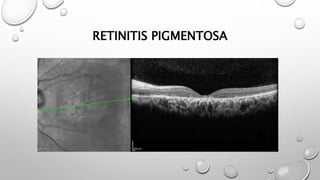
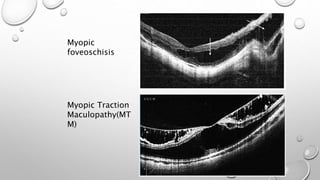
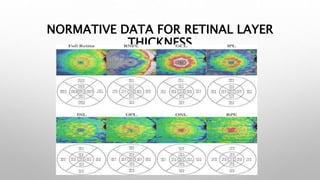
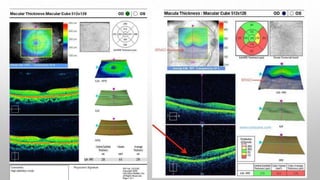
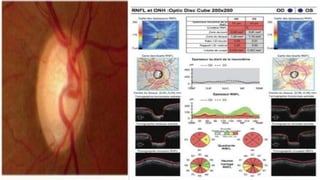
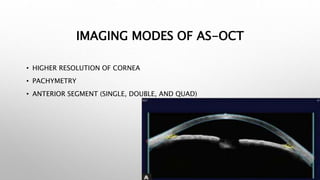
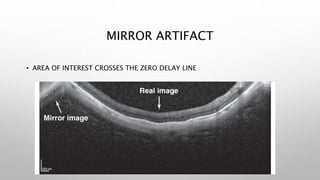
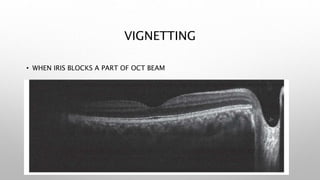
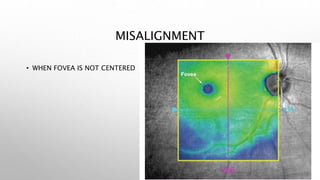
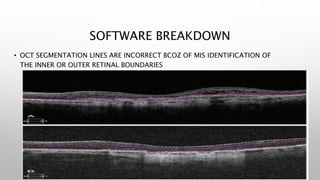
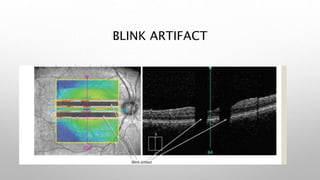
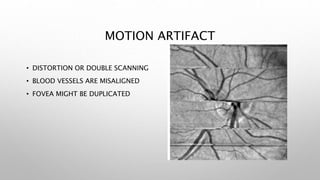
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technology that uses infrared light to produce high-resolution cross-sectional images of tissues, particularly in the eye. It offers advantages such as rapid imaging and minimal cooperation requirements, while having limitations in penetration through certain ocular conditions. The document also details the principles, parameters, types of scans, and clinical applications associated with OCT, including various retinal diseases and their qualitative assessments.